

临床荟萃 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (9): 779-787.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.09.002
收稿日期:2022-09-24
出版日期:2023-09-20
发布日期:2023-11-21
通讯作者:
周利明,Email:基金资助:Received:2022-09-24
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-11-21
Contact:
Zhou Liming,Email: 摘要:
目的 分析肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)启动子308位点多态性与胃癌易感性的关系。方法 检索Pubmed、Embase、Web of Science、Cochrane library、万方数据和中国知网数据库中有关TNF-α-308基因多态性与胃癌发病风险的病例对照研究,时间截至2022年6月。由2位研究者独立进行文献筛选、提取数据及评价偏倚风险,通过Stata16.0软件进行Meta分析。结果 纳入41项病例-对照研究,共7528例胃癌患者和10924例对照。Meta分析结果显示:等位,杂合和显性模型TNF-α-308位点多态性与增加胃癌患病风险相关[A vs G:
中图分类号:
吕畅, 周利明. TNF-α-308基因多态性与胃癌易感相关性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(9): 779-787.
Lyu Chang, Zhou Liming. Correlation between the TNF-α-308 gene polymorphism and gastric cancer susceptibility: A meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(9): 779-787.
| 纳入研究 | 国家 | 地区 | 检测方式 | 病例组 | 对照组 | HWE 检验 | NOS 评分 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GG | GA | AA | GG | GA | AA | |||||||
| Jang 2001[ | 朝鲜 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 46 | 4 | 2 | 85 | 7 | 0 | 0.704 | 8 | |
| Wu 2002[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | 直接分型 | 114 | 27 | 9 | 180 | 27 | 13 | <0.01 | 6 | |
| El-Omar 2003[ | 美国 | 美洲 | Taqman | 201 | 87 | 26 | 152 | 52 | 6 | 0.548 | 8 | |
| Machado 2003[ | 葡萄牙 | 欧洲 | PCR/SSCP | 179 | 105 | 3 | 231 | 69 | 4 | 0.650 | 8 | |
| Wu 2003[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | 直接分型 | 176 | 31 | 13 | 185 | 29 | 16 | <0.01 | 8 | |
| Glas 2004[ | 德国 | 欧洲 | RFLP | 66 | 19 | 3 | 105 | 36 | 4 | 0.669 | 8 | |
| Lee 2004[ | 朝鲜 | 亚洲 | 直接分型 | 297 | 43 | 1 | 218 | 42 | 1 | 0.493 | 8 | |
| Wu 2004[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 163 | 29 | 12 | 171 | 26 | 13 | <0.01 | 7 | |
| Garza-González 2005[ | 墨西哥 | 美洲 | 直接分型 | 0 | 8 | 55 | 1 | 35 | 179 | 0.608 | 6 | |
| Lee 2005[ | 朝鲜 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 112 | 10 | 0 | 103 | 17 | 0 | 0.404 | 8 | |
| Li 2005[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 55 | 4 | 0 | 228 | 34 | 2 | 0.560 | 8 | |
| Lu 2005[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | DNPLC | 214 | 36 | 0 | 274 | 24 | 2 | 0.081 | 8 | |
| Perri 2005[ | 意大利 | 欧洲 | RFLP | 152 | 30 | 2 | 290 | 65 | 7 | 0.146 | 8 | |
| Zambon 2005[ | 意大利 | 欧洲 | Taqman | 95 | 31 | 3 | 496 | 138 | 10 | 0.910 | 7 | |
| Kamanrar 2006[ | 芬兰 | 欧洲 | Taqman | 86 | 23 | 3 | 154 | 52 | 2 | 0.292 | 6 | |
| Kim 2006[ | 朝鲜 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 199 | 34 | 4 | 400 | 59 | 2 | 0.911 | 8 | |
| Morgan 2006[ | 洪都拉斯 | 美洲 | Taqman | 151 | 17 | 0 | 149 | 12 | 0 | 0.623 | 8 | |
| 邢培祥2006[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | 芯片检测 | 36 | 27 | 2 | 50 | 20 | 1 | 0.523 | 8 | |
| Hou 2007[ | 波兰 | 欧洲 | Taqman | 186 | 98 | 21 | 304 | 109 | 15 | 0.187 | 8 | |
| Sugimoto 2007[ | 日本 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 101 | 4 | 0 | 169 | 3 | 0 | 0.908 | 7 | |
| 曾庆东2007[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | 芯片检测 | 72 | 54 | 4 | 100 | 40 | 2 | 0.367 | 8 | |
| Crusius 2008[ | 欧洲 | 欧洲 | Real-time PCR | 170 | 64 | 2 | 820 | 274 | 31 | 0.165 | 8 | |
| Barbosa 2009[ | 巴西 | 美洲 | RFLP | 24 | 5 | 1 | 86 | 13 | 1 | 0.528 | 7 | |
| 贾皑2009[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | PCR | 96 | 2 | 8 | 91 | 3 | 14 | <0.01 | 7 | |
| Burada 2012[ | 罗马 | 欧洲 | Taqman | 78 | 26 | 1 | 196 | 44 | 2 | 0.784 | 8 | |
| 王美丽2012[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 16 | 75 | 21 | 14 | 64 | 21 | 0.003 | 7 | |
| 尹东2011[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | PCR | 265 | 43 | 3 | 398 | 79 | 8 | 0.085 | 7 | |
| Bhayal 2013[ | 印度 | 亚洲 | ARMSPCR | 32 | 76 | 6 | 76 | 128 | 25 | 0.007 | 8 | |
| Hong 2012[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | Taqman | 746 | 179 | 11 | 895 | 156 | 9 | 0.448 | 8 | |
| Gonzalez 2014[ | 智利 | 美洲 | Taqman | 128 | 18 | 1 | 147 | 23 | 2 | 0.322 | 8 | |
| 张军喜2014[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | PCR | 56 | 9 | 0 | 113 | 16 | 1 | 0.608 | 8 | |
| Oliveira 2015[ | 巴西 | 美洲 | RFLP | 138 | 66 | 3 | 167 | 69 | 4 | 0.297 | 8 | |
| Stubljar 2015[ | 斯洛文尼亚 | 欧洲 | RFLP | 27 | 5 | 0 | 83 | 22 | 3 | 0.312 | 7 | |
| Zabaglia 2015[ | 巴西 | 美洲 | RFLP | 17 | 4 | 3 | 33 | 4 | 3 | 0.001 | 6 | |
| 张德忠2015[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 373 | 112 | 15 | 396 | 95 | 9 | 0.243 | 8 | |
| Du 2017[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 204 | 184 | 12 | 326 | 60 | 14 | <0.01 | 7 | |
| Xu 2016[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 142 | 66 | 88 | 237 | 50 | 32 | <0.01 | 8 | |
| Fukayama 2019[ | 日本 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 120 | 2 | 7 | 101 | 2 | 0 | 0.921 | 8 | |
| Bounder 2020[ | 摩洛哥 | 非洲 | 直接测序 | 26 | 6 | 8 | 56 | 4 | 3 | <0.01 | 7 | |
| Dantas 2020[ | 巴西 | 美洲 | DSASP | 74 | 0 | 28 | 8 | 41 | 53 | 0.986 | 8 | |
| Nezamzadeh 2021[ | 伊朗 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 41 | 7 | 3 | 73 | 5 | 1 | 0.020 | 7 | |
表1 纳入研究的基本特征
Tab. 1 Basic characteristics of the included studies
| 纳入研究 | 国家 | 地区 | 检测方式 | 病例组 | 对照组 | HWE 检验 | NOS 评分 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GG | GA | AA | GG | GA | AA | |||||||
| Jang 2001[ | 朝鲜 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 46 | 4 | 2 | 85 | 7 | 0 | 0.704 | 8 | |
| Wu 2002[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | 直接分型 | 114 | 27 | 9 | 180 | 27 | 13 | <0.01 | 6 | |
| El-Omar 2003[ | 美国 | 美洲 | Taqman | 201 | 87 | 26 | 152 | 52 | 6 | 0.548 | 8 | |
| Machado 2003[ | 葡萄牙 | 欧洲 | PCR/SSCP | 179 | 105 | 3 | 231 | 69 | 4 | 0.650 | 8 | |
| Wu 2003[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | 直接分型 | 176 | 31 | 13 | 185 | 29 | 16 | <0.01 | 8 | |
| Glas 2004[ | 德国 | 欧洲 | RFLP | 66 | 19 | 3 | 105 | 36 | 4 | 0.669 | 8 | |
| Lee 2004[ | 朝鲜 | 亚洲 | 直接分型 | 297 | 43 | 1 | 218 | 42 | 1 | 0.493 | 8 | |
| Wu 2004[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 163 | 29 | 12 | 171 | 26 | 13 | <0.01 | 7 | |
| Garza-González 2005[ | 墨西哥 | 美洲 | 直接分型 | 0 | 8 | 55 | 1 | 35 | 179 | 0.608 | 6 | |
| Lee 2005[ | 朝鲜 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 112 | 10 | 0 | 103 | 17 | 0 | 0.404 | 8 | |
| Li 2005[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 55 | 4 | 0 | 228 | 34 | 2 | 0.560 | 8 | |
| Lu 2005[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | DNPLC | 214 | 36 | 0 | 274 | 24 | 2 | 0.081 | 8 | |
| Perri 2005[ | 意大利 | 欧洲 | RFLP | 152 | 30 | 2 | 290 | 65 | 7 | 0.146 | 8 | |
| Zambon 2005[ | 意大利 | 欧洲 | Taqman | 95 | 31 | 3 | 496 | 138 | 10 | 0.910 | 7 | |
| Kamanrar 2006[ | 芬兰 | 欧洲 | Taqman | 86 | 23 | 3 | 154 | 52 | 2 | 0.292 | 6 | |
| Kim 2006[ | 朝鲜 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 199 | 34 | 4 | 400 | 59 | 2 | 0.911 | 8 | |
| Morgan 2006[ | 洪都拉斯 | 美洲 | Taqman | 151 | 17 | 0 | 149 | 12 | 0 | 0.623 | 8 | |
| 邢培祥2006[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | 芯片检测 | 36 | 27 | 2 | 50 | 20 | 1 | 0.523 | 8 | |
| Hou 2007[ | 波兰 | 欧洲 | Taqman | 186 | 98 | 21 | 304 | 109 | 15 | 0.187 | 8 | |
| Sugimoto 2007[ | 日本 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 101 | 4 | 0 | 169 | 3 | 0 | 0.908 | 7 | |
| 曾庆东2007[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | 芯片检测 | 72 | 54 | 4 | 100 | 40 | 2 | 0.367 | 8 | |
| Crusius 2008[ | 欧洲 | 欧洲 | Real-time PCR | 170 | 64 | 2 | 820 | 274 | 31 | 0.165 | 8 | |
| Barbosa 2009[ | 巴西 | 美洲 | RFLP | 24 | 5 | 1 | 86 | 13 | 1 | 0.528 | 7 | |
| 贾皑2009[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | PCR | 96 | 2 | 8 | 91 | 3 | 14 | <0.01 | 7 | |
| Burada 2012[ | 罗马 | 欧洲 | Taqman | 78 | 26 | 1 | 196 | 44 | 2 | 0.784 | 8 | |
| 王美丽2012[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 16 | 75 | 21 | 14 | 64 | 21 | 0.003 | 7 | |
| 尹东2011[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | PCR | 265 | 43 | 3 | 398 | 79 | 8 | 0.085 | 7 | |
| Bhayal 2013[ | 印度 | 亚洲 | ARMSPCR | 32 | 76 | 6 | 76 | 128 | 25 | 0.007 | 8 | |
| Hong 2012[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | Taqman | 746 | 179 | 11 | 895 | 156 | 9 | 0.448 | 8 | |
| Gonzalez 2014[ | 智利 | 美洲 | Taqman | 128 | 18 | 1 | 147 | 23 | 2 | 0.322 | 8 | |
| 张军喜2014[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | PCR | 56 | 9 | 0 | 113 | 16 | 1 | 0.608 | 8 | |
| Oliveira 2015[ | 巴西 | 美洲 | RFLP | 138 | 66 | 3 | 167 | 69 | 4 | 0.297 | 8 | |
| Stubljar 2015[ | 斯洛文尼亚 | 欧洲 | RFLP | 27 | 5 | 0 | 83 | 22 | 3 | 0.312 | 7 | |
| Zabaglia 2015[ | 巴西 | 美洲 | RFLP | 17 | 4 | 3 | 33 | 4 | 3 | 0.001 | 6 | |
| 张德忠2015[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 373 | 112 | 15 | 396 | 95 | 9 | 0.243 | 8 | |
| Du 2017[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 204 | 184 | 12 | 326 | 60 | 14 | <0.01 | 7 | |
| Xu 2016[ | 中国 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 142 | 66 | 88 | 237 | 50 | 32 | <0.01 | 8 | |
| Fukayama 2019[ | 日本 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 120 | 2 | 7 | 101 | 2 | 0 | 0.921 | 8 | |
| Bounder 2020[ | 摩洛哥 | 非洲 | 直接测序 | 26 | 6 | 8 | 56 | 4 | 3 | <0.01 | 7 | |
| Dantas 2020[ | 巴西 | 美洲 | DSASP | 74 | 0 | 28 | 8 | 41 | 53 | 0.986 | 8 | |
| Nezamzadeh 2021[ | 伊朗 | 亚洲 | RFLP | 41 | 7 | 3 | 73 | 5 | 1 | 0.020 | 7 | |
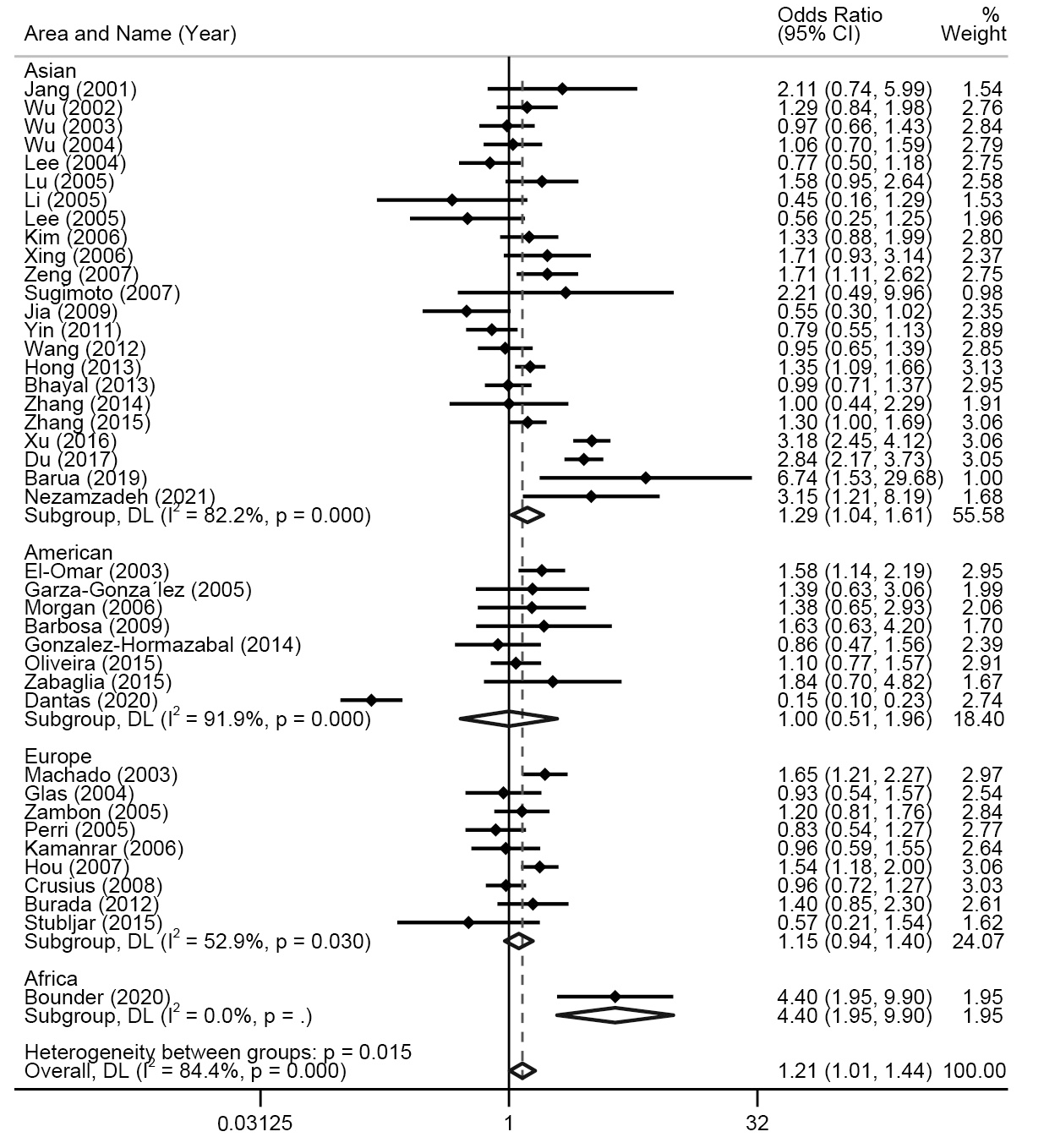
图2 基于不同地区对TNF-α-308多态性与胃癌易感性的森林图(等位模型,A vs G) 注:点表示各项研究的OR值;横线表示95%CI;底部菱形表示合并后的OR值和95%CI
Fig.2 Forest plot of TNF-α-308 polymorphism and gastric cancer susceptibility based on different regions (Allele model, A vs G) Note: Dots indicate OR of each study; horizontal lines indicate 95%CI; bottom diamonds indicate combined OR and 95%CI
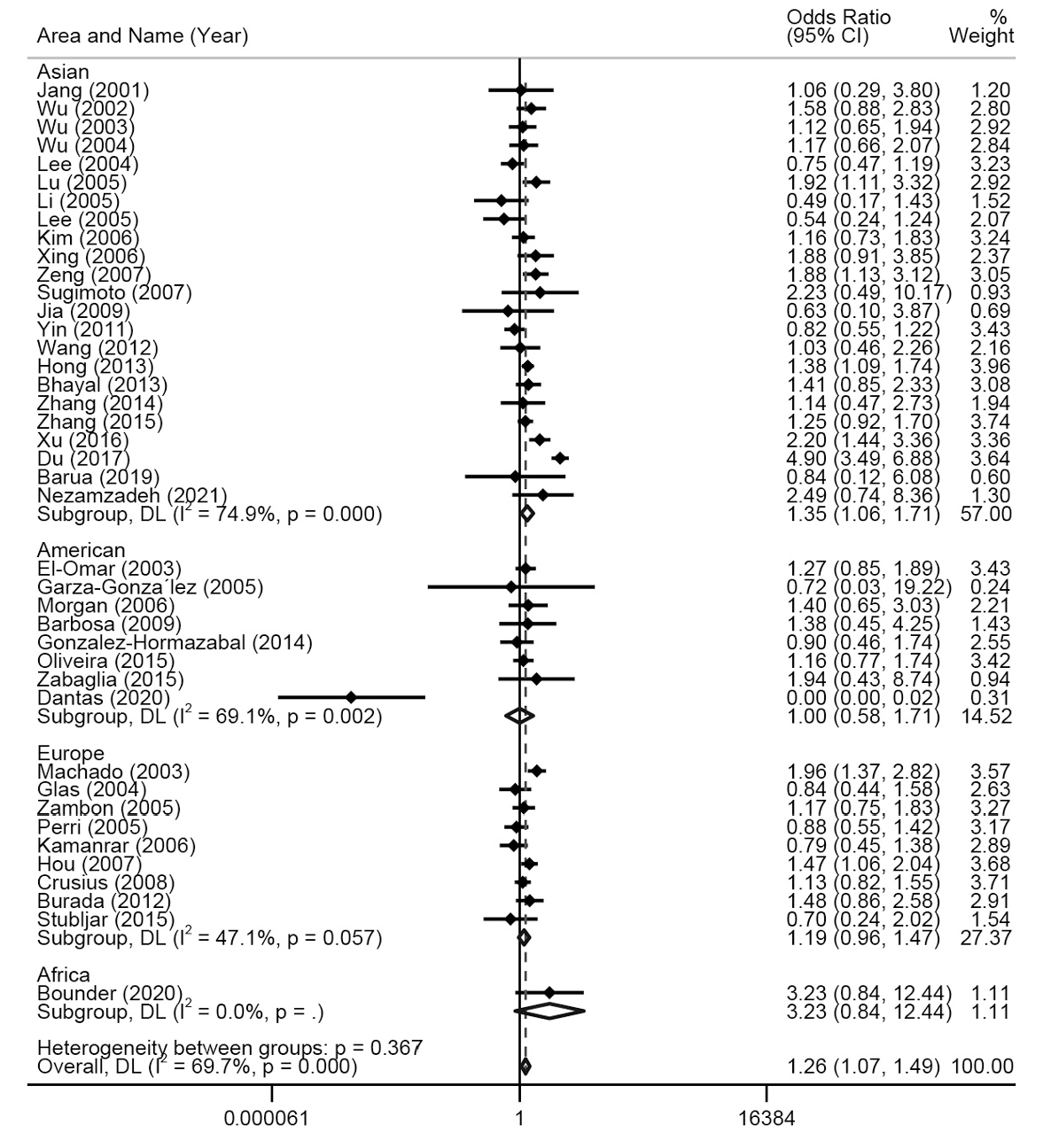
图3 基于不同地区对TNF-α-308多态性与胃癌易感性的森林图(杂合模型,AG vs GG)
Fig. 3 Forest plot of TNF-α-308 polymorphism and gastric cancer susceptibility based on different regions (Heterozygote model, AG vs GG)
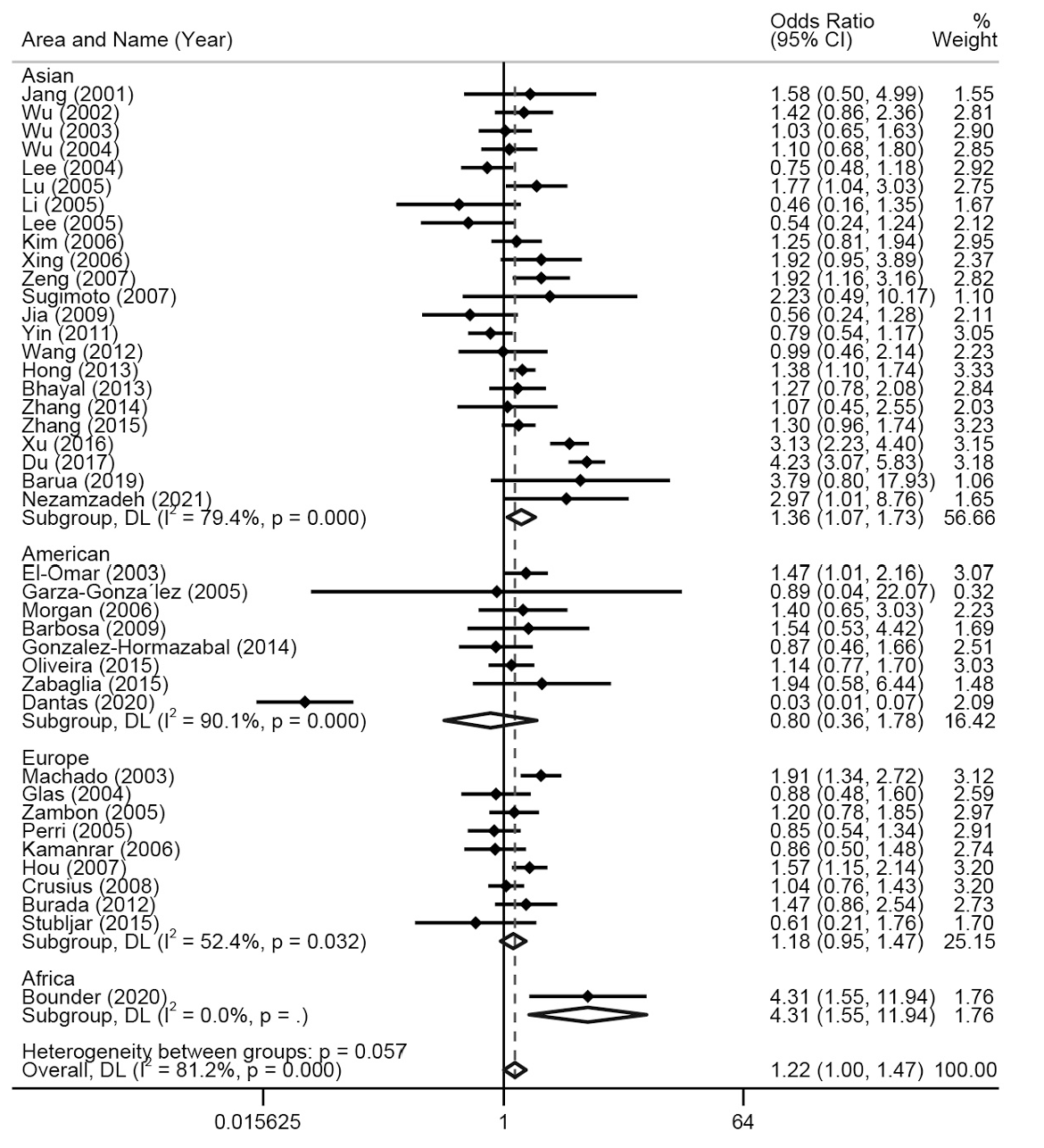
图4 基于不同地区对TNF-α-308多态性与胃癌易感性的森林图(显性模型,AA+AG vs GG)
Fig. 4 Forest plot of TNF-α-308 polymorphism and gastric cancer susceptibility based on different regions (Dominant model, AA+AG vs GG)
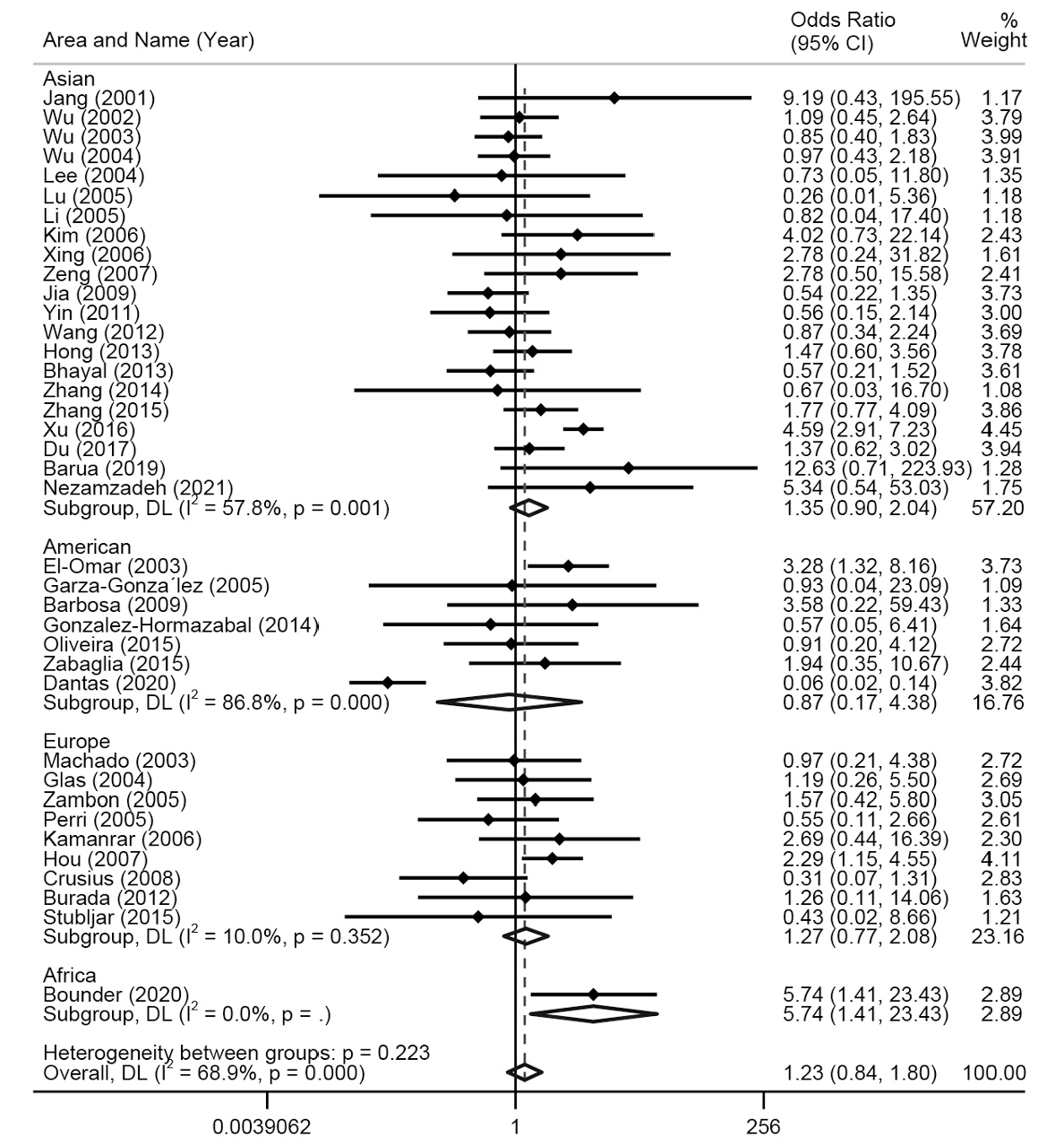
图5 基于不同地区对TNF-α-308多态性与胃癌易感性的森林图(纯合模型,AA vs GG)
Fig. 5 Forest plot of TNF-α-308 polymorphism and gastric cancer susceptibility based on different regions (Homozygote model, AA vs GG)
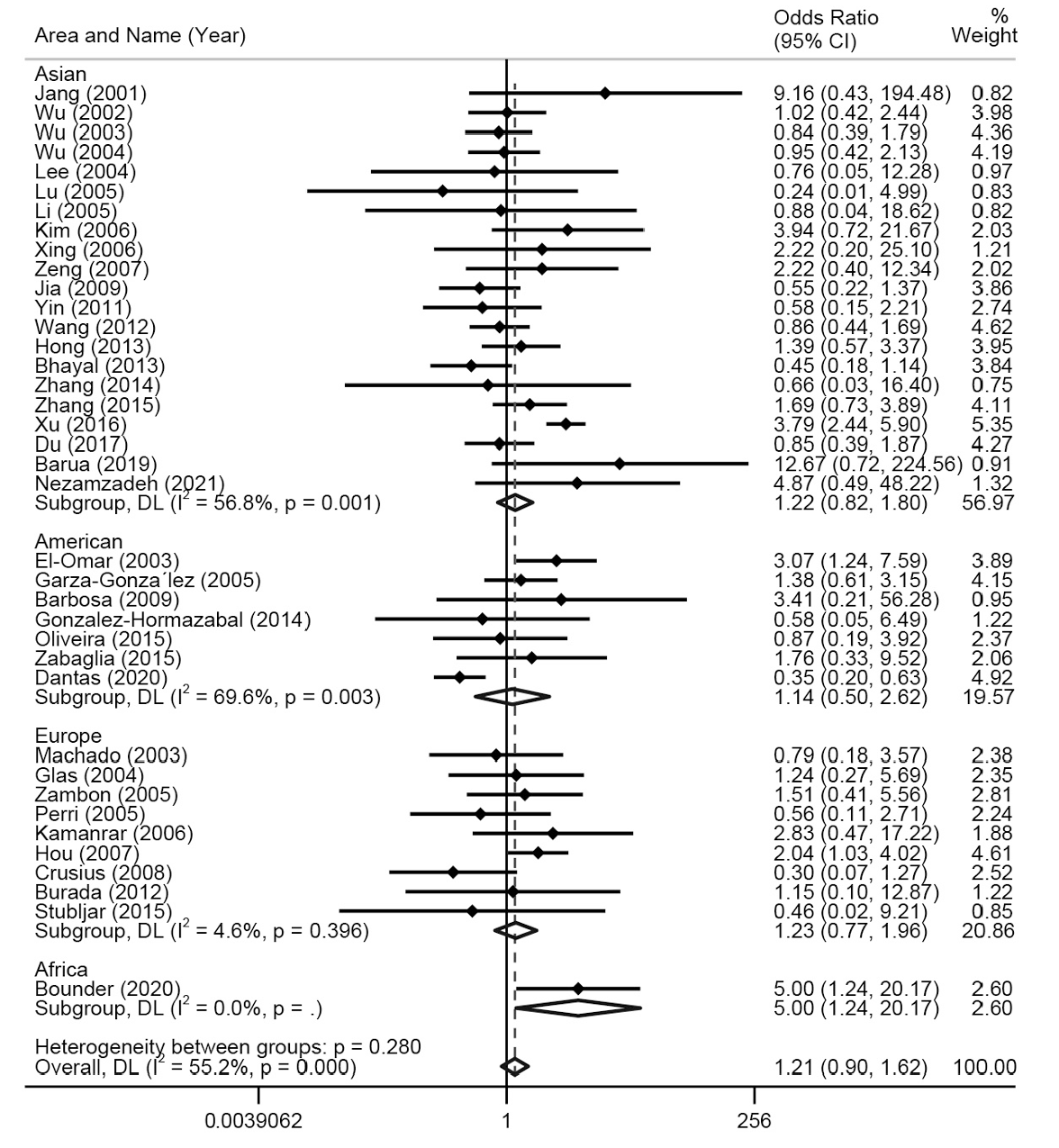
图6 基于不同地区对TNF-α-308多态性与胃癌易感性的森林图(隐性模型,AA vs AG+GG)
Fig. 6 Forest plot of TNF-α-308 polymorphism and gastric cancer susceptibility based on different regions (Recessive model, AA vs AG+GG)
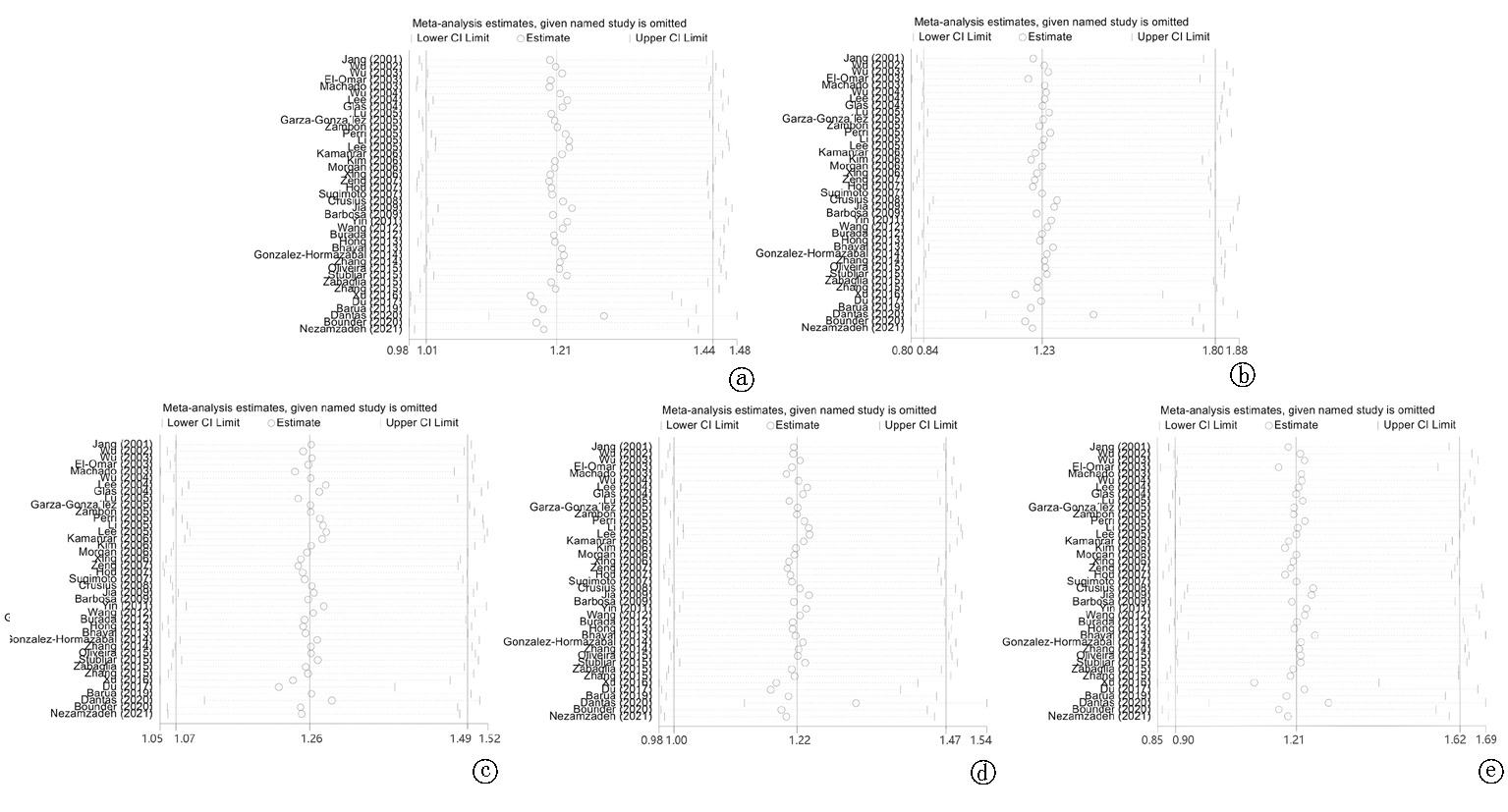
图7 TNF-α-308多态性与胃癌易感性的敏感性分析 a:等位模型,A vs G; b:纯合模型,AA vs GG; c:杂合模型,AG vs GG; d: 显性模型,AA+AG vs GG; e: 隐性模型,AA vs AG+GG 注:圆圈表示剔除该项研究后的合并 O R值;横线表示置信区间的上下边界
Fig. 7 Sensitivity analysis of TNF-α-308 polymorphism and susceptibility to gastric cancer a:Allele model, A vs G; b:Homozygote model, AA vs GG; c:Heterozygote model, AG vs GG; d:Dominant model, AA+AG vs GG; e:Recessive model, AA vs AG+GG Note: Circles indicate the combined O R after excluding the study; horizontal lines indicate the upper and lower bounds of the confidence intervals
| [1] |
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel R L, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v71.3 URL |
| [2] |
Rudnicka K, Backert S, Chmiela M. Genetic polymorphisms in inflammatory and other regulators in gastric cancer: Risks and clinical consequences[J]. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol, 2019, 421: 53-76.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-15138-6_3 pmid: 31123885 |
| [3] |
Ikeda S, Sasazuki S, Natsukawa S, et al. Screening of 214 single nucleotide polymorphisms in 44 candidate cancer susceptibility genes: a case-control study on gastric and colorectal cancers in the Japanese population[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2008, 103(6): 1476-1487.
doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.01810.x pmid: 18510611 |
| [4] |
Al-Meghaiseeb ES, Al-Robayan AA, Al-Otaibi MM, et al. Association of tumor necrosis factor-α and -β gene polymorphisms in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2016, 9: 133-140.
doi: 10.2147/JIR.S101225 pmid: 27382325 |
| [5] |
Feng H, Kuai J H, Zhang M Y, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene -308G > A polymorphism alters the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a Han Chinese population[J]. Diagn Pathol, 2014, 9: 199.
doi: 10.1186/s13000-014-0199-3 pmid: 25420786 |
| [6] | Min L, Chen D, Qu L, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-a polymorphisms and colorectal cancer risk: a meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e85187. |
| [7] |
Jang WH, Yang YI, Yea SS, et al. The -238 tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter polymorphism is associated with decreased susceptibility to cancers[J]. Cancer Lett, 2001, 166(1): 41-46.
doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(01)00438-4 pmid: 11295285 |
| [8] |
Wu MS, Huang SP, Chang YT, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10 promoter polymorphisms in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma[J]. J Infect Dis, 2002, 185(1): 106-109.
doi: 10.1086/jid.2002.185.issue-1 URL |
| [9] |
El-Omar EM, Rabkin CS, Gammon MD, et al. Increased risk of noncardia gastric cancer associated with proinflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms[J]. Gastroenterology, 2003, 124(5): 1193-1201.
doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(03)00157-4 pmid: 12730860 |
| [10] |
Machado JC, Figueiredo C, Canedo P, et al. A proinflammatory genetic profile increases the risk for chronic atrophic gastritis and gastric carcinoma[J]. Gastroenterology, 2003, 125(2): 364-371.
doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(03)00899-0 pmid: 12891537 |
| [11] |
Wu MS, Wu CY, Chen CJ, et al. Interleukin-10 genotypes associate with the risk of gastric carcinoma in Taiwanese Chinese[J]. Int J Cancer, 2003, 104(5): 617-623.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.v104:5 URL |
| [12] |
Glas J, Torok HP, Schneider A, et al. Allele 2 of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene is associated with early gastric cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2004, 22(23): 4746-4752.
pmid: 15570075 |
| [13] |
Lee SG, Kim B, Yook JH, et al. TNF/LTA polymorphisms and risk for gastric cancer/duodenal ulcer in the Korean population[J]. Cytokine, 2004, 28(2): 75-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2004.06.009 URL |
| [14] |
Wu MS, Chen LT, Shun CT, et al. Promoter polymorphisms of tumor necrosis factor-alpha are associated with risk of gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma[J]. Int J Cancer, 2004, 110(5): 695-700.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.v110:5 URL |
| [15] |
Garza-González E, Bosques-Padilla FJ, El-Omar E, et al. Role of the polymorphic IL-1B, IL-1RN and TNF-A genes in distal gastric cancer in Mexico[J]. Int J Cancer, 2005, 114(2): 237-241.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.20718 pmid: 15540224 |
| [16] |
Lee JY, Kim HY, Kim KH, et al. Association of polymorphism of IL-10 and TNF-A genes with gastric cancer in Korea[J]. Cancer Lett, 2005, 225(2): 207-214.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.11.028 pmid: 15978325 |
| [17] |
Li C, Xia B, Yang Y, et al. TNF gene polymorphisms and Helicobacter Pylori infection in gastric carcinogenesis in Chinese population[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2005, 100(2): 290-294.
doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.40806.x pmid: 15667484 |
| [18] |
Lu W, Pan K, Zhang L, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of interleukin (IL)-1B, IL-1RN, IL-8, IL-10 and tumor necrosis factor {alpha} and risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2005, 26(3): 631-636.
doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh349 pmid: 15579481 |
| [19] |
Perri F, Piepoli A, Bonvicini C, et al. Cytokine gene polymorphisms in gastric cancer patients from two Italian areas at high and low cancer prevalence[J]. Cytokine, 2005, 30(5): 293-302.
doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2005.01.011 pmid: 15927855 |
| [20] |
Zambon CF, Basso D, Navaglia F, et al. Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines gene polymorphisms and Helicobacter pylori infection: interactions influence outcome[J]. Cytokine, 2005, 29(4): 141-152.
doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2004.10.013 URL |
| [21] |
Kamangar F, Abnet CC, Hutchinson AA, et al. Polymorphisms in inflammation-related genes and risk of gastric cancer (Finland)[J]. Cancer Causes Control, 2006, 17(1): 117-125.
doi: 10.1007/s10552-005-0439-7 URL |
| [22] |
Kim N, Cho SI, Yim JY, et al. The effects of genetic polymorphisms of IL-1 and TNF-A on Helicobacter pylori-induced gastroduodenal diseases in Korea[J]. Helicobacter, 2006, 11(2): 105-112.
pmid: 16579840 |
| [23] |
Morgan DR, Dominguez RL, Keku TO, et al. Gastric cancer and the high combination prevalence of host cytokine genotypes and Helicobacter pylori in Honduras[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2006, 4(9): 1103-1111.
doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2006.05.025 URL |
| [24] | 邢培祥, 肖东杰, 胡安拉, 等. TNF-α及IL-6基因多态性与胃腺癌易感性的关系[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2006, 44(9): 949-953. |
| [25] |
Hou L, El-Omar EM, Chen J, et al. Polymorphisms in Th1-type cell-mediated response genes and risk of gastric cancer[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2007, 28(1): 118-123.
doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgl130 pmid: 16885196 |
| [26] |
Sugimoto M, Furuta T, Shirai N, et al. Different effects of polymorphisms of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta on development of peptic ulcer and gastric cancer[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2007, 22(1): 51-59.
doi: 10.1111/jgh.2007.22.issue-1 URL |
| [27] | 曾庆东, 吕丽红, 邢培祥, 等. 细胞因子基因多态性与胃腺癌关系的探讨[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2007, 87(15): 1037-1039. |
| [28] |
Crusius JB, Canzian F, Capella G, et al. Cytokine gene polymorphisms and the risk of adenocarcinoma of the stomach in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC-EURGAST)[J]. Ann Oncol, 2008, 19(11): 1894-1902.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdn400 pmid: 18628242 |
| [29] |
Melo Barbosa HP, Martins LC, Dos Santos SE, et al. Interleukin-1 and TNF-alpha polymorphisms and Helicobacter pylori in a Brazilian Amazon population[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2009, 15(12): 1465-1471.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1465 URL |
| [30] | 贾皑, 龚均, 厉英超, 等. IL-1β-511位点和TNF-α-308位点基因多态性与陕西汉族非贲门胃癌的关系[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2009, 30(1): 70-73, 127. |
| [31] |
Burada F, Angelescu C, Mitrut P, et al. Interleukin-4 receptor -3223T→C polymorphism is associated with increased gastric adenocarcinoma risk[J]. Can J Gastroenterol, 2012, 26(8): 532-536.
doi: 10.1155/2012/804173 URL |
| [32] | 王美丽, 李佳, 杨力, 等. 宁夏惠农区回、汉族人群肿瘤坏死因子α-308位点基因多态性与胃癌前疾病及胃癌相关性研究[J]. 宁夏医学杂志, 2012, 34(1): 22-24, 前插21. |
| [33] | 尹东, 王琦三, 王飞, 等. TNF-A基因多态性及其单体型与新疆维、汉民族胃癌的关系[J]. 癌变·畸变·突变, 2012, 24(4): 261-265. |
| [34] |
Bhayal AC, Krishnaveni D, RangaRao KP, et al. Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha 308 G/A promoter polymorphism in gastric cancer[J]. Saudi J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(4): 182-186.
doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.114513 pmid: 23828749 |
| [35] | Hong Y, Ge Z, Jing C, et al. Functional promoter -308G>A variant in tumor necrosis factor alpha gene is associated with risk and progression of gastric cancer in a Chinese population[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(1): e50856. |
| [36] |
Gonzalez-Hormazabal P, Musleh M, Bustamante M, et al. Role of cytokine gene polymorphisms in gastric cancer risk in Chile[J]. Anticancer Res, 2014, 34(7): 3523-3530.
pmid: 24982364 |
| [37] | 张军喜, 郭爱叶, 李宗辉, 等. TNF-α-308基因多态性与胃癌的关系研究[J]. 中国现代药物应用, 2014, 8(10): 1-2. |
| [38] |
de Oliveira J G, Rossi A F, Nizato D M, et al. Influence of functional polymorphisms in TNF-alpha, IL-8, and IL-10 cytokine genes on mRNA expression levels and risk of gastric cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36(12): 9159-9170.
doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3593-x URL |
| [39] |
Stubljar D, Jeverica S, Jukic T, et al. The influence of cytokine gene polymorphisms on the risk of developing gastric cancer in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection[J]. Radiol Oncol, 2015, 49(3): 256-264.
doi: 10.2478/raon-2014-0041 pmid: 26401131 |
| [40] |
Zabaglia LM, Ferraz MA, Pereira WN, et al. Lack of association among TNF-alpha gene expression, -308 polymorphism (G > A) and virulence markers of Helicobacter pylori[J]. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis, 2015, 21: 54.
doi: 10.1186/s40409-015-0054-3 pmid: 26719751 |
| [41] | 张德忠, 江伟春, 刘泽洪, 等. 肿瘤坏死因子α-308基因多态性与胃癌患者血清胃蛋白酶原的关系[J]. 中华临床实验室管理电子杂志, 2015, 3(4): 249-252. |
| [42] |
Du LC, Gao R. Role of TNF-alpha -308G/A gene polymorphism in gastric cancer risk: A case control study and meta-analysis[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2017, 28(4): 272-282.
doi: 10.5152/tjg URL |
| [43] |
Xu Y, Cao X, Jiang J, et al. TNF-alpha-308/-238 polymorphisms are associated with gastric cancer: A case-control family study in China[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2017, 41(1): 103-109.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2016.05.014 URL |
| [44] |
Fukayama M, Uozaki H, Chong JM, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α polymorphism in helicobacter pylori associated gastric carcinoma[J]. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull, 2019, 45(3): 170-174.
doi: 10.3329/bmrcb.v45i3.44647 URL |
| [45] |
Bounder G, Jouimyi MR, Boura H, et al. Associations of the -238(G/A) and -308(G/A) TNF-alpha Promoter Polymorphisms and TNF-alpha Serum Levels with the Susceptibility to Gastric Precancerous Lesions and Gastric Cancer Related to Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Moroccan Population[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2020, 21(6): 1623-1629.
doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.6.1623 URL |
| [46] |
Dantas RN, Souza AM, Herrero SST, et al. Association between PSCA, TNF-alpha, PARP1 and TP53 Gene Polymorphisms and Gastric Cancer Susceptibility in the Brazilian Population[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2020, 21(1): 43-48.
doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.1.43 URL |
| [47] |
Nezamzadeh F, Asadyun M, Anbiyaiee A, et al. Association of specific haplotype of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β polymorphisms with Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinogenesis[J]. Germs, 2021, 11(4): 554-561.
doi: 10.18683/germs.2021.1290 pmid: 35096672 |
| [48] |
Yang JP, Hyun MH, Yoon JM, et al. Association between TNF-alpha-308 G/A gene polymorphism and gastric cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Cytokine, 2014, 70(2): 104-114.
doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.07.005 URL |
| [49] |
Jiang X, Naikoo NA, Gao S. A meta-analysis of tumor necrosis factor-α-308 G>A polymorphism in gastric cancer[J]. Asian Biomedicine, 2020, 14(3): 91-96.
doi: 10.1515/abm-2020-0014 URL |
| [1] | 龚财芳, 赵俊宇, 游川. 接纳与承诺疗法对癌症患者心理健康和生活质量影响的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(2): 101-107. |
| [2] | 肖煌怡, 袁建坤, 严梓予, 曾雯姝, 鲁兰莫, 王峻. 认知干预对遗忘型轻度认知障碍老年患者干预效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 12-19. |
| [3] | 赵旭辉, 黄小敏, 达德转, 许焱, 崔晓东, 李红玲. 基于生物信息学筛选影响胃癌患者预后的糖酵解相关基因[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 20-29. |
| [4] | 李海, 刘文虎, 彭绍鹏, 王飞. 控制性阶梯式减压术对比快速标准大骨瓣减压术治疗重度颅脑损伤疗效的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(9): 788-795. |
| [5] | 侯有玲, 李奕, 关红玉, 罗红霞. 目标导向液体治疗在脑肿瘤切除术中应用效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(8): 686-693. |
| [6] | 金家辉, 杨阳, 秦铜, 何雨欣, 苏美华. 补充益生菌对2型糖尿病患者糖代谢改善的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 581-587. |
| [7] | 肖王静, 李欣梦, 卢松玲, 孙雪华. 重复经颅磁刺激治疗中枢神经源性吞咽障碍疗效及安全性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 588-599. |
| [8] | 尤奕, 高淑清, 徐浩. 肠内营养对食管癌患者术后临床结局影响的系统综述[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 485-492. |
| [9] | 倪艺芸, 刘彬, 梁琪, 李晓凤. 白细胞介素6和C反应蛋白预测新型冠状病毒肺炎严重程度的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 493-499. |
| [10] | 沃拉孜汗·玛德尼亚提, 迪力夏提·图尔迪麦麦提, 李梦晨, 拜合提尼沙·吐尔地. 宏基因组二代测序技术在肺结核诊断中应用价值的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 389-398. |
| [11] | 赵哲, 穆培娟, 张冬. 恩度联合顺铂胸腔灌注治疗肺癌合并恶性胸腔积液疗效的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 399-404. |
| [12] | 王英南, 赵琦, 白海威, 武丹娜, 魏金梅, 李省江, 李锐凌, 张瑞星. 胃癌合并脑梗死的临床特点及危险因素分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 417-422. |
| [13] | 马明福, 魏志国, 何铁英. 急性胰腺炎并发胰腺假性囊肿危险因素的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 293-301. |
| [14] | 曹宇萌, 张海燕, 刘立新. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的病理改变与血清铁蛋白和血清铁含量变化关系的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(3): 197-207. |
| [15] | 马宏莉, 陆皓, 王丹, 焦海星, 李一珂, 李思雨, 吕静. 脑卒中患者残疾危险因素的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(2): 111-116. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 50
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 172
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
