

临床荟萃 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (8): 677-685.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.08.001
• 循证研究 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-02-13
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-09-27
通讯作者:
霍丽娟
E-mail:mymail5296@163.com
Received:2023-02-13
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-09-27
Contact:
Huo Lijuan
E-mail:mymail5296@163.com
摘要:
目的 探讨血清总胆红素(serum total bilirubin, STB)在炎症性肠病(Inflammatory Bowel Disease,IBD)患者中的临床意义。方法 计算机检索PubMed、Embase、Web of Science、Cochrane Library、中国知网、维普、万方、中国生物医学文献(CBM)等数据库从建库至2022年11月有关STB与IBD相关性的病例对照研究, 使用NOS评分对纳入文献进行评价,采用RevMan5.4.1和Stata13.1软件进行统计学分析。结果 共纳入14篇文献18项研究,包括6067例参与者(IBD组2972例和对照组3905例)。Meta分析结果显示:①IBD患者STB水平低于对照组(SMD=-0.80, 95%CI: -0.99~-0.61, P<0.01);②活动期IBD患者STB水平较缓解期更低(SMD=-0.76, 95%CI: -1.33~-0.19, P=0.009);③随着IBD严重程度的增加,STB呈下降趋势(轻度比中度:SMD=-0.35,95%CI: -0.52~-0.18, P<0.01;中度比重度:SMD=-0.59,95%CI: -0.78~-0.39, P<0.01;轻度比重度:SMD=-0.88,95%CI: -1.10~-0.66,P<0.01); ④STB水平与血沉(Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate,ESR)、C反应蛋白(C-reactive protein,CRP)及IBD疾病活动度评分呈负相关,与血红蛋白(Hemoglobin,Hb)呈正相关(ESR:r=-0.41, 95%CI:-0.45~-0.35,P<0.01; CRP: r=-0.37, 95%CI: -0.48~-0.26, P<0.01;临床评分: r=-0.54, 95%CI:-0.70~-0.39, P<0.01; Hb: r=0.45, 95%CI: 0.40~0.50, P<0.01);⑤正常范围内低水平的STB发生IBD的风险为高水平的3.15倍(OR=3.15,95%CI:2.24~4.44,P<0.01)。结论 正常范围内低水平的STB可能与IBD的发生风险增加有关,且其水平与IBD疾病活动性及严重程度相关,对于IBD的临床评估可能有参考价值。
中图分类号:
陈晓天, 霍丽娟. 血清总胆红素水平在炎症性肠病中临床意义的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(8): 677-685.
Chen Xiaotian, Huo Lijuan. Meta-analysis of clinical significance of serum total bilirubin level in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(8): 677-685.
| 作者 | 年份 | 国家 | 病例组 | 对照组 | 样本量(男/女) | 结局指标 | STB水平分组 | 低水平STB发生 IBD的OR值 | NOS 评分 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病例组 | 对照组 | |||||||||
| 2014 | 捷克 | CD | 健康人 | 31/59 | 126/103 | ① | - | - | 7 | |
| Schieffer[ | 2017 | 美国 | UC | 健康人 | 187 | 187 | ①⑧ | ≤0.5 mg/dl 0.51~0.60 mg/dl 0.61~0.80 mg/dl ≥0.81 | 1.98(1.09-3.63) 0.84(0.42-1.69) 0.78(0.40-1.55) 参照 | 7 |
| Schieffer[ | 2017 | 美国 | CD | 健康人 | 254 | 254 | ①⑧ | ≤0.5 mg/dl 0.51~0.60 mg/dl 0.61~0.80 mg/dl ≥0.81 | 1.91(1.26-2.91) 1.00(0.62-1.63) 1.11(0.69-1.79) 参照 | 7 |
| Schieffer[ | 2017 | 美国 | UC | 健康人 | 124 | 124 | ①⑧ | ≤0.4 mg/dl 0.41~0.50 mg/dl 0.51~0.67 mg/dl ≥0.68 | 6.07(3.01-12.75) 4.68(2.17-10.45) 2.73(1.22-6.21) 参照 | 7 |
| Schieffer [ | 2017 | 美国 | CD | 健康人 | 233 | 233 | ①⑧ | ≤0.4 mg/dl 0.41~0.50 mg/dl 0.51~0.67 mg/dl ≥0.68 | 3.60(2.19-5.99) 1.55(0.85-2.81) 1.35(0.76-2.41) 参照 | 7 |
| Tian [ | 2018 | 中国武汉 | UC | 健康人 | 170 | 200 | ①⑧ | <8.14 μmol/L 8.14~11.01 mg/dl 11.02~14.77 mg/dl >14.77 | 2.56(1.54-4.25) 2.42(1.44-4.07) 1.52(0.97-2.51) 参照 | 7 |
| 陈影影[ | 2018 | 中国徐州 | UC | 肠镜无异常者 | 27/28 | 38/37 | ①③ | - | - | 6 |
| 蒋传林[ | 2018 | 中国武汉 | CD | 健康人 | 50/30 | 92/68 | ①⑧ | <7.63 μmol/L 7.63~11.00 μmol/L 11.01~14.72 μmol/L >14.72 | 4.86(1.87-10.75) 3.14(1.38-8.44) 2.82(0.56-3.78) 参照 | 7 |
| Su[ | 2019 | 中国广西 | CD | 健康人 | 47/24 | 82/43 | ①②③ | - | - | 9 |
| Shi [ | 2019 | 中国西安 | UC | 健康人 | 47/53 | 68/72 | ①②③④⑤⑧ | <8.3 μmol/L 8.3~11.1 μmol/L 11.1~14.472 μmol/L ≥14.472 | 5.14(2.32-11.39) 2.69(1.23-5.90) 1.99(0.90-4.39) 参照 | 7 |
| Zhao [ | 2019 | 中国南京 | UC | 健康人 | 124/87 | 134/121 | ①④⑤⑥⑦ | - | - | 8 |
| Zhao [ | 2019 | 中国南京 | CD | 健康人 | 169/73 | 134/121 | ①④⑤⑥⑦ | - | - | 8 |
| 王春莹[ | 2020 | 中国西安 | UC | 健康人 | 58/32 | 56/34 | ①②③⑥ | - | - | 6 |
| 谭丽[ | 2020 | 中国吉林 | UC | 健康人 | 189/172 | 43/68 | ①③ | - | - | 7 |
| Zhang[ | 2020 | 中国南京 | UC | 健康人 | 264/184 | 190/118 | ①④⑤⑦ | - | - | 7 |
| Zhou[ | 2022 | 中国四川 | CD | 健康人 | 66/76 | 125/114 | ①⑥ | - | - | 7 |
| 刘奇[ | 2022 | 中国河南 | UC | 肠镜无异常者 | 28/30 | 32/33 | ①③ | - | - | 6 |
| 黄冠华[ | 2022 | 中国河南 | UC | 健康人 | 31/23 | 28/22 | ①②③⑥ | - | - | 6 |
表1 纳入文献的基本特征
Tab.1 Basic characteristics of the eligible literature
| 作者 | 年份 | 国家 | 病例组 | 对照组 | 样本量(男/女) | 结局指标 | STB水平分组 | 低水平STB发生 IBD的OR值 | NOS 评分 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病例组 | 对照组 | |||||||||
| 2014 | 捷克 | CD | 健康人 | 31/59 | 126/103 | ① | - | - | 7 | |
| Schieffer[ | 2017 | 美国 | UC | 健康人 | 187 | 187 | ①⑧ | ≤0.5 mg/dl 0.51~0.60 mg/dl 0.61~0.80 mg/dl ≥0.81 | 1.98(1.09-3.63) 0.84(0.42-1.69) 0.78(0.40-1.55) 参照 | 7 |
| Schieffer[ | 2017 | 美国 | CD | 健康人 | 254 | 254 | ①⑧ | ≤0.5 mg/dl 0.51~0.60 mg/dl 0.61~0.80 mg/dl ≥0.81 | 1.91(1.26-2.91) 1.00(0.62-1.63) 1.11(0.69-1.79) 参照 | 7 |
| Schieffer[ | 2017 | 美国 | UC | 健康人 | 124 | 124 | ①⑧ | ≤0.4 mg/dl 0.41~0.50 mg/dl 0.51~0.67 mg/dl ≥0.68 | 6.07(3.01-12.75) 4.68(2.17-10.45) 2.73(1.22-6.21) 参照 | 7 |
| Schieffer [ | 2017 | 美国 | CD | 健康人 | 233 | 233 | ①⑧ | ≤0.4 mg/dl 0.41~0.50 mg/dl 0.51~0.67 mg/dl ≥0.68 | 3.60(2.19-5.99) 1.55(0.85-2.81) 1.35(0.76-2.41) 参照 | 7 |
| Tian [ | 2018 | 中国武汉 | UC | 健康人 | 170 | 200 | ①⑧ | <8.14 μmol/L 8.14~11.01 mg/dl 11.02~14.77 mg/dl >14.77 | 2.56(1.54-4.25) 2.42(1.44-4.07) 1.52(0.97-2.51) 参照 | 7 |
| 陈影影[ | 2018 | 中国徐州 | UC | 肠镜无异常者 | 27/28 | 38/37 | ①③ | - | - | 6 |
| 蒋传林[ | 2018 | 中国武汉 | CD | 健康人 | 50/30 | 92/68 | ①⑧ | <7.63 μmol/L 7.63~11.00 μmol/L 11.01~14.72 μmol/L >14.72 | 4.86(1.87-10.75) 3.14(1.38-8.44) 2.82(0.56-3.78) 参照 | 7 |
| Su[ | 2019 | 中国广西 | CD | 健康人 | 47/24 | 82/43 | ①②③ | - | - | 9 |
| Shi [ | 2019 | 中国西安 | UC | 健康人 | 47/53 | 68/72 | ①②③④⑤⑧ | <8.3 μmol/L 8.3~11.1 μmol/L 11.1~14.472 μmol/L ≥14.472 | 5.14(2.32-11.39) 2.69(1.23-5.90) 1.99(0.90-4.39) 参照 | 7 |
| Zhao [ | 2019 | 中国南京 | UC | 健康人 | 124/87 | 134/121 | ①④⑤⑥⑦ | - | - | 8 |
| Zhao [ | 2019 | 中国南京 | CD | 健康人 | 169/73 | 134/121 | ①④⑤⑥⑦ | - | - | 8 |
| 王春莹[ | 2020 | 中国西安 | UC | 健康人 | 58/32 | 56/34 | ①②③⑥ | - | - | 6 |
| 谭丽[ | 2020 | 中国吉林 | UC | 健康人 | 189/172 | 43/68 | ①③ | - | - | 7 |
| Zhang[ | 2020 | 中国南京 | UC | 健康人 | 264/184 | 190/118 | ①④⑤⑦ | - | - | 7 |
| Zhou[ | 2022 | 中国四川 | CD | 健康人 | 66/76 | 125/114 | ①⑥ | - | - | 7 |
| 刘奇[ | 2022 | 中国河南 | UC | 肠镜无异常者 | 28/30 | 32/33 | ①③ | - | - | 6 |
| 黄冠华[ | 2022 | 中国河南 | UC | 健康人 | 31/23 | 28/22 | ①②③⑥ | - | - | 6 |
| 分组方法 | 亚组 | 研究数量 | 异质性(I2) | SMD(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疾病类型 | UC | 11 | 79.2% | -0.63(-0.79~-0.47) | <0.01 |
| CD | 7 | 94.9% | -1.05(-1.43~-0.68) | <0.01 | |
| 研究国家 | 美国 | 4 | 93.3% | -0.49(-0.59~-0.39) | <0.01 |
| 中国 | 13 | 0.0% | -0.89(-1.15~-0.63) | <0.01 | |
| 捷克 | 1 | 0.0% | -0.94(-1.19~-0.69) | <0.01 | |
| 对照组人群 | 健康人 | 16 | 92.3% | -0.78(-0.98~-0.58) | <0.01 |
| 肠镜检查无异常者 | 2 | 0.0% | -1.02(-1.29~-0.76) | <0.01 | |
| NOS评分 | 6分 | 4 | 0.0% | -0.93(-1.09~-0.76) | <0.01 |
| 7分 | 11 | 90.0% | -0.65(-0.85~-0.44) | <0.01 | |
| ≥8分 | 3 | 97.1% | -1.24(-2.01~-0.47) | 0.002 |
表2 IBD组与对照组STB水平比较的亚组分析结果
Tab. 2 Subgroup analysis of comparison of STB level between IBD group and control group
| 分组方法 | 亚组 | 研究数量 | 异质性(I2) | SMD(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疾病类型 | UC | 11 | 79.2% | -0.63(-0.79~-0.47) | <0.01 |
| CD | 7 | 94.9% | -1.05(-1.43~-0.68) | <0.01 | |
| 研究国家 | 美国 | 4 | 93.3% | -0.49(-0.59~-0.39) | <0.01 |
| 中国 | 13 | 0.0% | -0.89(-1.15~-0.63) | <0.01 | |
| 捷克 | 1 | 0.0% | -0.94(-1.19~-0.69) | <0.01 | |
| 对照组人群 | 健康人 | 16 | 92.3% | -0.78(-0.98~-0.58) | <0.01 |
| 肠镜检查无异常者 | 2 | 0.0% | -1.02(-1.29~-0.76) | <0.01 | |
| NOS评分 | 6分 | 4 | 0.0% | -0.93(-1.09~-0.76) | <0.01 |
| 7分 | 11 | 90.0% | -0.65(-0.85~-0.44) | <0.01 | |
| ≥8分 | 3 | 97.1% | -1.24(-2.01~-0.47) | 0.002 |
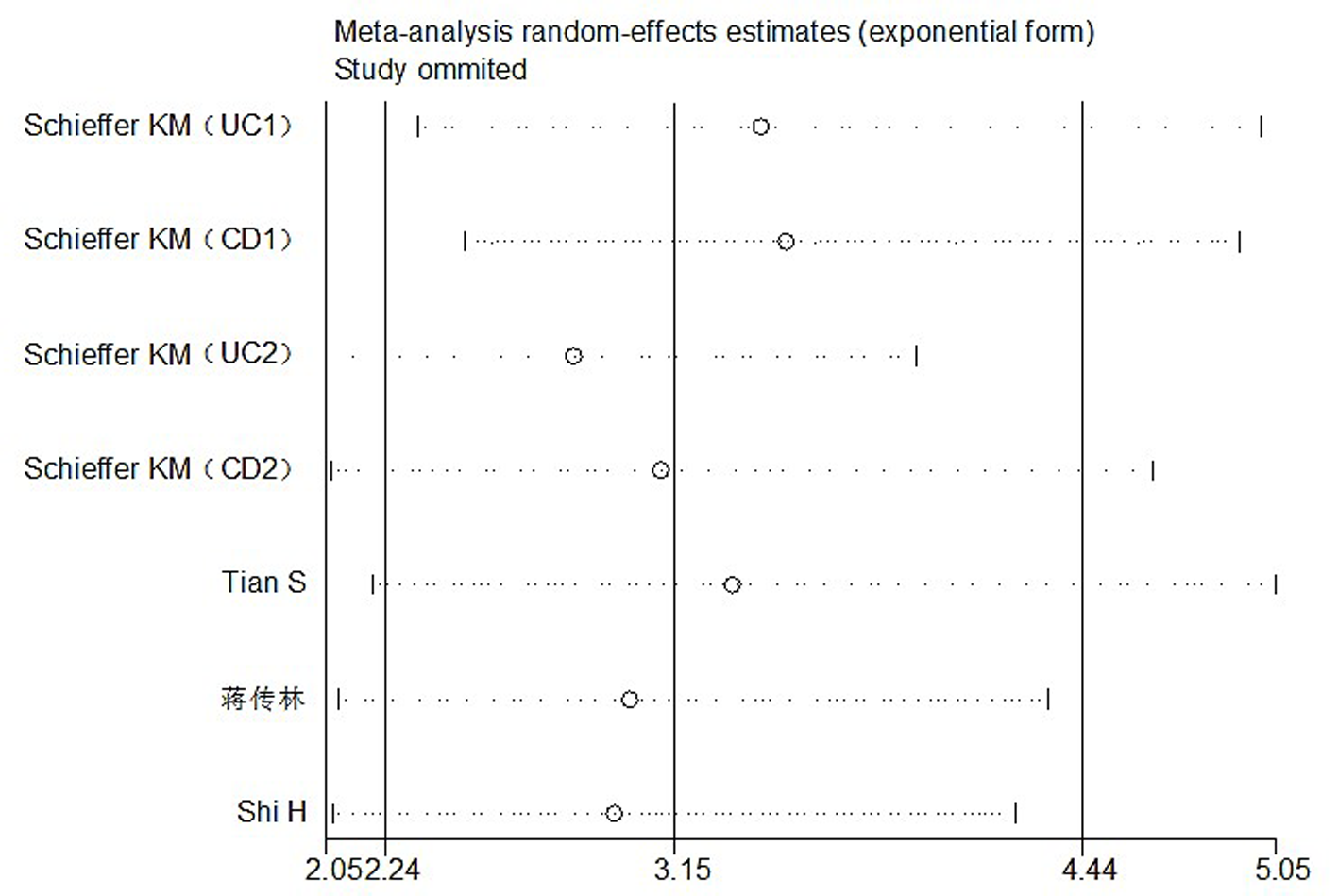
图12 分析低水平STB发生IBD的风险时纳入研究的敏感性分析——逐一剔除法
Fig. 12 Sensitivity analysis of all studies when analyzing the risk of IBD in low level STB--step-wise rejection method
| [1] | 中华医学会消化病学分会炎症性肠病学组. 炎症性肠病诊断与治疗的共识意见(2018年8136A63北京)[J]. 中华炎性肠病杂志, 2018, 2(3): 173-190. |
| [2] |
Idelman G, Smith DLH, Zucker SD. Bilirubin inhibits the up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase by scavenging reactive oxygen species generated by the toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase[J]. Redox Biol, 2015, 5:398-408.
doi: S2213-2317(15)00059-2 pmid: 26163808 |
| [3] |
Chen SC, Lin CP, Hsu HC, et al. Serum bilirubin improves the risk predictions of cardiovascular and total death in diabetic patients[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2019, 488:1-6.
doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.10.028 URL |
| [4] | Neubauer K, Kempinski R, Matusiewicz M, et al. Nonenzymatic serum antioxidant capacity in IBD and its association with the severity of bowel inflammation and corticosteroids treatment[J]. Medicina (Kaunas), 2019, 55(4):88. |
| [5] |
Leníček M, Duricová D, Hradsky O, et al. The relationship between serum bilirubin and Crohn's disease[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2014, 20(3):481-487.
doi: 10.1097/01.MIB.0000440817.84251.98 pmid: 24407487 |
| [6] |
Schieffer KM, Bruffy SM, Rauscher R, et al. Reduced total serum bilirubin levels are associated with ulcerative colitis[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(6):e0179267.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179267 URL |
| [7] |
Zhou Z, Zhang Y, Yang X, et al. Clinical significance of novel neutrophil-based biomarkers in the diagnosis and prediction of response to infliximab therapy in crohn's disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13:865968.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.865968 URL |
| [8] | 罗德惠, 万翔, 刘际明, 等. 如何实现从样本量、中位数、极值或四分位数到均数与标准差的转换[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2017, 17(11):1350-1356. |
| [9] |
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the newcastle-ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2010, 25(9):603-605.
doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z pmid: 20652370 |
| [10] |
Chalkidou A, Landau DB, Odell EW, et al. Correlation between Ki-67 immunohistochemistry and 18F-Fluorothymidine uptake in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2012, 48(18): 3499-3513.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.05.001 pmid: 22658807 |
| [11] |
Tian S, Li J, Li R, et al. Decreased serum bilirubin levels and increased uric acid levels are associated with ulcerative colitis[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2018, 24:6298-6304.
doi: 10.12659/MSM.909692 URL |
| [12] | 陈影影, 甄玲玲, 费素娟. 血清总胆红素及胆碱酯酶与活动期溃疡性结肠炎之间的关系[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2018, 27(10):1152-1156. |
| [13] | 蒋传林, 田山, 贾雪梅, 等. 克罗恩病与血浆总胆红素及尿酸的相关性研究[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2018, 17(8):803-807. |
| [14] |
Su Q, Li X, Mo W, et al. Low serum bilirubin, albumin, and uric acid levels in patients with Crohn's disease[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98(19):e15664.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015664 URL |
| [15] |
Shi H, Feng Y, Jiang J, et al. Correlations between the serum bilirubin level and ulcerative colitis: A case-control study[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 31(8):992-997.
doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001466 URL |
| [16] | Zhao X, Li L, Li X, et al. The relationship between serum bilirubin and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2019:5256460. |
| [17] | 王春莹, 焦婕英, 张永欢, 等. 溃疡性结肠炎患者血清总胆红素和尿酸水平与炎性因子的相关性研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2020, 20(24):4726-4729. |
| [18] | 谭丽. 溃疡性结肠炎与血清胆红素、尿酸、胆碱酯酶及Ca-(2+)之间的相关性[D]. 吉林大学, 2020. |
| [19] | Zhang MH, Wang HG, Shi YT, et al. Efficacy of serum total bilirubin in predicting the severity of ulcerative colitis: A cross-sectional study[J]. Ann Clin Lab Sci, 2020, 50(2):228-232. |
| [20] | 刘奇. 血清总胆红素、胆碱酯酶水平与活动期溃疡性结肠炎病情的关系[J]. 中国肛肠病杂志, 2022, 42(2):50-52. |
| [21] | 黄冠华. 溃疡性结肠炎患者血清总胆红素和尿酸水平与炎症因子的相关性研究[J]. 中国肛肠病杂志, 2022, 42(2):47-49. |
| [22] |
Liao SL. The role of bilirubin and phototherapy in the oxidative/antioxidant balance[J]. Pediatr Neonatol, 2015, 56(2):77-78.
doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2015.01.001 URL |
| [23] |
Zucker SD, Vogel ME, Kindel TL, et al. Bilirubin prevents acute DSS-induced colitis by inhibiting leukocyte infiltration and suppressing upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2015, 309(10):G841-854.
doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00149.2014 URL |
| [24] |
Lee Y, Sugihara K, Gillilland MG 3rd, et al. Hyaluronic acid-bilirubin nanomedicine for targeted modulation of dysregulated intestinal barrier, microbiome and immune responses in colitis[J]. Nat Mater, 2020, 19(1):118-126.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0462-9 pmid: 31427744 |
| [25] |
Zheng JD, He Y, Yu HY, et al. Unconjugated bilirubin alleviates experimental ulcerative colitis by regulating intestinal barrier function and immune inflammation[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(15):1865-1878.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i15.1865 URL |
| [26] |
Shiraishi K, Furukawa S, Yagi S, et al. Association between serum bilirubin and mucosal healing among Japanese patients with ulcerative colitis: A cross-sectional study[J]. Int J Colorectal Dis, 2021, 36(2):377-382.
doi: 10.1007/s00384-020-03774-w pmid: 33040190 |
| [1] | 陈思晗, 熊虎, 税典雅, 高小瞻, 刘泽伟. 超微血管成像技术诊断乳腺肿瘤的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(2): 108-114. |
| [2] | 祝成楼, 吴琼, 达明绪. 西格列汀治疗2型糖尿病的胰腺癌风险评估:来自随机对照试验的荟萃分析结果[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(12): 1061-1066. |
| [3] | 齐玉敏, 王友军. 新生儿胆汁淤积性黄疸血清胆红素水平与肠道菌群失调的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(12): 1117-1121. |
| [4] | 周子涵, 崔炜. 心血管系统常用药物对新型冠状病毒肺炎感染风险及不良预后的影响[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(10): 869-888. |
| [5] | 才可新, 郭宏举, 于淑霞, 常李荣. 左旋甲状腺素对妊娠期亚临床甲状腺功能减退症妊娠结局影响的荟萃分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(9): 773-777. |
| [6] | 安增岳, 张俏俏, 张沂洁, 李玉美, 姜红. 早产危险因素的1∶1病例对照研究[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(6): 540-544. |
| [7] | 金晖, 刘尚全. 2型糖尿病患者血清胆红素水平与颈动脉斑块的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(4): 340-343. |
| [8] | 佟晶晶1,施克新2,冷飞2,李凤萍2. 血清胆红素水平与2型糖尿病视网膜病变的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2020, 35(9): 816-822. |
| [9] | 周晔1,金庸1,王学鹏1,陈艳曙2a,徐淼2a,刘佳宁2b,杨茜2b,励丽2a. 基线非结合胆红素对肥胖人群早期生活方式减重达标的切点预测[J]. 临床荟萃, 2020, 35(9): 811-815. |
| [10] | 葛超毅, 王化虹. 炎症性肠病营养支持治疗进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(8): 650-655,660. |
| [11] | 宋岩1,杨虎2,姜葵1,王邦茂1. 沙利度胺及其类似物治疗炎症性肠病的系统性回顾[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(5): 434-439. |
| [12] | 李玥,钱家鸣. 炎症性肠病合并艰难梭菌感染的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(5): 394-397. |
| [13] | 郭兆明,熊英. 新生儿高胆红素血症对心肌影响的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(4): 361-364. |
| [14] | 张梦,陈慧冬,詹枝华. 超声支气管镜引导经支气管针吸活检在胸内淋巴结核诊断中的准确性和安全性分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(12): 1071-1076. |
| [15] | 周园媛1,王战建2,丘红梅1,李薇1. 2型糖尿病肾病与血清胆红素的关系[J]. 临床荟萃, 2017, 32(9): 767-769,773. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 59
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 217
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
