

临床荟萃 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (12): 1061-1072.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.12.001
• 循证研究 • 下一篇
张琦1,2, 孙增鑫2,3, 赵越1, 袁野2,3, 秦小露2,3, 吕红香4, 尹昱1,2,3( ), 张雅文5
), 张雅文5
收稿日期:2024-08-21
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2025-01-10
通讯作者:
尹昱,Email:基金资助:
Zhang Qi1,2, Sun Zengxin2,3, Zhao Yue1, Yuan Ye2,3, Qin Xiaolu2,3, Lyu Hongxiang4, Yin Yu1,2,3( ), Zhang Yawen5
), Zhang Yawen5
Received:2024-08-21
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2025-01-10
Contact:
Yin Yu; Email: 摘要:
目的 采用网状meta分析比较不同刺激方式的经颅直流电刺激(transcranial direct current stimulation, tDCS)对脑卒中后单侧忽略(unilateral spatial neglect, USN)患者的康复疗效。方法 计算机检索中国知网(CNKI)、万方数据知识服务平台(Wanfang Data)、维普网(VIP)、PubMed、Embase、Cochrane Library、Web of Science、ProQuest数据库中有关tDCS治疗USN的随机对照试验(RCT)和随机交叉实验(RCE),对照组采用假刺激或常规物理治疗,试验组为不同刺激方式的tDCS治疗,检索时间为建库至2024年5月。由两名研究员对文献进行筛选及数据的提取,采用RevMen5.3以及Stata14.0软件进行数据分析。结果 最终纳入11篇文献,共462例患者。结果显示:多靶点刺激、阳极刺激以及阴极刺激对于提高USN患者的二等分线段测试(LBT)、星形消去测试(SCT)评分均高于对照组,阳极刺激和多靶点刺激对USN患者行为忽略测试(BIT)评分较假刺激改善明显。不同措施改善USN患者LBT评分的累积排序概率曲线下面积(SUCRA)排序结果显示:多靶点刺激(84.4%)>阳极刺激(82.4%)>阴极刺激(77.8%)>双通道刺激(76.3%)>假刺激(52.5%)>双通道刺激联合物理治疗(30.3%)>阳极联合物理治疗(22.7%)>多靶点刺激联合物理治疗(17.9%)>物理治疗(5.8%),提高SCT评分的SUCRA排序结果显示:多靶点刺激(67.1%)>阳极刺激(66.7%)>双通道刺激(56.0%)>阳极刺激联合物理治疗(47.7%)>阴极刺激(43.2%)>假刺激(41.6%)>多靶点刺激联合物理治疗(27.7%),降低BIT评分的SUCRA排序结果显示:多靶点刺激(99.7%)>阳极刺激联合物理治疗(61.1%)>多靶点刺激联合物理治疗(59.8%)>阳极刺激(59.4%)>假刺激(20.0%)>阴极刺激联合物理治疗(0.0%)。结论 现有证据表明,在假刺激及常规对照的基础上,多靶点刺激和阳极刺激改善脑卒中患者USN的效果优于阴极刺激以及各种刺激联合物理治疗。受所纳入的试验的数量和质量限制,上述结果仍需谨慎采用,未来还需要引用更多更高质量的研究进一步验证。
中图分类号:
张琦, 孙增鑫, 赵越, 袁野, 秦小露, 吕红香, 尹昱, 张雅文. 经颅直流电刺激对脑卒中患者单侧忽略康复效果的影响: 网状meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(12): 1061-1072.
Zhang Qi, Sun Zengxin, Zhao Yue, Yuan Ye, Qin Xiaolu, Lyu Hongxiang, Yin Yu, Zhang Yawen. Rehabilitation effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on unilateral spatial neglect in stroke patients: a network meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(12): 1061-1072.
| 纳入研究 | 国家 | 样本量 (EG/CG) | 年龄 (岁) | 干预措施(CG/EG) | 刺激强度 | 干预时长 | 结局 指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhao等[ | 中国 | 10(10/10) | 42~63 | 假刺激(阳极置于右侧顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧肩膀)/单靶点刺激(阳极置于右侧顶叶皮层,阴极置于对侧肩膀)/多靶点刺激(阳极依次置于右侧顶下小叶、右侧颞中回和右侧前额叶,阴极置于对侧肩膀) | 2mA | 5次/周,共3周 | ①②③ |
| Sunwoo等[ | 韩国 | 10(10/10) | 37~81 | 假刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘)/单通道刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘)/双通道刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧后顶叶皮层) | 1mA | 共4次 | ① |
| Bang等[ | 韩国 | 6/6 | 60~72 | 阳极tDCS联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘联合反馈训练)/物理治疗(反馈训练) | 1mA | 5次/周,共3周 | ① |
| Ladavas等[ | 意大利 | 11(11/8) | 59~80 | 假刺激联合物理治疗(5例阴极置于左侧后顶叶皮层,阳极置于右侧眶上缘,6例阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左眶上缘联合棱镜训练)/阳极联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上联合棱镜训练)/阴极联合物理治疗(阴极置于左侧后顶叶皮层,阳极置于右侧眶上缘联合棱镜训练) | 2mA | 5次/周,共2周 | ③ |
| 毛阗睿[ | 中国 | 12/12 | 26~75 | 假刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘)/阳极tDCS(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘) | 1.6mA | 5次/周,共2周 | ①② |
| 姜春静等[ | 中国 | 10/10 | 37~78 | 假刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘)/阳极tDCS(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘) | 1mA | 5次/周,共2周 | ① |
| 易琼等[ | 中国 | 41/41 | 42~86 | 假刺激联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧后顶叶后部,阴极置于左侧肩部联合高压氧)/阳极tDCS联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧后顶叶后部,阴极置于左侧肩部联合高压氧) | 1.4mA | 5次/周,共4周 | ① |
| 成帅等[ | 中国 | 30(30/30) | 20~80 | 假刺激联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧顶下小叶,阴极置于左侧肩部联合针刺)/单部位刺激联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧顶下小叶,阴极置于左侧肩部联合针刺)/多部位刺激联合物理治疗(阳极依次置于右侧顶下小叶、颞上回、前额叶,阴极置于左侧肩部联合针刺) | 未交代 | 5次/周,共3周 | ①② |
| Yi等[ | 韩国 | 10(10/10) | 39~82 | 假刺激[阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于中央点(Cz区)]/阳极tDCS[阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于中央点(Cz区)]/阴极tDCS[阴极置于左侧后顶叶皮层,阳极置于中央点(Cz区)] | 2mA | 5次/周,共3周 | ①② |
| 王雅楠等[ | 中国 | 15/15 | 假刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧肩部)/阳极tDCS刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧肩部) | 1.4mA | 5次/周,共4周 | ① | |
| 甄巧霞等[ | 中国 | 15/15 | 34~72 | 假刺激联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧顶叶皮质,阴极置于左侧顶叶皮质联合认知训练)/双极刺激联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧顶叶皮质,阴极置于左侧顶叶皮质联合认知训练) | 1mA | 5次/轴,共4周 | ① |
表1 纳入文献的基本特征
Tab. 1 Basic characteristics of included literatures
| 纳入研究 | 国家 | 样本量 (EG/CG) | 年龄 (岁) | 干预措施(CG/EG) | 刺激强度 | 干预时长 | 结局 指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhao等[ | 中国 | 10(10/10) | 42~63 | 假刺激(阳极置于右侧顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧肩膀)/单靶点刺激(阳极置于右侧顶叶皮层,阴极置于对侧肩膀)/多靶点刺激(阳极依次置于右侧顶下小叶、右侧颞中回和右侧前额叶,阴极置于对侧肩膀) | 2mA | 5次/周,共3周 | ①②③ |
| Sunwoo等[ | 韩国 | 10(10/10) | 37~81 | 假刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘)/单通道刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘)/双通道刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧后顶叶皮层) | 1mA | 共4次 | ① |
| Bang等[ | 韩国 | 6/6 | 60~72 | 阳极tDCS联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘联合反馈训练)/物理治疗(反馈训练) | 1mA | 5次/周,共3周 | ① |
| Ladavas等[ | 意大利 | 11(11/8) | 59~80 | 假刺激联合物理治疗(5例阴极置于左侧后顶叶皮层,阳极置于右侧眶上缘,6例阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左眶上缘联合棱镜训练)/阳极联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上联合棱镜训练)/阴极联合物理治疗(阴极置于左侧后顶叶皮层,阳极置于右侧眶上缘联合棱镜训练) | 2mA | 5次/周,共2周 | ③ |
| 毛阗睿[ | 中国 | 12/12 | 26~75 | 假刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘)/阳极tDCS(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘) | 1.6mA | 5次/周,共2周 | ①② |
| 姜春静等[ | 中国 | 10/10 | 37~78 | 假刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘)/阳极tDCS(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧眶上缘) | 1mA | 5次/周,共2周 | ① |
| 易琼等[ | 中国 | 41/41 | 42~86 | 假刺激联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧后顶叶后部,阴极置于左侧肩部联合高压氧)/阳极tDCS联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧后顶叶后部,阴极置于左侧肩部联合高压氧) | 1.4mA | 5次/周,共4周 | ① |
| 成帅等[ | 中国 | 30(30/30) | 20~80 | 假刺激联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧顶下小叶,阴极置于左侧肩部联合针刺)/单部位刺激联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧顶下小叶,阴极置于左侧肩部联合针刺)/多部位刺激联合物理治疗(阳极依次置于右侧顶下小叶、颞上回、前额叶,阴极置于左侧肩部联合针刺) | 未交代 | 5次/周,共3周 | ①② |
| Yi等[ | 韩国 | 10(10/10) | 39~82 | 假刺激[阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于中央点(Cz区)]/阳极tDCS[阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于中央点(Cz区)]/阴极tDCS[阴极置于左侧后顶叶皮层,阳极置于中央点(Cz区)] | 2mA | 5次/周,共3周 | ①② |
| 王雅楠等[ | 中国 | 15/15 | 假刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧肩部)/阳极tDCS刺激(阳极置于右侧后顶叶皮层,阴极置于左侧肩部) | 1.4mA | 5次/周,共4周 | ① | |
| 甄巧霞等[ | 中国 | 15/15 | 34~72 | 假刺激联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧顶叶皮质,阴极置于左侧顶叶皮质联合认知训练)/双极刺激联合物理治疗(阳极置于右侧顶叶皮质,阴极置于左侧顶叶皮质联合认知训练) | 1mA | 5次/轴,共4周 | ① |
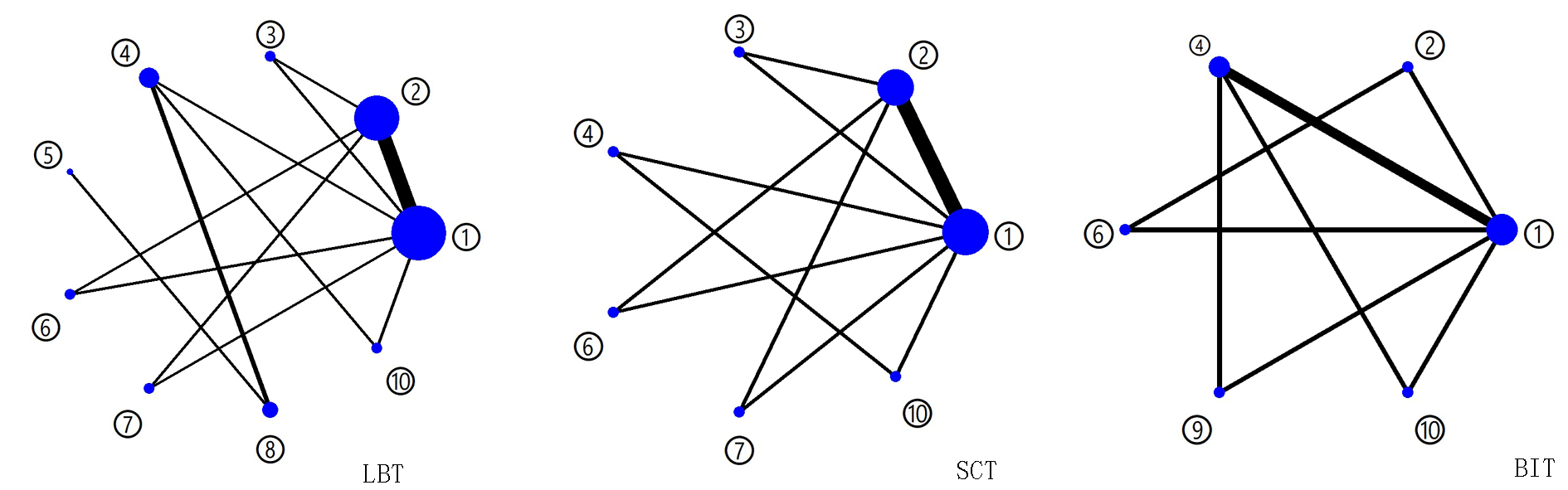
图3 不同结局指标下各干预措施间的网状关系 ①假刺激;②阳极刺激;③阴极刺激;④阳极刺激联合物理治疗;⑤双通道刺激(一侧阳极一侧阴极)联合物理治疗;⑥多靶点刺激(阳极);⑦双通道刺激(一侧阳极一侧阴极);⑧物理治疗;⑨阴极刺激联合物理治疗;⑩多靶点刺激(阳极)联合物理治疗
Fig. 3 Network diagram of each intervention under different outcome indicators ①Sham stimulation;②Anode stimulation;③Cathodic stimulation; ④Anodic stimulation combined with physical therapy; ⑤Dual-channel stimulation (one anode stimulation and the other cathode stimulation) combined with physical therapy; ⑥Multi-target stimulation (anodic stimulation); ⑦Dual-channel stimulation (one anode stimulation and the other cathode stimulation);⑧Physical therapy; ⑨Cathodic stimulation combined with physical therapy; ⑩Multi-target stimulation (anodic stimulation) combined with physical therapy
| [1] |
Feigin VL, Norrving B, Mensah GA. Global burden of stroke[J]. Circ Res, 2017, 120(3): 439-448.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308413 pmid: 28154096 |
| [2] |
Friedland RP, Weinstein EA. Hemi-inattention and hemisphere specialization: Introduction and historical review[J]. Adv Neurol, 1977, 18: 1-31.
pmid: 411354 |
| [3] | da Silva TR, de Carvalho Nunes HR, Martins LG, et al. Non-invasive brain stimulation can reduce unilateral spatial neglect after stroke: ELETRON Trial[J]. Ann Neurol, 2022, 92(3): 400-410. |
| [4] | 张仁刚, 何成晓, 王迪, 等. 视动刺激干预脑卒中后单侧忽略的研究进展[J]. 中国康复, 2021, 36(8): 495-498. |
| [5] |
Vallar G, Bottini G, Paulesu E. Neglect syndromes: The role of the parietal cortex[J]. Adv Neurol, 2003, 93: 293-319.
pmid: 12894416 |
| [6] |
Middag-Van SM, Schuhmann T, Nijboer T, et al. Study protocol of transcranial electrical stimulation at alpha frequency applied during rehabilitation: A randomized controlled trial in chronic stroke patients with visuospatial neglect[J]. BMC Neurol, 2022, 22(1): 402.
doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02932-7 pmid: 36324088 |
| [7] |
Corbetta M, Shulman GL. Spatial neglect and attention networks[J]. Annu Rev Neurosci, 2011, 34: 569-599.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113731 pmid: 21692662 |
| [8] |
Luvizutto GJ, Rizzati GR, Fogaroli MO, et al. Treatment of unilateral spatial neglect after stroke using transcranial direct current stimulation (ELETRON trial): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial[J]. Trials, 2016, 17(1): 479.
pmid: 27716442 |
| [9] | Kinsbourne M. Hemi-neglect and hemisphere rivalry[J]. Adv Neurol, 1977,18:41-49. |
| [10] |
Posner MI, Walker JA, Friedrich FJ, et al. Effects of parietal injury on covert orienting of attention[J]. J Neurosci, 1984, 4(7): 1863-1874.
pmid: 6737043 |
| [11] | 朱玉连, 习冲. 不同刺激靶点在经颅直流电刺激介导的帕金森病康复中的应用[J]. 康复学报, 2023, 33(2): 180-185. |
| [12] |
Geiger M, Supiot A, Zory R, et al. The effect of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on locomotion and balance in patients with chronic stroke: Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial[J]. Trials, 2017, 18(1): 492.
doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2219-6 pmid: 29061169 |
| [13] | Wright JM, Krekelberg B. Transcranial direct current stimulation over posterior parietal cortex modulates visuospatial localization[J]. J Vis, 2014, 14(9):5. |
| [14] |
Medina J, Beauvais J, Datta A, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation accelerates allocentric target detection[J]. Brain Stimul, 2013, 6(3): 433-439.
doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2012.05.008 pmid: 22784444 |
| [15] | Smit M, Schutter DJ, Nijboer TC, et al. [Transcranial direct current stimulation; potential new treatment for unilateral neglect][J]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd, 2013, 157(27): A6056. |
| [16] | Harrison JE, Weber S, Jakob R, et al. ICD-11: An international classification of diseases for the twenty-first century[J]. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak, 2021, 21(Suppl 6): 206. |
| [17] | 李若薇, 夏渊, 李永杰, 等. 不同刺激方式的经颅直流电刺激对脑卒中患者上肢运动功能和日常生活活动能力的影响:网状meta分析[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2023, 38(3): 394-402. |
| [18] |
Zhao Y, Li W, Huang D, et al. The therapeutic effect of transcranial direct current stimulation combined with cognitive training on patients with unilateral neglect after stroke[J]. NeuroRehabilitation, 2023, 52(3): 477-483.
doi: 10.3233/NRE-220265 pmid: 37005898 |
| [19] |
Sunwoo H, Kim YH, Chang WH, et al. Effects of dual transcranial direct current stimulation on post-stroke unilateral visuospatial neglect[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2013, 554: 94-98.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.08.064 pmid: 24021804 |
| [20] | Bang DH, Bong SY. Effect of combination of transcranial direct current stimulation and feedback training on visuospatial neglect in patients with subacute stroke: A pilot randomized controlled trial[J]. J Phys Ther Sci, 2015, 27(9): 2759-2761. |
| [21] | Ladavas E, Giulietti S, Avenanti A, et al. a-tDCS on the ipsilesional parietal cortex boosts the effects of prism adaptation treatment in neglect[J]. Restor Neurol Neurosci, 2015, 33(5): 647-662. |
| [22] | 毛阗睿. 经颅直流电刺激对脑卒中后单侧忽略治疗疗效的研究[D]. 太原: 山西医科大学, 2019. |
| [23] | 姜春静, 单桂香, 张大华, 等. 经颅直流电刺激对脑卒中后视觉空间忽略不同参考框架成分的影响[J]. 中国康复, 2021, 36(6): 323-326. |
| [24] | 易琼, 孙文琳, 祁玉军. 经颅直流电刺激联合高压氧疗治疗脑卒中后单侧空间忽略患者的临床效果研究[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2022, 30(2): 24-28. |
| [25] | 成帅, 尹昱, 张少华, 等. 针刺联合经颅直流电刺激治疗脑卒中后偏侧忽略疗效观察[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2022, 31(14): 1950-1956. |
| [26] |
Yi YG, Chun MH, Do KH, et al. The effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on neglect syndrome in stroke patients[J]. Ann Rehabil Med, 2016, 40(2): 223-229.
doi: 10.5535/arm.2016.40.2.223 pmid: 27152271 |
| [27] | 王雅楠, 孙乐影, 刘田, 等. 经颅直流电刺激改善偏侧空间忽略及运动功能的疗效观察[J]. 中国康复, 2019, 34(8): 403-406. |
| [28] | 甄巧霞, 刘爱贤, 郄淑燕, 等. 经颅直流电刺激结合认知训练治疗单侧空间忽略的临床研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2018, 33(7): 855-857. |
| [29] | Qurat UA, Ahmad Z, Ishtiaq S, et al. Short term effects of anodal cerebellar vs. anodal cerebral transcranial direct current stimulation in stroke patients, a randomized control trial[J]. Front Neurosci, 2022, 16:1035558. |
| [30] | 汪文静, 李甲笠, 张思聪, 等. 经颅直流电刺激的作用机制及在脑卒中康复中的应用进展[J]. 中国康复, 2019, 34(10): 535-539. |
| [31] | Shaker HA, Sawan S, Fahmy EM, et al. Effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on cognitive function in stroke patients[J]. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatr Neurosurg, 2018, 54(1): 32. |
| [32] |
郭华珍, 恽晓萍, 张慧丽, 等. 左侧空间忽略患者远空间忽略的表现与评定研究[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2022, 28(5): 520-523.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2022.05.005 |
| [33] |
华玲, 张一楠, 郑玉, 等. 手控节律音乐治疗对脑卒中后单侧空间忽略的效果[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2023, 29(7): 833-838.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2023.07.013 |
| [34] |
杨宇轩, 张晗, 杜娟, 等. 眼动追踪的动态任务评估脑卒中后单侧空间忽略的价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4020-4025.
doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0791 |
| [35] | 赵健乐, 李景琦, 牛森林, 等. 硬膜外植入式皮质刺激脑卒中患者提高神经网络功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014(30): 4900-4905. |
| [36] |
Heilman KM, Van Den Abell T. Right hemisphere dominance for attention: The mechanism underlying hemispheric asymmetries of inattention (neglect)[J]. Neurology, 1980, 30(3): 327-330.
doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.3.327 pmid: 7189037 |
| [37] |
Andres M, Masson N, Larigaldie N, et al. Transcranial electric stimulation optimizes the balance of visual attention across space[J]. Clin Neurophysiol, 2020, 131(4): 912-920.
doi: S1388-2457(20)30029-8 pmid: 32078920 |
| [38] | 池林, 李红玲. 经颅直流电刺激及其在脑损伤中的应用[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2018, 40(5): 385-388. |
| [39] | Liu M, Li Q, Bao Y, et al. Effect of low frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) combined with hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) on awakening of coma patients with traumatic brain injury[J]. J Healthc Eng, 2022, 2022: 6133626. |
| [40] | Zhang JP, Xing XX, Zheng MX, et al. Effects of cortico-cortical paired associative stimulation based on multisensory integration to brain network connectivity in stroke patients: Study protocol for a randomized doubled blind clinical trial[J]. BMC Neurol, 2023, 23(1): 176. |
| [41] | Esposito E, Shekhtman G, CHEN P. Prevalence of spatial neglect post-stroke: A systematic review[J]. Ann Phys Rehabil Med, 2021, 64(5): 101459. |
| [42] | Millot S, Beis JM, Pierret J, et al. Innovative therapy combining neck muscle vibration and transcranial direct current stimulation in association with conventional rehabilitation in left unilateral spatial neglect patients: HEMISTIM protocol for a randomized controlled trial[J]. Brain Sci, 2023, 13(4). |
| [43] |
Yang NY, Fong KN, Li-Tsang CW, et al. Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with sensory cueing on unilateral neglect in subacute patients with right hemispheric stroke: A randomized controlled study[J]. Clin Rehabil, 2017, 31(9): 1154-1163.
doi: 10.1177/0269215516679712 pmid: 27920261 |
| [44] | 陈颜峰, 王茂源, 罗云, 等. 理论模型及刺激靶点在重复经颅磁刺激促进中风患者上肢运动功能恢复中的研究进展[J]. 中医康复, 2024, 1(1): 51-57. |
| [45] | Zhang X, Liu B, Li Y, et al. Multi-target and multi-session transcranial direct current stimulation in patients with prolonged disorders of consciousness: A controlled study[J]. Front Neurosci, 2021, 15: 641951. |
| [46] |
Gossmann A, Kastrup A, Kerkhoff G, et al. Prism adaptation improves ego-centered but not allocentric neglect in early rehabilitation patients[J]. Neurorehabil Neural Repair, 2013, 27(6): 534-541.
doi: 10.1177/1545968313478489 pmid: 23471178 |
| [47] |
申嘉怡, 张通, 胡雪艳, 等. 动作观察疗法对脑卒中后单侧忽略的效果[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2018, 24(8): 930-937.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2018.08.012 |
| [1] | 王琳, 王婷, 蒲晓岚, 鞠梅. 老年人口腔健康状况与认知功能纵向队列研究的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(8): 677-683. |
| [2] | 叶智博, 李可勇, 阙昌浩, 王亚平, 苟云久. 腹腔镜Heller肌切开术与经口内镜下肌切开术治疗贲门失弛缓症疗效及安全性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(8): 684-692. |
| [3] | 岳江红, 王恒, 蔡钢, 张选明, 彭曦. 索格列净治疗2型糖尿病疗效和安全性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(7): 581-592. |
| [4] | 王彩贞, 苗丽娜, 陈源, 李双成. 高频迷走神经刺激治疗难治性癫痫有效性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(7): 593-597. |
| [5] | 徐玉萍, 沈滔. 乳脂球表皮生长因子8对缺血性脑卒中后认知功能障碍的预测价值[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(6): 524-530. |
| [6] | 高铭, 刘昊, 于航, 林霖, 张紫杰, 熊颖. 超声造影对局灶性睾丸病变诊断价值的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(5): 389-395. |
| [7] | 刘秀颖, 崔凯歌, 刘丽莹, 吴艳凯, 于佳琪, 杨冀萍. 基于静息态功能磁共振成像探讨卒中后疲劳的中枢机制[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(5): 401-407. |
| [8] | 师丽琪, 雷普文, 钱宝堂. 高强度间歇训练在接受经皮冠状动脉介入治疗冠心病患者心脏康复中的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(5): 466-469. |
| [9] | 员笑笑, 李淑芬, 孙芳. 免疫功能正常成人腺病毒肺炎患者临床特征的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(4): 293-303. |
| [10] | 孙帅刚, 翟亚玲, 张文惠, 田慧娟. 扁桃体切除术治疗IgA肾病的疗效评价:一项meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(3): 197-207. |
| [11] | 李冠珠, 杨亚婷, 邓金和, 邵兰, 曾朝坤. 垂体后叶素联合肾上腺素应用于心肺复苏治疗效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(3): 208-215. |
| [12] | 宋梦姣, 王睿琪, 曹灿, 程光森, 刘羽, 李忠亮, 杨建豪. 血尿酸与首次急性缺血性脑卒中患者TOAST分型及预后的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(3): 216-221. |
| [13] | 包娟, 王婷, 刘红, 周维娟, 张敏. 脑小血管病患者认知障碍及步态异常的康复研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(3): 269-273. |
| [14] | 龚财芳, 赵俊宇, 游川. 接纳与承诺疗法对癌症患者心理健康和生活质量影响的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(2): 101-107. |
| [15] | 李雯琳, 张志. 心房颤动患者左心耳形态结构和功能与左心耳血栓及心源性卒中的关系研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(2): 168-171. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||