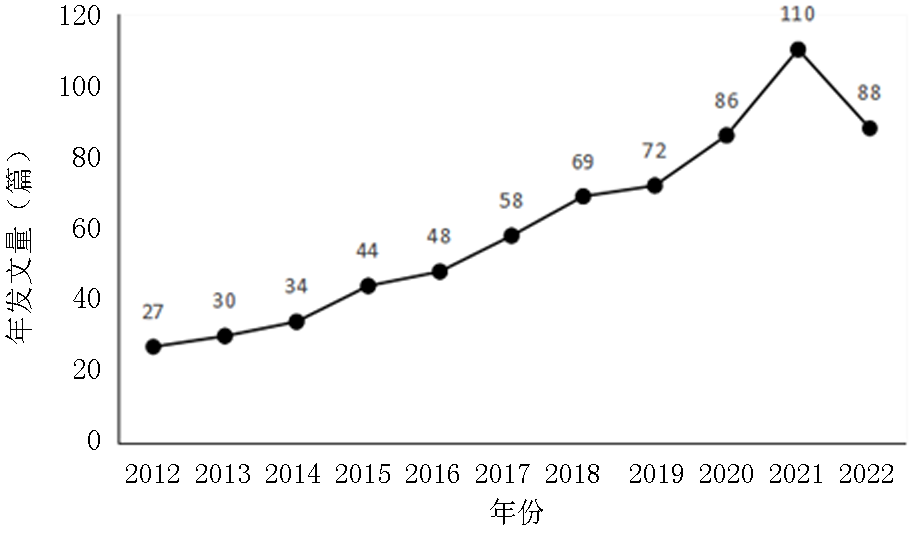
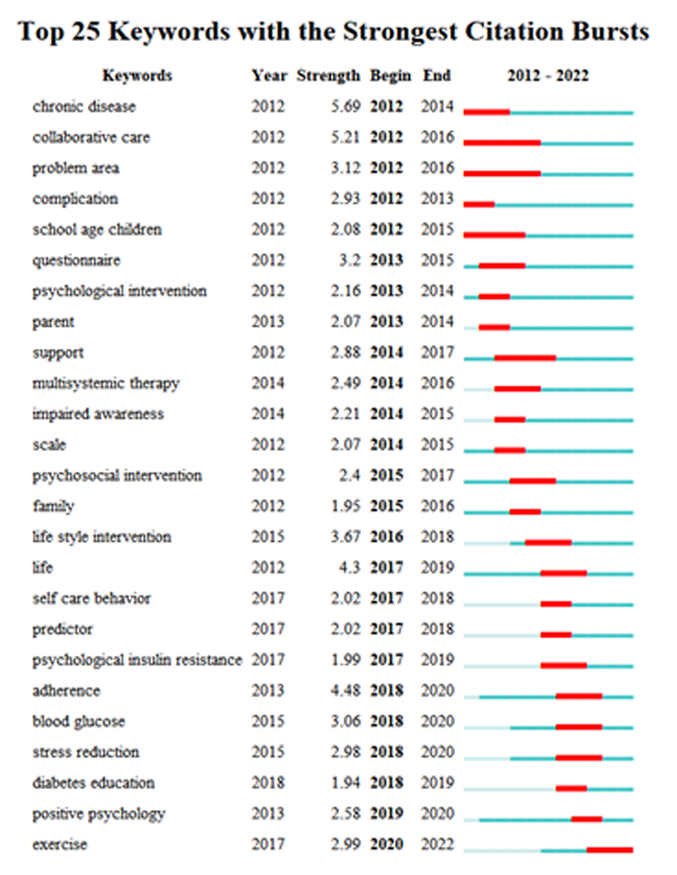
Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (8): 731-736.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.08.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bibliometric analysis of literatures reporting psychological intervention of patients with diabetes mellitus: Based on Web of Science
- 1. School of Nursing, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
2. Department of Nursing, Jinshan Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai 201508, China
-
Received:2023-06-11Online:2023-08-20Published:2023-09-28 -
Contact:Xu Huajiao E-mail:xuhuajiao66@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Xin, Xu Huajiao. Bibliometric analysis of literatures reporting psychological intervention of patients with diabetes mellitus: Based on Web of Science[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(8): 731-736.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.08.010
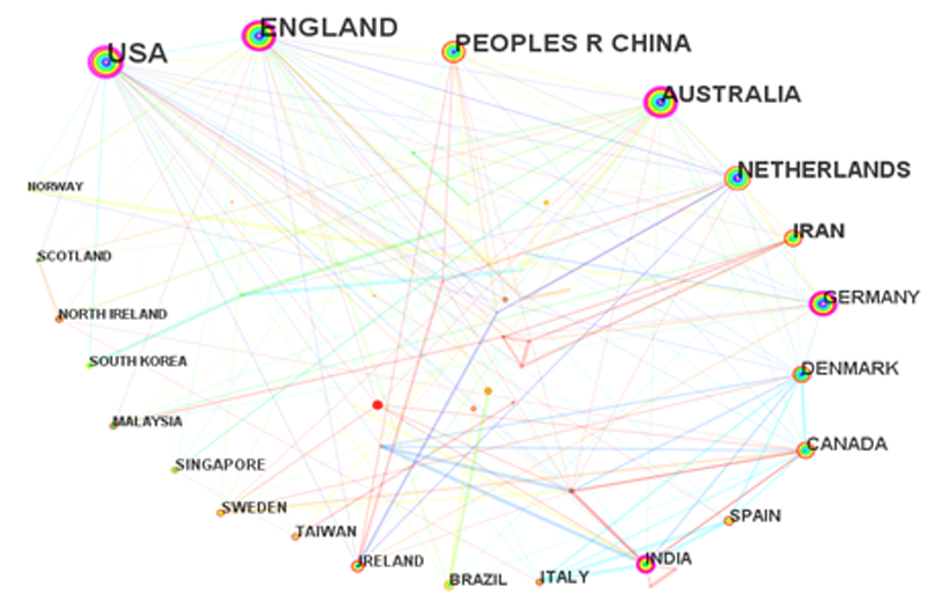
Fig. 2 Co-occurrence knowledge map of international collaboration network in research publications on psychological interventions for diabetes mellitus, 2012-2022

Fig. 3 Co-occurrence knowledge map of institutional collaboration network in research publications on psychological interventions for diabetes mellitus, 2012-2022
| 排序 | 研究机构 | 发文量(篇) | 中介中心性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kings Coll London(英国) | 42 | 0.22 |
| 2 | Univ Melbourne(澳大利亚) | 22 | 0.08 |
| 3 | Deakin Univ(澳大利亚) | 18 | 0.09 |
| 4 | Vrije Univ Amsterdam(荷兰) | 12 | 0.04 |
| 5 | Harvard Med Sch(美国) | 10 | 0.04 |
| 6 | Baylor Coll Med(美国) | 10 | 0.07 |
| 7 | Monash Univ(澳大利亚) | 9 | 0.05 |
| 8 | Northwestern Univ(美国) | 8 | 0.08 |
| 9 | Peking Univ(中国) | 8 | 0.01 |
| 10 | UCL(英国) | 8 | 0.04 |
Tab. 1 Top 10 research institutions in terms of publication count on psychological interventions for diabetes mellitus, 2012-2022
| 排序 | 研究机构 | 发文量(篇) | 中介中心性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kings Coll London(英国) | 42 | 0.22 |
| 2 | Univ Melbourne(澳大利亚) | 22 | 0.08 |
| 3 | Deakin Univ(澳大利亚) | 18 | 0.09 |
| 4 | Vrije Univ Amsterdam(荷兰) | 12 | 0.04 |
| 5 | Harvard Med Sch(美国) | 10 | 0.04 |
| 6 | Baylor Coll Med(美国) | 10 | 0.07 |
| 7 | Monash Univ(澳大利亚) | 9 | 0.05 |
| 8 | Northwestern Univ(美国) | 8 | 0.08 |
| 9 | Peking Univ(中国) | 8 | 0.01 |
| 10 | UCL(英国) | 8 | 0.04 |
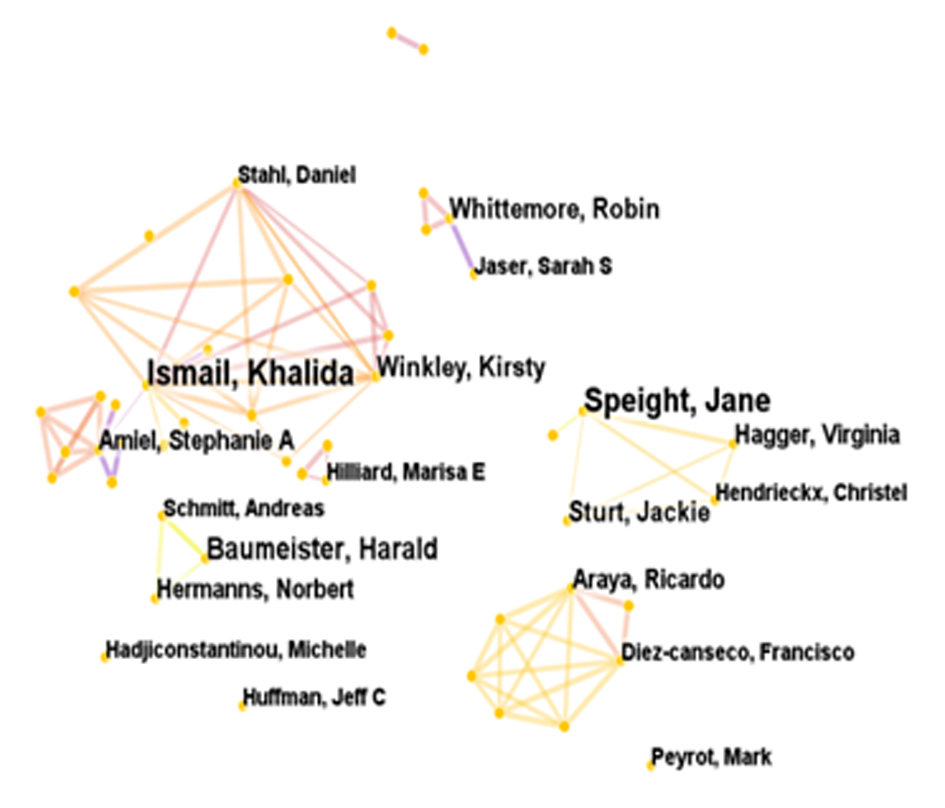
Fig. 4 Co-occurrence knowledge map of authors collaboration network in research publications on psychological interventions for diabetes mellitus, 2012-2022
| 序号 | 关键词 | 频次 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 抑郁(depression) | 204 |
| 2 | 血糖控制(glycemic control) | 197 |
| 3 | 生活质量(quality of life) | 155 |
| 4 | 心理健康(mental health) | 140 |
| 5 | 成年人(adult) | 124 |
| 6 | 心理痛苦(distress) | 118 |
| 7 | 干预(intervention) | 114 |
| 8 | 随机对照试验(randomized controlled trial) | 109 |
| 9 | 照护(care) | 108 |
| 10 | 管理(management) | 98 |
| 11 | 青少年(adolescent) | 94 |
| 12 | 患病率(prevalence) | 89 |
| 13 | meta分析(meta analysis) | 69 |
| 14 | 危险因素(risk factor) | 55 |
| 15 | 焦虑(anxiety) | 54 |
| 16 | 儿童(children) | 53 |
| 17 | 相关性(association) | 53 |
| 18 | 依从性(adherence) | 48 |
| 19 | 认知行为疗法(cognitive behavioural therapy) | 45 |
| 20 | 治疗(therapy) | 43 |
Tab. 2 Top 20 high-frequency keywords in research publications on psychological interventions for diabetes mellitus, 2012-2022
| 序号 | 关键词 | 频次 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 抑郁(depression) | 204 |
| 2 | 血糖控制(glycemic control) | 197 |
| 3 | 生活质量(quality of life) | 155 |
| 4 | 心理健康(mental health) | 140 |
| 5 | 成年人(adult) | 124 |
| 6 | 心理痛苦(distress) | 118 |
| 7 | 干预(intervention) | 114 |
| 8 | 随机对照试验(randomized controlled trial) | 109 |
| 9 | 照护(care) | 108 |
| 10 | 管理(management) | 98 |
| 11 | 青少年(adolescent) | 94 |
| 12 | 患病率(prevalence) | 89 |
| 13 | meta分析(meta analysis) | 69 |
| 14 | 危险因素(risk factor) | 55 |
| 15 | 焦虑(anxiety) | 54 |
| 16 | 儿童(children) | 53 |
| 17 | 相关性(association) | 53 |
| 18 | 依从性(adherence) | 48 |
| 19 | 认知行为疗法(cognitive behavioural therapy) | 45 |
| 20 | 治疗(therapy) | 43 |
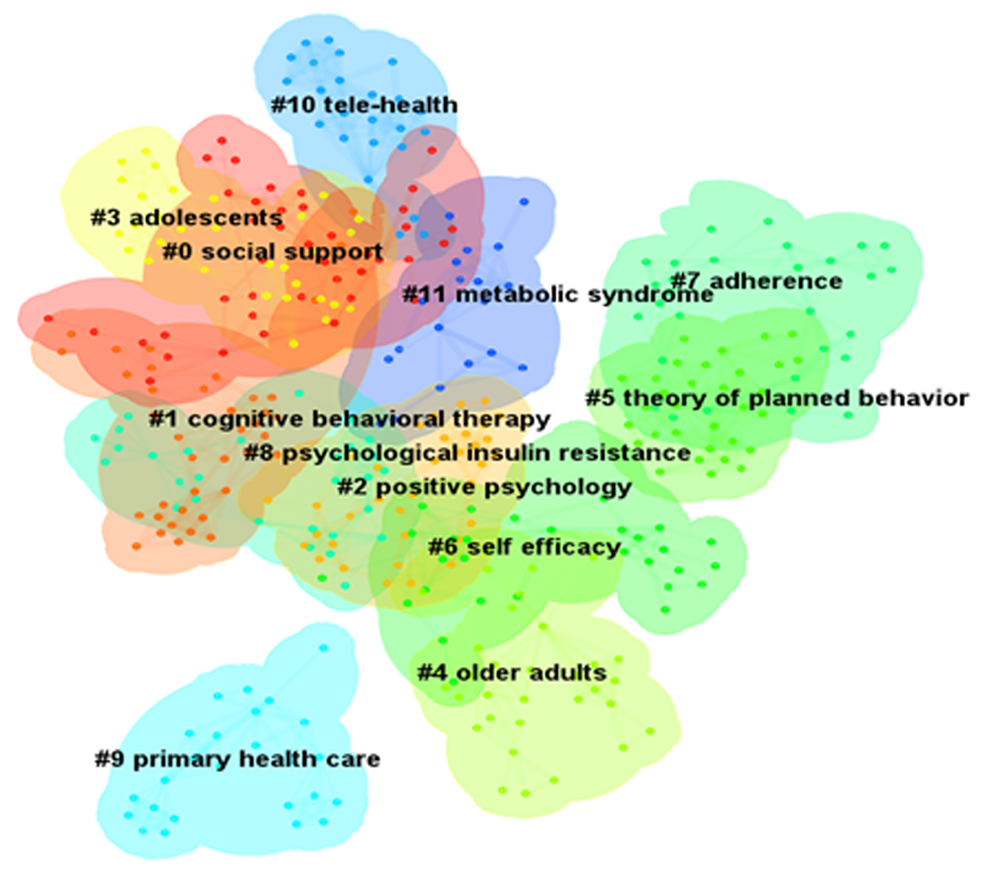
| 聚类ID | 聚类标签 | 节点数 | Silhouette | 主要研究内容 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #0 | 社会支持(social support) | 41 | 0.918 | social support;motivational interviewing;diabetes distress;lifestyle intervention |
| #1 | 认知行为疗法(cognitive behavioral therapy) | 40 | 0.974 | care;prevalence;adult;cognitive behavioral therapy |
| #2 | 积极心理学(positive psychology) | 35 | 0.912 | positive psychology;health behavior;physical activity |
| #3 | 青少年(adolescents) | 33 | 0.905 | type 1 diabetes;adolescents;children;youth |
| #4 | 老年人(older adults) | 33 | 0.884 | older adults;type 1 diabetes;education;dementia |
| #5 | 计划行为理论(theory of planned behavior) | 32 | 0.889 | type 2 diabetes;theory of planned behavior;mobile phone |
| #6 | 自我效能(self efficacy) | 30 | 0.922 | primary care;self efficacy;health |
| #7 | 依从性(adherence) | 30 | 0.883 | Adherence;economic evaluation;management;hospital anxiety |
| #8 | 心理胰岛素抵抗(psychological insulin resistance) | 29 | 0.954 | psychological insulin resistance;systematic review;collaborative care |
| #9 | 初级卫生保健(primary health care) | 25 | 0.900 | primary health care;coronary heart disease;psychological outcomes;peer educators |
| #10 | 远程医疗(tele-health) | 24 | 0.963 | tele-health;dependent diabetes mellitus;randomized controlled trials;health literacy |
| #11 | 代谢综合征(metabolic syndrome) | 19 | 0.925 | metabolic syndrome;family systems therapy |
Tab. 3 Cluster labels and major research themes in research publications on psychological interventions for diabetes mellitus, 2012-2022
| 聚类ID | 聚类标签 | 节点数 | Silhouette | 主要研究内容 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #0 | 社会支持(social support) | 41 | 0.918 | social support;motivational interviewing;diabetes distress;lifestyle intervention |
| #1 | 认知行为疗法(cognitive behavioral therapy) | 40 | 0.974 | care;prevalence;adult;cognitive behavioral therapy |
| #2 | 积极心理学(positive psychology) | 35 | 0.912 | positive psychology;health behavior;physical activity |
| #3 | 青少年(adolescents) | 33 | 0.905 | type 1 diabetes;adolescents;children;youth |
| #4 | 老年人(older adults) | 33 | 0.884 | older adults;type 1 diabetes;education;dementia |
| #5 | 计划行为理论(theory of planned behavior) | 32 | 0.889 | type 2 diabetes;theory of planned behavior;mobile phone |
| #6 | 自我效能(self efficacy) | 30 | 0.922 | primary care;self efficacy;health |
| #7 | 依从性(adherence) | 30 | 0.883 | Adherence;economic evaluation;management;hospital anxiety |
| #8 | 心理胰岛素抵抗(psychological insulin resistance) | 29 | 0.954 | psychological insulin resistance;systematic review;collaborative care |
| #9 | 初级卫生保健(primary health care) | 25 | 0.900 | primary health care;coronary heart disease;psychological outcomes;peer educators |
| #10 | 远程医疗(tele-health) | 24 | 0.963 | tele-health;dependent diabetes mellitus;randomized controlled trials;health literacy |
| #11 | 代谢综合征(metabolic syndrome) | 19 | 0.925 | metabolic syndrome;family systems therapy |
| [1] |
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2022, 183: 109119.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119 URL |
| [2] |
Li H, Chang GY, Jiang YH, et al. System dynamic model simulates the growth trend of diabetes mellitus in Chinese population: Implications for future urban public health governance[J]. Int J Public Health, 2022, 67: 1605064.
doi: 10.3389/ijph.2022.1605064 URL |
| [3] |
Carreira M, Ruiz de Adana MS, Pinzón JL, et al. Internet-based cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for depressive symptomatology in individuals with type 1 diabetes (WEB_TDDI1 study): a randomized controlled trial protocol[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(9): e0274551.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274551 URL |
| [4] | 沈琰, 黄诗纯, 陈怡, 等. 焦虑和抑郁心理状态对糖尿病肾病影响的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(11):1029-1033. |
| [5] |
Chatterjee S, Bakhla AK, Biswas P, et al. Psychosocial morbidity among children with type-1 diabetes mellitus[J]. J Family Med Prim Care, 2020, 9(2):652-656.
doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1216_19 pmid: 32318398 |
| [6] |
Berhe KK, Gebru HB, Kahsay HB. Effect of motivational interviewing intervention on HgbA1C and depression in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (systematic review and meta-analysis)[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(10): e0240839.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240839 URL |
| [7] |
de Groot M, Golden SH, Wagner J. Psychological conditions in adults with diabetes[J]. Am Psychol, 2016, 71(7): 552-562.
pmid: 27690484 |
| [8] | 徐春蕾, 王志超, 薛雅卓. 基于Cite Space的奥马哈系统的国内外研究热点可视化分析[J]. 护理研究, 2018, 32(23):3758-3762. |
| [9] | 张倩, 程金莲. 护理管理相关研究的可视化分析[J]. 护理研究, 2019, 33(5):781-786. |
| [10] | 鲍丙豪, 王彬, 王继升, 等. 基于 CiteSpace 软件的中医治疗新冠肺炎等疫病研究状况及趋势的可视化分析[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2020, 22(3):650-657. |
| [11] | 李德胜. 中国近10 年竞争情报研究的文献计量分析[J]. 科技情报开发与经济, 2015, 24(16):130-132. |
| [12] | 周丹, 尹安春, 张秀杰. 基于Web of Science的肾脏病学领域护理研究的可视化分析[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2020, 36(4):315-321. |
| [13] | 邵梦琪, 杜辉, 霍霞. 基于CiteSpace的近10年我国老年衰弱研究文献的计量学分析[J]. 中华老年多器官疾病杂志, 2020, 19(12):925-929. |
| [14] |
Uchendu C, Blake H. Effectiveness of cognitive-behavioural therapy on glycaemic control and psychological outcomes in adults with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Diabet Med, 2017, 34(3): 328-339.
doi: 10.1111/dme.2017.34.issue-3 URL |
| [15] |
Tovote KA, Fleer J, Snippe E, et al. Individual mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and cognitive behavior therapy for treating depressive symptoms in patients with diabetes: Results of a randomized controlled trial[J]. Diabetes Care, 2014, 37(9): 2427-2434.
doi: 10.2337/dc13-2918 pmid: 24898301 |
| [16] |
Nobis S, Lehr D, Ebert DD, et al. Efficacy and cost-effectiveness of a web-based intervention with mobile phone support to treat depressive symptoms in adults with diabetes mellitus type 1 and type 2: design of a randomised controlled trial[J]. BMC Psychiatry, 2013, 13: 306.
doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-306 pmid: 24238346 |
| [17] |
van Bastelaar KM, Pouwer F, Cuijpers P, et al. Web-based depression treatment for type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized, controlled trial[J]. Diabetes Care, 2011, 34(2): 320-325.
doi: 10.2337/dc10-1248 pmid: 21216855 |
| [18] |
Amsberg S, Wijk I, Livheim F, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) for adult type 1 diabetes management: Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial[J]. BMJ Open, 2018, 8(11): e022234.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022234 URL |
| [19] |
Bendig E, Bauereiss N, Schmitt A, et al. ACTonDiabetes-a guided psychological internet intervention based on Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) for adults living with type 1 or 2 diabetes: results of a randomised controlled feasibility trial[J]. BMJ Open, 2021, 11(7): e049238.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-049238 URL |
| [20] |
Bassi G, Donadello I, Gabrielli S, et al. Early Development of a Virtual Coach for Healthy Coping Interventions in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Validation Study[J]. JMIR Form Res, 2022, 6(2): e27500.
doi: 10.2196/27500 URL |
| [21] |
Alessi J, de Oliveira GB, Franco DW, et al. Mental health in the era of COVID-19: Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in a cohort of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes during the social distancing[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2020, 12: 76.
doi: 10.1186/s13098-020-00584-6 pmid: 32879637 |
| [22] |
Alessi J, de Oliveira GB, Franco DW, et al. Telehealth strategy to mitigate the negative psychological impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Acta Diabetol, 2021, 58(7): 899-909.
doi: 10.1007/s00592-021-01690-1 |
| [23] | 谢彩霞, 贾平, 吴娟, 等. 国内护士职业倦怠研究的热点分析[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2019, 36(2):32-36. |
| [24] | 赵庆, 姜武佳, 周莉萍, 等. 基于CiteSpace的国内非计划性拔管护理研究热点的可视化分析[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2022, 37(8):685-689. |
| [25] |
Sayadi AR, Seyed Bagheri SH, Khodadadi A, et al. The effect of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) training on serum cortisol levels, depression, stress, and anxiety in type 2 diabetic older adults during the COVID-19 outbreak[J]. J Med Life, 2022, 15(12):1493-1501.
doi: 10.25122/jml-2021-0437 pmid: 36762327 |
| [26] |
Luo L, Ayaz M, Tian H. Psychological issues among diabetic patients and the effect of psychological nursing on patients' well-being: An overview of the literature[J]. Altern Ther Health Med, 2021, 27(S1):72-79.
pmid: 33711818 |
| [27] |
Jaser SS, Whittemore R, Choi L, et al. Randomized trial of a positive psychology intervention for adolescents with type 1 diabetes[J]. J Pediatr Psychol, 2019, 44(5):620-629.
doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsz006 pmid: 30840084 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||