Clinical Focus ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (12): 1110-1113.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.12.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluation value of severity and prognosis of Lung ultrasound combined with serum NT-proBNP and sFlt-1 on acute respiratory distress syndrome in patient
- Department of cardiovascular and respiratory medicine, the People's Hospital of Linxia, Linxia 731100, China
-
Received:2021-05-07Online:2021-12-20Published:2021-12-24 -
Contact:Ma Guilan E-mail:yuubb53@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Guilan, Min Ju. Evaluation value of severity and prognosis of Lung ultrasound combined with serum NT-proBNP and sFlt-1 on acute respiratory distress syndrome in patient[J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(12): 1110-1113.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.12.011
| 组别 | 例数 | LUS (分) | NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | sFlt-1 (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重度组 | 58 | 24.82±4.47 | 819.31±72.17 | 603.57±58.49 |
| 中度组 | 51 | 18.43±3.86* | 729.46±62.47* | 526.78±47.25* |
| 轻度组 | 29 | 12.10±3.15*# | 522.28±70.16*# | 417.32±53.21*# |
| F值 | 102.316 | 183.092 | 118.523 | |
| P值 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| 组别 | 例数 | LUS (分) | NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | sFlt-1 (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重度组 | 58 | 24.82±4.47 | 819.31±72.17 | 603.57±58.49 |
| 中度组 | 51 | 18.43±3.86* | 729.46±62.47* | 526.78±47.25* |
| 轻度组 | 29 | 12.10±3.15*# | 522.28±70.16*# | 417.32±53.21*# |
| F值 | 102.316 | 183.092 | 118.523 | |
| P值 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| 项目 | 预后不良组 (n=41) | 预后良好组 (n=97) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 27(65.85) 14(34.15) | 55(56.70) 42(43.30) | χ2=0.193 | 0.660 |
| 年龄(岁) | 57.10±7.93 | 55.83±8.12 | t=0.845 | 0.399 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 22.53±2.72 | 22.31±2.61 | t=0.447 | 0.656 |
| 入住ICU时间(天) | 14.20±2.36 | 11.15±1.72 | t=8.482 | <0.01 |
| 既往史[例(%)] | ||||
| 冠心病史 | 5(12.20) | 11(11.34) | χ2=0.021 | 0.886 |
| 糖尿病史 | 6(14.63) | 9(9.28) | χ2=0.853 | 0.356 |
| 高血压史 | 9(21.95) | 17(17.53) | χ2=0.369 | 0.543 |
| 高血脂症史 | 8(19.51) | 15(15.46) | χ2=0.340 | 0.560 |
| 吸烟史 | 13(31.70) | 24(24.74) | χ2=0.712 | 0.399 |
| 饮酒史 | 10(24.39) | 21(21.65) | χ2=0.124 | 0.724 |
| 呼吸频率(次/min) | 25.48±3.24 | 24.71±3.05 | t=1.330 | 0.186 |
| 发病原因[例(%)] | ||||
| 脓毒血症 | 16(39.02) | 36(37.11) | ||
| 脑血管事件 | 9(21.95) | 22(22.68) | χ2=0.052 | 0.997 |
| 外伤 | 8(19.51) | 20(20.62) | ||
| 开胸术后 | 8(19.51) | 19(19.59) | ||
| MAP(mmHg) | 69.27±10.21 | 72.52±9.71 | t=1.770 | 0.079 |
| PEEP(cmH2O) | 12.57±3.76 | 11.92±3.57 | t=0.962 | 0.338 |
| PaCO2(mmHg) | 36.18±6.64 | 39.53±6.97 | t=2.616 | 0.010 |
| PaO2(mmHg) | 69.49±8.06 | 72.87±8.56 | t=2.156 | 0.033 |
| OI(mmHg) | 115.06±9.17 | 157.96±13.79 | t=18.266 | <0.01 |
| LUS(分) | 24.98±4.83 | 17.11±3.76 | t=16.841 | <0.01 |
| NT-proBNP(pg/mL) | 821.73±62.97 | 546.85±51.76 | t=26.687 | <0.01 |
| sFlt-1(ng/L) | 605.17±49.84 | 451.43±50.32 | t=16.448 | <0.01 |
| 项目 | 预后不良组 (n=41) | 预后良好组 (n=97) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 27(65.85) 14(34.15) | 55(56.70) 42(43.30) | χ2=0.193 | 0.660 |
| 年龄(岁) | 57.10±7.93 | 55.83±8.12 | t=0.845 | 0.399 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 22.53±2.72 | 22.31±2.61 | t=0.447 | 0.656 |
| 入住ICU时间(天) | 14.20±2.36 | 11.15±1.72 | t=8.482 | <0.01 |
| 既往史[例(%)] | ||||
| 冠心病史 | 5(12.20) | 11(11.34) | χ2=0.021 | 0.886 |
| 糖尿病史 | 6(14.63) | 9(9.28) | χ2=0.853 | 0.356 |
| 高血压史 | 9(21.95) | 17(17.53) | χ2=0.369 | 0.543 |
| 高血脂症史 | 8(19.51) | 15(15.46) | χ2=0.340 | 0.560 |
| 吸烟史 | 13(31.70) | 24(24.74) | χ2=0.712 | 0.399 |
| 饮酒史 | 10(24.39) | 21(21.65) | χ2=0.124 | 0.724 |
| 呼吸频率(次/min) | 25.48±3.24 | 24.71±3.05 | t=1.330 | 0.186 |
| 发病原因[例(%)] | ||||
| 脓毒血症 | 16(39.02) | 36(37.11) | ||
| 脑血管事件 | 9(21.95) | 22(22.68) | χ2=0.052 | 0.997 |
| 外伤 | 8(19.51) | 20(20.62) | ||
| 开胸术后 | 8(19.51) | 19(19.59) | ||
| MAP(mmHg) | 69.27±10.21 | 72.52±9.71 | t=1.770 | 0.079 |
| PEEP(cmH2O) | 12.57±3.76 | 11.92±3.57 | t=0.962 | 0.338 |
| PaCO2(mmHg) | 36.18±6.64 | 39.53±6.97 | t=2.616 | 0.010 |
| PaO2(mmHg) | 69.49±8.06 | 72.87±8.56 | t=2.156 | 0.033 |
| OI(mmHg) | 115.06±9.17 | 157.96±13.79 | t=18.266 | <0.01 |
| LUS(分) | 24.98±4.83 | 17.11±3.76 | t=16.841 | <0.01 |
| NT-proBNP(pg/mL) | 821.73±62.97 | 546.85±51.76 | t=26.687 | <0.01 |
| sFlt-1(ng/L) | 605.17±49.84 | 451.43±50.32 | t=16.448 | <0.01 |
| 因素 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 入住ICU时间 | 1.372 | 0.361 | 14.444 | 0.015 | 3.943 | 1.362 | 6.524 |
| LUS | 1.318 | 0.312 | 17.845 | 0.002 | 3.736 | 2.631 | 4.841 |
| NT-proBNP | 1.205 | 0.297 | 16.461 | 0.006 | 3.337 | 2.776 | 3.898 |
| sFlt-1 | 1.456 | 0.307 | 22.493 | <0.01 | 4.289 | 2.283 | 6.295 |
| 因素 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 入住ICU时间 | 1.372 | 0.361 | 14.444 | 0.015 | 3.943 | 1.362 | 6.524 |
| LUS | 1.318 | 0.312 | 17.845 | 0.002 | 3.736 | 2.631 | 4.841 |
| NT-proBNP | 1.205 | 0.297 | 16.461 | 0.006 | 3.337 | 2.776 | 3.898 |
| sFlt-1 | 1.456 | 0.307 | 22.493 | <0.01 | 4.289 | 2.283 | 6.295 |
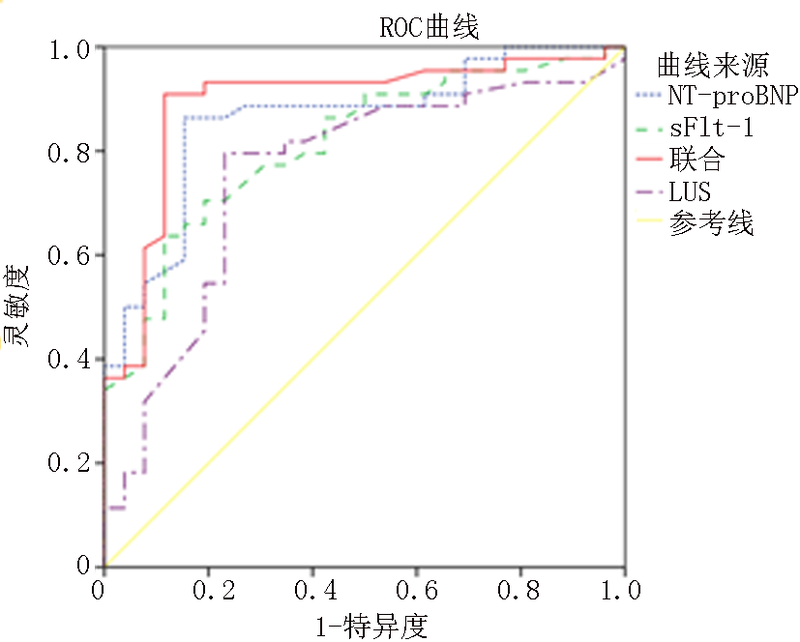
| 预测项目 | AUC | 标准误 | 值 | 95% | 敏感度(%) | 特异度(%) | 约登指数 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||||
| LUS | 0.751 | 0.034 | 0.002 | 0.632 | 0.869 | 75.61 | 78.35 | 0.540 | 18.12分 |
| NT-proBNP | 0.844 | 0.030 | 0.001 | 0.740 | 0.947 | 80.49 | 81.44 | 0.619 | 598.36 ng/L |
| sFlt-1 | 0.773 | 0.031 | 0.002 | 0.661 | 0.885 | 78.05 | 79.38 | 0.574 | 487.52 ng/L |
| 联合 | 0.896 | 0.028 | 0.000 | 0.819 | 0.974 | 82.93 | 84.54 | 0.675 | - |
| 预测项目 | AUC | 标准误 | 值 | 95% | 敏感度(%) | 特异度(%) | 约登指数 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||||
| LUS | 0.751 | 0.034 | 0.002 | 0.632 | 0.869 | 75.61 | 78.35 | 0.540 | 18.12分 |
| NT-proBNP | 0.844 | 0.030 | 0.001 | 0.740 | 0.947 | 80.49 | 81.44 | 0.619 | 598.36 ng/L |
| sFlt-1 | 0.773 | 0.031 | 0.002 | 0.661 | 0.885 | 78.05 | 79.38 | 0.574 | 487.52 ng/L |
| 联合 | 0.896 | 0.028 | 0.000 | 0.819 | 0.974 | 82.93 | 84.54 | 0.675 | - |
| [1] |
Huang D, Ma H, Xiao Z, et al. Diagnostic value of cardiopulmonary ultrasound in elderly patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2018, 18(1):136.
doi: 10.1186/s12890-018-0666-9 URL |
| [2] |
Allinovi M, Parise A, Giacalone M, et al. Lung ultrasound may support diagnosis and monitoring of COVID-19 pneumonia[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2020, 46(11):2908-2917.
doi: S0301-5629(20)30333-1 pmid: 32807570 |
| [3] |
Grasselli G, Tonetti T, Protti A, et al. Pathophysiology of COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: A multicentre prospective observational study[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2020, 8(12):1201-1208.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30370-2 pmid: 32861276 |
| [4] | 张萌, 李聪, 王克诚. 心肺联合超声判断急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者预后的价值[J]. 临床超声医学杂志, 2020, 22(12):911-915. |
| [5] |
Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin definition[J]. JAMA, 2012, 307(23):2526-2533.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.5669 pmid: 22797452 |
| [6] |
Hiles M, Culpan AM, Watts C, et al. Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome: Chest X-ray or lung ultrasound? A systematic review[J]. Ultrasound, 2017, 25(2):80-91.
doi: 10.1177/1742271X16689374 URL |
| [7] |
Islam M, Levitus M, Eisen L, et al. Lung ultrasound for the diagnosis and management of acute respiratory failure[J]. Lung, 2020, 198(1):1-11.
doi: 10.1007/s00408-019-00309-1 URL |
| [8] | 高延秋, 张根生, 李双凤, 等. 血管外肺水指数联合血管内皮生长因子受体1对重症肺炎ARDS合并感染性休克患者预后的评估[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2018, 27(12):1381-1387. |
| [9] |
Elsayed YN, Hinton M, Graham R, et al. Lung ultrasound predicts histological lung injury in a neonatal model of acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Pediatr Pulmonol, 2020, 55(11):2913-2923.
doi: 10.1002/ppul.v55.11 URL |
| [10] |
Lai CC, Sung MI, Ho CH, et al. The prognostic value of N-terminal proB-type natriuretic peptide in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(4):44784.
doi: 10.1038/srep44784 URL |
| [11] | 杨慧亮, 李颖, 巴晓彤. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者血清PCT、 NT-proBNP水平变化及意义[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2020, 12(4):469-472, 477. |
| [12] |
Karge A, Beckert L, Moog P, et al. Role of sFlt-1/PIGF ratio and uterine Doppler in pregnancies with chronic kidney disease suspected with Pre-eclampsia or HELLP syndrome[J]. Pregnancy Hypertens, 2020, 22(10):160-166.
doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2020.09.007 URL |
| [13] | 曾天星, 田婵婵, 陈丽珺, 等. 血浆NT-proBNP与急性呼吸窘迫综合征严重程度的相关性分析[J]. 中华肺部疾病杂志(电子版), 2016, 9(4):417-419. |
| [14] |
Umbrello M, Fumagalli J, Pesenti A, et al. Pathophysiology and management of acute respiratory distress syndrome in obese patients[J]. Semin Respir Crit Care Med, 2019, 40(1):40-56.
doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1685179 pmid: 31060087 |
| [15] | 郭鑫鑫. 血浆sTREM-1、sFLT-1水平与重症肺炎APACHE Ⅱ评分的关联性[J]. 牡丹江医学院学报, 2021, 42(1):71-74. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 38
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 438
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||