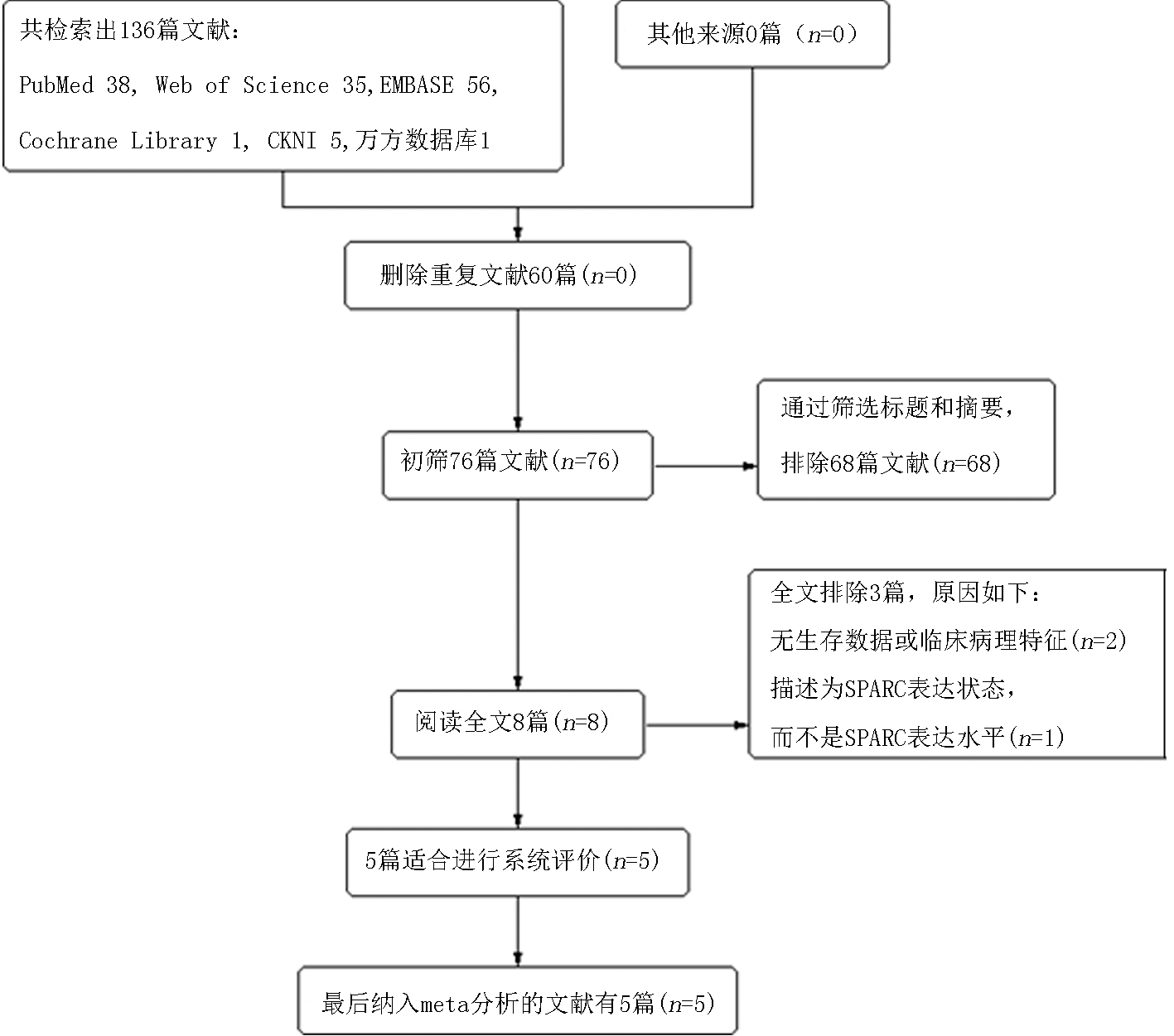
Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 972-978.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.11.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation between the expression level of SPARC and prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis
Zhang Na, Sun Yue, Dong Han, Zhao Peng, Yang Xin, Qi Yuan, Wang Lingling( )
)
- Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, the Fourth People's Hospital of Shenyang,Shenyang 110000,China
-
Received:2023-02-04Online:2023-11-20Published:2024-01-17 -
Contact:Wang Lingling E-mail:hongtao7@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Na, Sun Yue, Dong Han, Zhao Peng, Yang Xin, Qi Yuan, Wang Lingling. Correlation between the expression level of SPARC and prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(11): 972-978.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.11.002
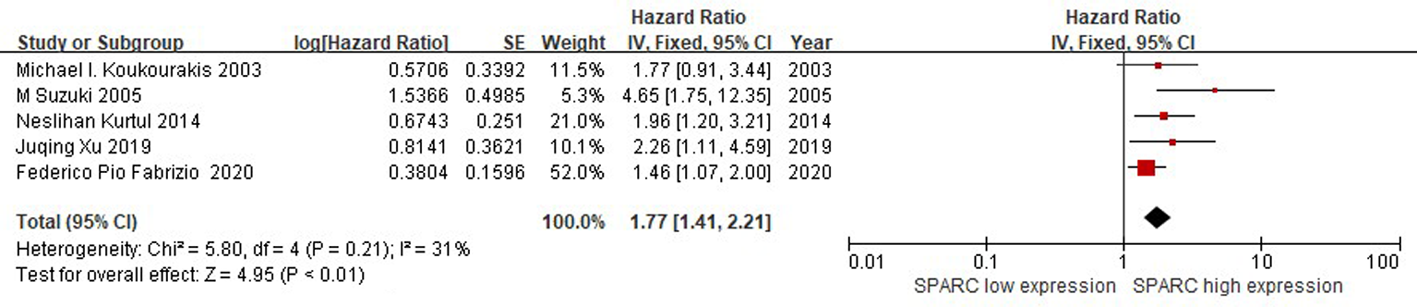
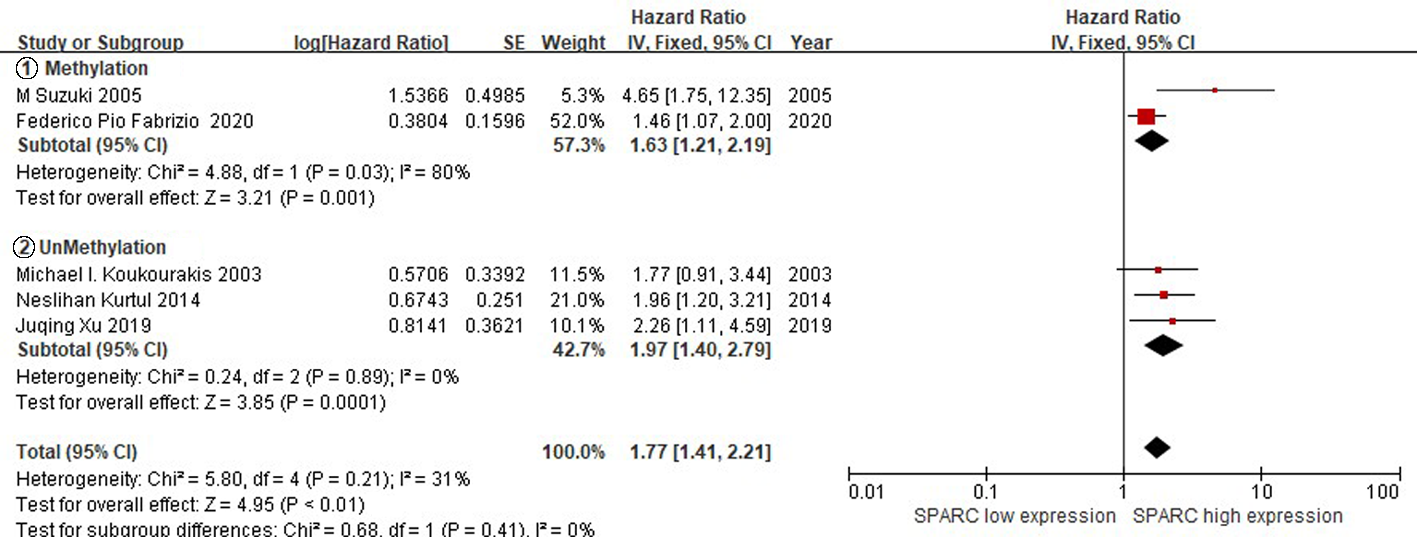
| 第一作者 | 出版 年份 | 国家 | 病例数 | 检测 方法 | 随访 时间 | 组织学 类型 | 分级 | 生存时间 | 无病生存期 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% | 95% | |||||||||||
| Fabrizio[ | 2020 | Italy | 59 | IHC | 52 | NSCLC | Ⅰ-Ⅲ | 1.46 | 1.07-2.00 | 0.98 | 0.61-1.57 | |
| Kurtul[ | 2014 | Turkey | 84 | IHC | 12.5 | NSCLC | Ⅲ | 1.97 | 1.20-3.21 | 1.67 | 1.05-2.66 | |
| Suzuki[ | 2005 | Japan | 84 | IHC | NA | NSCLC | Ⅰ-Ⅳ | 4.65 | 1.75-12.35 | NA | NA | |
| Xu[ | 2019 | China | 90 | IHC | NA | SCC | Ⅰ-Ⅳ | 2.26 | 1.11-4.59 | NA | NA | |
| Koukourakis[ | 2003 | Britain | 113 | IHC | 55.9 | NSCLC | Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 1.77 | 0.91-3.44 | NA | NA | |
Tab.1 Basic characteristics of enrolled studies
| 第一作者 | 出版 年份 | 国家 | 病例数 | 检测 方法 | 随访 时间 | 组织学 类型 | 分级 | 生存时间 | 无病生存期 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% | 95% | |||||||||||
| Fabrizio[ | 2020 | Italy | 59 | IHC | 52 | NSCLC | Ⅰ-Ⅲ | 1.46 | 1.07-2.00 | 0.98 | 0.61-1.57 | |
| Kurtul[ | 2014 | Turkey | 84 | IHC | 12.5 | NSCLC | Ⅲ | 1.97 | 1.20-3.21 | 1.67 | 1.05-2.66 | |
| Suzuki[ | 2005 | Japan | 84 | IHC | NA | NSCLC | Ⅰ-Ⅳ | 4.65 | 1.75-12.35 | NA | NA | |
| Xu[ | 2019 | China | 90 | IHC | NA | SCC | Ⅰ-Ⅳ | 2.26 | 1.11-4.59 | NA | NA | |
| Koukourakis[ | 2003 | Britain | 113 | IHC | 55.9 | NSCLC | Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 1.77 | 0.91-3.44 | NA | NA | |
| [1] |
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v68.6 URL |
| [2] | Griffin R, Ramirez RA. Molecular targets in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Ochsner J, 2017, 17(4): 388-392. |
| [3] |
Santarpia M, Rolfo C, Peters GJ, et al. On the pharmacogenetics of non-small cell lung cancer treatment[J]. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol, 2016, 12(3): 307-317.
doi: 10.1517/17425255.2016.1141894 URL |
| [4] | Melouane A, Yoshioka M, Kanzaki M, et al. Sparc, an EPS-induced gene, modulates the extracellular matrix and mitochondrial function via ILK/AMPK pathways in C2C12 cells[J]. Life ences, 2019, 229:277-287. |
| [5] | Wong SL, Sukkar MB. The SPARC protein: An overview of its role in lung cancer and pulmonary fibrosis and its potential role in chronic airways disease[J]. Pharmacol, 2017, (174):3-14. |
| [6] | Critselis E, Rava M, Marquez M, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic performance of secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) assay for detecting primary and recurrent urinary bladder cancer[J]. Proteomics Clin Appl, 2019, 13(2):e1800148. |
| [7] |
Han W, Cao F, Chen MB, et al. Prognostic value of SPARC in patients with pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1): e0145803.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145803 URL |
| [8] |
Zhu A, Yuan P, Du F, et al. SPARC overexpression in primary tumors correlates with disease recurrence and overall survival in patients with triple negative breast cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(47):76628-76634.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10532 pmid: 27421134 |
| [9] | Critselis E, Rava M, Marquez M, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic performance of secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) assay for detecting primary and recurrent urinary bladder cancer[J]. Proteomics Clin Appl, 2019, 13(2):e1800148. |
| [10] |
Gao ZW, Liu C, Yang L, et al. SPARC overexpression promotes liver cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2021, 8:775743.
doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.775743 URL |
| [11] | Gao YY, Han RB, Wang X, et al. Change of SPARC expression after chemotherapy in gastric cancer[J]. Cancer Biol Med, 2015, 12(1):33-40. |
| [12] |
Fabrizio FP, Sparaneo A, Fontana A, et al. Potential prognostic role of SPARC methylation in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(6):1523.
doi: 10.3390/cells9061523 URL |
| [13] |
Kurtul N, Eroglu C, Unal D, et al. Prognostic value of SPARC expression in unresectable NSCLC treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2014, 15(20):8911-8916.
doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.20.8911 URL |
| [14] |
Suzuki M, Hao C, Takahashi T, et al. Aberrant methylation of SPARC in human lung cancers[J]. Br J Cancer, 2005, 92(5):942-948.
doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602376 |
| [15] |
Xu J, Yang S, Gu X, et al. SPARC correlates with unfavorable outcome and promotes tumor growth in lung squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2019, 110:104276.
doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104276 URL |
| [16] |
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Brekken RA, et al. Enhanced expression of SPARC/osteonectin in the tumor-associated stroma of non-small cell lung cancer is correlated with markers of hypoxia/acidity and with poor prognosis of patients[J]. Cancer Res, 2003, 63(17):5376-5380.
pmid: 14500371 |
| [17] |
Huang Y, Zhang J, Zhao YY, et al. SPARC expression and prognostic value in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Chin J Cancer, 2012, 31(11):541-548.
doi: 10.5732/cjc.012.10212 pmid: 23114088 |
| [18] |
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2010, 25(9):603-605.
doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z pmid: 20652370 |
| [19] |
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al. Meta -analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting[J]. JAMA, 2000, 283( 15) : 2008-2012.
doi: 10.1001/jama.283.15.2008 URL |
| [20] |
Wang J, Sheng Z, Yang W, et al. Elevated serum concentration of chitinase 3-like 1 is an independent prognostic biomarker for poor survival in lung cancer patients[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2016, 38(2): 461-468.
doi: 10.1159/000438643 pmid: 26828595 |
| [21] |
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints[J]. Stat Med, 1998, 17(24): 2815-2834.
doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0258(19981230)17:24<2815::aid-sim110>3.0.co;2-8 pmid: 9921604 |
| [22] |
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis[J]. Stat Med, 2002, 21(11): 1539-1558.
doi: 10.1002/sim.1186 pmid: 12111919 |
| [23] |
Qiu ZX, Zhang K, Qiu XS, et al. The prognostic value of phosphorylated AKT expression in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta -analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(12): e81451.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081451 URL |
| [24] |
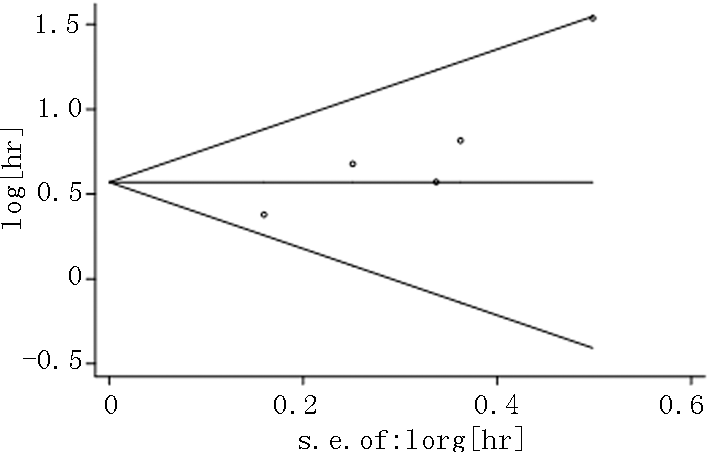
Begg CB, Mazu m dar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias[J]. Biometrics, 1994, 50(4): 1088-1101.
pmid: 7786990 |
| [25] |
Egger M, Davey SG, Schneider M, et al. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test[J]. BM J, 1997, 315(7109): 629-634.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629 URL |
| [26] |
Schneider S, Yochim J, Brabender J, et al. Osteopontin but not osteonectin messenger RNA expression is a prognostic marker in curatively resected non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10(5):1588-1596.
pmid: 15014008 |
| [27] | 张志平, 王洲, 刘相燕, 等. KLF4和SPARC在非小细胞肺癌中的表达及其相关性研究[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2012, 15(12):720-724. |
| [28] |
Wong SL, Sukkar MB. The SPARC protein: An overview of its role in lung cancer and pulmonary fibrosis and its potential role in chronic airways disease[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2017, 174(1): 3-14.
doi: 10.1111/bph.v174.1 URL |
| [29] | Wang B, Zhang Z, Tang J, et al. Correlation between SPARC, TGFβ1, endoglin and angiogenesis mechanism in lung cancer[J]. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, 2018, 32(6):1525-1531. |
| [30] |
Bao JM, Dang Q, Lin CJ, et al. SPARC is a key mediator of TGF-β-induced renal cancer metastasis[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(3):1926-1938.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.v236.3 URL |
| [31] |
Yang M, Qu H, Liu A, et al. Efficacy and safety of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel as neoadjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-negative breast cancer[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2019, 15(7):1561-1566.
doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_241_19 pmid: 31939438 |
| [32] |
Shintakuya R, Kondo N, Murakami Y, et al. The high stromal SPARC expression is independently associated with poor survival of patients with resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma treated with adjuvant gemcitabine in combination with S-1 or adjuvant gemcitabine alone[J]. Pancreatology, 2018, 18(2):191-197.
doi: S1424-3903(17)30913-4 pmid: 29295776 |
| [33] |
Gorantla B, Bhoopathi P, Chetty C, et al. Notch signaling regulates tumor-induced angiogenesis in SPARC-overexpressed neuroblastoma[J]. Angiogenesis, 2013, 16(1) :85-100.
doi: 10.1007/s10456-012-9301-1 pmid: 22956186 |
| [34] |
Al-Batran SE, Geissler M, Seufferlein T, et al. Nab-paclitaxel for metastatic pancreatic cancer: Clinical outcomes and potential mechanisms of action[J]. Oncol Res Treat, 2014, 37(3):128-134.
doi: 10.1159/000358890 URL |
| [35] |
Gong L, Mao W, Chen Q, et al. Analysis of SPARC and TUBB3 as predictors for prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma receiving nab-paclitaxel plus cisplatin neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a prospective study[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2019, 83(4) :639-647.
doi: 10.1007/s00280-019-03769-7 |
| [36] |
Nakazawa Y, Nakazawa S, Kurozumi S, et al. The pathological complete response and secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine expression in patients with breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant nab-paclitaxel chemotherapy[J]. Oncology Letters, 2020, 19(4): 2705-2712.
doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11354 pmid: 32218821 |
| [37] |
Cohen AL, Ray A, Brocklin MV, et al. A phase I trial of azacitidine and nanoparticle albumin bound paclitaxel in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 8(32):52413-52419.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v8i32 URL |
| [38] |
Jing Y, Jin Y, Wang Y, et al. SPARC promotes the proliferation and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by PI3K/AKT/PDGFB/PDGFRβ axis[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(9):15581-15593.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.28205 |
| [39] |
Thomas SL, Schultz CR, Mouzon E, et al. Loss of SPARC in p53-null astrocytes promotes macrophage activation and phagocytosis resulting in decreased tumor size and tumor cell survival[J]. Brain Pathol, 2015, 25(4):391-400.
doi: 10.1111/bpa.2015.25.issue-4 URL |
| [40] | Wang B, Zhang Z, Tang J, et al. Correlation between SPARC, TGFβ1, Endoglin and angiogenesis mechanism in lung cancer[J]. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, 2018, 32(6):1525-1531. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||