Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 485-493.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.06.001
Safety and efficacy of rivaroxaban in the treatment of discharged COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis
Yu Jingyi1, Si Yuanguo2, Lan Cuixia2, Xing Jiaxuan1( )
)
- 1. Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, 250012, China
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Qingdao Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Qingdao Hiser Hospital), Qingdao 266034,China
-
Received:2023-11-19Online:2024-06-20Published:2024-07-18 -
Contact:Xing Jiaxuan, Email:202135960@mail.sdu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Jingyi, Si Yuanguo, Lan Cuixia, Xing Jiaxuan. Safety and efficacy of rivaroxaban in the treatment of discharged COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(6): 485-493.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.06.001
| 数据库 | 检索策略 | 结果 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Embase | #1 ‘covid-19’ | 382, 015 | |
| #2 ‘novel coronavirus’ | 14, 176 | ||
| #3 ‘sars-cov-2’ | 160, 591 | ||
| #4 ‘2019-ncov’ | 2, 897 | 1020 | |
| #5 ‘coronavirus disease 2019’ | 359, 786 | ||
| #6 #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 | 452, 099 | ||
| #7 ‘rivaroxaban’ | 28, 586 | ||
| #8 #6 AND #7 | 1, 020 | ||
Tab.1 Search strategies of Embase database
| 数据库 | 检索策略 | 结果 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Embase | #1 ‘covid-19’ | 382, 015 | |
| #2 ‘novel coronavirus’ | 14, 176 | ||
| #3 ‘sars-cov-2’ | 160, 591 | ||
| #4 ‘2019-ncov’ | 2, 897 | 1020 | |
| #5 ‘coronavirus disease 2019’ | 359, 786 | ||
| #6 #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 | 452, 099 | ||
| #7 ‘rivaroxaban’ | 28, 586 | ||
| #8 #6 AND #7 | 1, 020 | ||
| 作者 | 年限 | 研究 类型 | 研究 范围 | 患者 类型 | 样本量 | 药物与剂量 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干预组 | 对照组 | 干预组 | 对照组 | |||||||
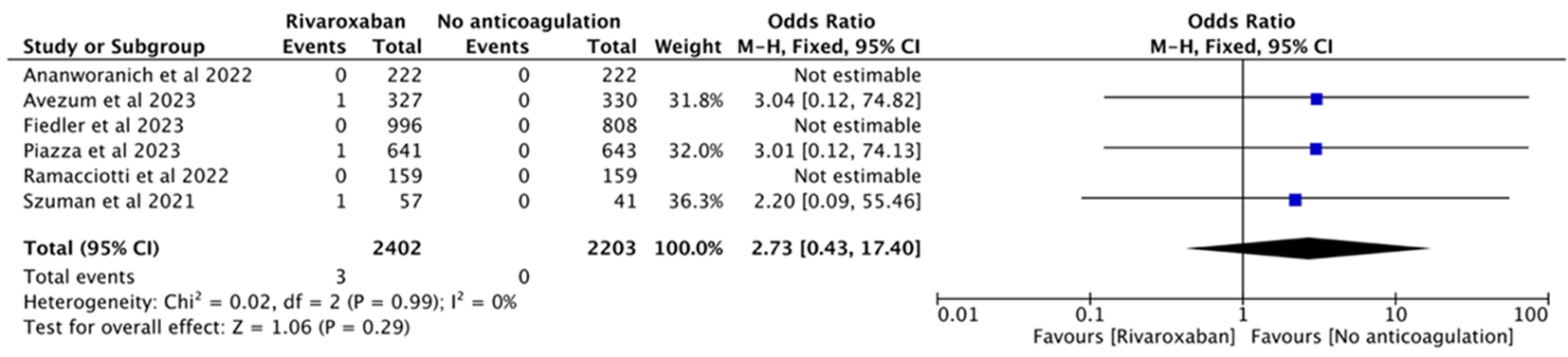
| 1 | Ananworanich et al[ | 2022 | RCT | 多中心 | Outpatients | 222 | 222 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | Placebo multivitamin 1 tablet qd | |
| 2 | Piazza et al[ | 2023 | RCT | 多中心 | Outpatients | 641 | 643 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | Placebo 1 tablet qd | |
| 3 | Avezum et al[ | 2023 | RCT | 多中心 | Outpatients | 327 | 330 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | Routine care | |
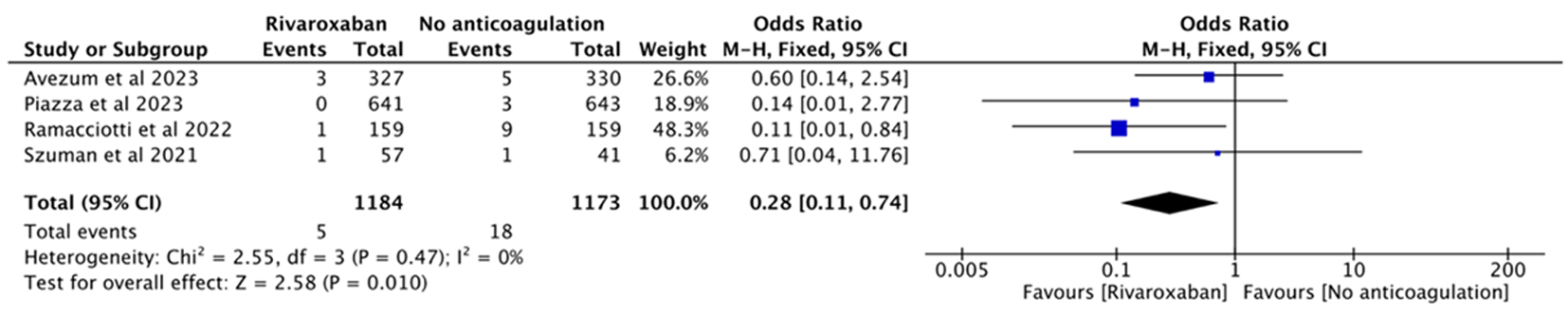
| 4 | Ramacciotti et al[ | 2022 | RCT | 多中心 | Discharged | 159 | 159 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | No anticoagulation | |
| 5 | Fiedler et al[ | 2023 | 队列研究 | 单中心 | Discharged | 996 | 808 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | No anticoagulation | |
| 6 | Szuman et al[ | 2021 | 队列研究 | 单中心 | Discharged | 57 | 41 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | No anticoagulation | |
Tab.2 Basic characteristics of the included studies
| 作者 | 年限 | 研究 类型 | 研究 范围 | 患者 类型 | 样本量 | 药物与剂量 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干预组 | 对照组 | 干预组 | 对照组 | |||||||
| 1 | Ananworanich et al[ | 2022 | RCT | 多中心 | Outpatients | 222 | 222 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | Placebo multivitamin 1 tablet qd | |
| 2 | Piazza et al[ | 2023 | RCT | 多中心 | Outpatients | 641 | 643 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | Placebo 1 tablet qd | |
| 3 | Avezum et al[ | 2023 | RCT | 多中心 | Outpatients | 327 | 330 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | Routine care | |
| 4 | Ramacciotti et al[ | 2022 | RCT | 多中心 | Discharged | 159 | 159 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | No anticoagulation | |
| 5 | Fiedler et al[ | 2023 | 队列研究 | 单中心 | Discharged | 996 | 808 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | No anticoagulation | |
| 6 | Szuman et al[ | 2021 | 队列研究 | 单中心 | Discharged | 57 | 41 | Rivaroxaban 10 mg qd | No anticoagulation | |
| Study | Selection | Comparability ⑤ | Outcome | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ① | ② | ③ | ④ | ⑥ | ⑦ | ⑧ | |||
| Fiedler et al | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 8 | |
| Szuman et al | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 6 | ||
Tab.3 The quality assessment of included cohort studies
| Study | Selection | Comparability ⑤ | Outcome | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ① | ② | ③ | ④ | ⑥ | ⑦ | ⑧ | |||
| Fiedler et al | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 8 | |
| Szuman et al | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 6 | ||
| [1] | Majumder J, Minko T. Recent developments on therapeutic and diagnostic approaches for COVID-19[J]. Aaps J, 2021, 23(1): 14. |
| [2] | Milross L, Majo J, Cooper N, et al. Post-mortem lung tissue: The fossil record of the pathophysiology and immunopathology of severe COVID-19[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2022, 10(1): 95-106. |
| [3] | Safiabadi Tali SH, Leblanc JJ, Sadiq Z, et al. Tools and techniques for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 detection[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2021, 34(3). |
| [4] | Yuan Y, Jiao B, Qu L, et al. The development of COVID-19 treatment[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1125246. |
| [5] |
Loo J, Spittle DA, Newnham M. COVID-19, immunothrombosis and venous thromboembolism: Biological mechanisms[J]. Thorax, 2021, 76(4): 412-420.
doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-216243 pmid: 33408195 |
| [6] | Chan N, Eikelboom J. Hypercoagulability and thrombosis in COVID-19: A modifiable cause for mortality?[J]. Eur Heart J, 2021, 42(33): 3143-3145. |
| [7] | Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid-19[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 383(2): 120-128. |
| [8] | Parra-Medina R, Herrera S, Mejia J. Systematic review of microthrombi in COVID-19 autopsies[J]. Acta Haematol, 2021, 144(5): 476-483. |
| [9] | Farge D, Frere C, Connors JM, et al. 2022 International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment and prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer, including patients with COVID-19[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2022, 23(7): E334-E347. |
| [10] | Barnes GD, Burnett A, Allen A, et al. Thromboembolic prevention and anticoagulant therapy during the COVID-19 pandemic: Updated clinical guidance from the anticoagulation forum[J]. J Thromb Thrombolysis, 2022, 54(2): 197-210. |
| [11] | Giossi R, Menichelli D, Pani A, et al. A systematic review and a meta-analysis comparing prophylactic and therapeutic low molecular weight heparins for mortality reduction in 32, 688 COVID-19 patients[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 698008. |
| [12] | Lawler PR, Goligher EC, Berger JS, et al. Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in noncritically ill patients with covid-19[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 385(9): 790-802. |
| [13] |
Spyropoulos AC, Goldin M, Giannis D, et al. Efficacy and safety of therapeutic-dose heparin vs standard prophylactic or intermediate-dose heparins for thromboprophylaxis in high-risk hospitalized patients with COVID-19: The HEP-COVID randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Intern Med, 2021, 181(12): 1612-1620.
doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6203 pmid: 34617959 |
| [14] | Dai MF, Xin WX, Kong S, et al. Effectiveness and safety of extended thromboprophylaxis in post-discharge patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Thromb Res., 2023, 221: 105-112. |
| [15] |
Verma AK, Brighton TA. The direct factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban[J]. Med J Aust, 2009, 190(7): 379-383.
doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.2009.tb02453.x pmid: 19351313 |
| [16] |
Lopes RD, Furtado RHM, et al. Therapeutic versus prophylactic anticoagulation for patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 and elevated D-dimer concentration (ACTION): An open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial[J]. Lancet, 2021, 397(10291): 2253-2263.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01203-4 pmid: 34097856 |
| [17] | Meroni PL, Croci S, Lonati PA, et al. Complement activation predicts negative outcomes in COVID-19: The experience from Northen Italian patients[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2023, 22(1): 103232. |
| [18] | Turner S, Khan MA, Putrino D, et al. Long COVID: Pathophysiological factors and abnormalities of coagulation[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2023, 34(6): 321-344. |
| [19] |
Sciaudone A, Corkrey H, Humphries F, et al. Platelets and SARS-CoV-2 During COVID-19: Immunity, thrombosis, and beyond[J]. Circ Res, 2023, 132(10): 1272-1289.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321930 pmid: 37167360 |
| [20] |
Conway EM, Mackman N, Warren RQ, et al. Understanding COVID-19-associated coagulopathy[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2022, 22(10): 639-649.
doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00762-9 pmid: 35931818 |
| [21] | Bikdeli B, Madhavan MV, Jimenez D, et al. COVID-19 and thrombotic or thromboembolic disease: Implications for prevention, antithrombotic therapy, and follow[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2020, 75(23): 2950-2973. |
| [22] | Scavone C, Mascolo A, Rafaniello C, et al. Therapeutic strategies to fight COVID-19: Which is the status artis?[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2022, 179(10): 2128-2148. |
| [23] |
Thachil J, Tang N, Gando S, et al. ISTH interim guidance on recognition and management of coagulopathy in COVID-19[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2020, 18(5): 1023-1026.
doi: 10.1111/jth.14810 pmid: 32338827 |
| [24] | Goligher EC, Bradbury CA, Mcverry BJ, et al. Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in critically Ill patients with covid-19[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 385(9): 777-789. |
| [25] | Chalmers JD, Crichton ML, Goeminne PC, et al. Management of hospitalised adults with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A European Respiratory Society living guideline[J]. Eur Respir J, 2021, 57(4): 2100048. |
| [26] |
Garcia D, Libby E, Crowther MA. The new oral anticoagulants[J]. Blood, 2010, 115(1): 15-20.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-241851 pmid: 19880491 |
| [27] |
Carter NJ, Plosker GL. Rivaroxaban: A review of its use in the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation[J]. Drugs, 2013, 73(7): 715-739.
doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0056-9 pmid: 23677801 |
| [28] |
Burness CB, Perry CM. Rivaroxaban: A review of its use in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism and the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism[J]. Drugs, 2014, 74(2): 243-262.
doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0174-4 pmid: 24430916 |
| [29] |
Hess CN, Debus ES, Nehler MR, et al. Reduction in acute limb ischemia with rivaroxaban versus placebo in peripheral artery disease after lower extremity revascularization: Insights from VOYAGER PAD[J]. Circulation, 2021, 144(23): 1831-1841.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055146 pmid: 34637332 |
| [30] | Mega JL, Braunwald E, Wiviott SD, et al. Rivaroxaban in patients with a recent acute coronary syndrome[J]. N Engl J Med, 2012, 366(1): 9-19. |
| [31] | Zannad F, Anker SD, Byra WM, et al. Rivaroxaban in patients with heart failure, sinus rhythm, and coronary disease[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 379(14): 1332-1342. |
| [32] | Zhou S, Xiao Y, Zhou C, et al. Effect of rivaroxaban vs enoxaparin on major cardiac adverse events and bleeding risk in the acute phase of acute coronary syndrome: The H-REPLACE randomized equivalence and noninferiority trial[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2023, 6(2): e2255709. |
| [33] |
Nopp S, Moik F, Jilma B, et al. Risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Res Pract Thromb Haemost, 2020, 4(7): 1178-1191.
doi: 10.1002/rth2.12439 pmid: 33043231 |
| [34] | Lund LC, Hedberg P, Andreasen AH, et al. Prophylactic anticoagulation with low molecular weight heparin in COVID-19: Cohort studies in Denmark and Sweden[J]. PClin Microbiol Infect, 2022, 28(9):1291.e1-1291.e5. |
| [35] |
Ramacciotti E, Agati LB, Calderaro D, et al. Rivaroxaban versus no anticoagulation for post-discharge thromboprophylaxis after hospitalisation for COVID-19 (MICHELLE): An open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial[J]. Lancet, 2022, 399(10319): 50-59.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02392-8 pmid: 34921756 |
| [36] |
Piazza GC, Spyropoulos A, Hsia J, et al. Rivaroxaban for prevention of thrombotic events, hospitalization, and death in outpatients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial[J]. Circulation, 2023, 147(25): 1891-1901.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.063901 pmid: 37154020 |
| [37] | Avezum A, Oliveira Junior HA, Neves PDMM, et al. Rivaroxaban to prevent major clinical outcomes in non-hospitalised patients with COVID-19: The CARE-COALITION VIII randomised clinical trial[J]. EClinicalMedicine, 2023, 60: 102004. |
| [38] | Nemetski SM, Ip A, Josephs J, et al. Clotting events among hospitalized patients infected with COVID-19 in a large multisite cohort in the United States[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(1): e0262352. |
| [39] | Fan Y, Li X, Zhang L, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Recent progress and future perspectives[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 141. |
| [40] |
Chan N, Sobieraj-Teague M, Eikelboom JW. Direct oral anticoagulants: Evidence and unresolved issues[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10264): 1767-1776.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32439-9 pmid: 33248499 |
| [41] |
Castellucci LA, Cameron C, Le Gal G, et al. Clinical and safety outcomes associated with treatment of acute venous thromboembolism a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. JAMA, 2014, 312(11): 1122-1135.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.10538 pmid: 25226478 |
| [42] | Fredenburgh JC, Weitz JI. News at XI: Moving beyond factor Xa inhibitors[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2023, 21(7): 1692-1702. |
| [43] | Ananworanich J, Mogg R, Dunne MW, et al. Randomized study of rivaroxaban vs placebo on disease progression and symptoms resolution in high-risk adults with mild coronavirus disease 2019[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2022, 75(1): e473-e481. |
| [44] | Fiedler L, Motloch LJ, Dieplinger AM, et al. Prophylactic rivaroxaban in the early post-discharge period reduces the rates of hospitalization for atrial fibrillation and incidence of sudden cardiac death during long-term follow-up in hospitalized COVID-19 survivors[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1093396. |
| [45] | Szuman A, Kirkham Z, Price R, et al. Extended outpatient thromboprophylaxis for individuals with COVID-19[J]. Res Pract Thromb Haemost, 2021, 5(SUPPL 2). |
| [1] | Zhi Bingdi, Liu Ying, Liu Ying, Zhang Fubo, Li Junfeng. SARS-CoV-2 infection combined with Listeria meningitis: A case report and literature review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(4): 347-351. |
| [2] | Huang Saihu, Long Zhongjie, Wu Shuiyan, Bai Zhenjiang. Clinical characteristics and etiological analysis of severe pneumonia complicated with acute respiratory failure in children before and after COVID-19 [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(2): 140-143. |
| [3] | Wang Yihan, Qin Xuyan, Han Xuanze, Wang Yingjie, Gao Feifei, Chen Chunhong, Zhang Lingnan, Zhang Fang. Efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban therapy in elderly patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation who had a HASBLED score≥3 [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(2): 121-124. |
| [4] | Peng Yimeng, Yao Yang, Li Siyu, Ding Ge, Sun Yanan, Wang Shengyu. Meta-analysis of the incidence of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation combined with incident thrombosis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 5-11. |
| [5] | Huang Huayan, Lin Chunguang, Wu Changru, Chen Yongdong, Huang Huanmou. Clinical characteristics of patients infected with Omicron and Delta variants in novel coronavirus [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(7): 600-605. |
| [6] | Ni Yiyun, Liu Bin, Liang Qi, Li Xiaofeng. Values of IL-6 and CRP in predicting the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: A meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(6): 493-499. |
| [7] | Zhou Huixian, Zhou Yaqing, Guo Ganlin, Cui Wei. Therapy on left ventricular thrombus:Systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(2): 101-110. |
| [8] | Liu Xiangdong, Cai Yandong, Qin Yanjun, Li Yunsong, Li Liang, Gao Ruijiao, Ren Lei, Zhang Yanrong. Exertional rhabdomyolysis complicated with acute renal insufficiency and catheter-related thrombosis: One case and literature review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(9): 831-833. |
| [9] | Hou Huiyu, Zhang Shaohua, Ma Xinxin, Zhang Jie, Wang Yazhen. Investigation and analysis of knowledge, attitude and practice of medical workers in public hospitals on the prevention & protection from COVID-19 [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(7): 631-634. |
| [10] | Lin Xinxin, Zhang Chuhan, Kong Haolin, He Muchen, Xu Lin, Yang Zhonghan. Analysis on impacts of diabetes on the severity and mortality of patients with COVID-19: A Meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(5): 389-399. |
| [11] | Huang Huayan, Lin Chunguang, Chen Yongdong, Zeng Qiyi, Wu Changru. Clinical characteristics of Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 of shipmate [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(4): 311-314. |
| [12] | Guo Ru, Liu Ruihong, Lin Xuefeng, Han Xuanmao, Zhang Zhu, Chen Ruiying. Correlation between cardiac troponin and D-dimer levels and mortality in COVID-19 critical illness patients: A meta analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(4): 293-298. |
| [13] | Chang Yajun, Guo Weina, Guo Qiaozhen, Wang Tianjun. Literature review on one case of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis mainly featured with isolated headache [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 271-274. |
| [14] | Guo Wenxiu, Wang Hailong, Wang Doudou. Correlation between heart type fatty acid binding protein and mild & severe COVID-19 [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(12): 1104-1107. |
| [15] | Zhou Zihan, Cui Wei. Effects of common cardiovascular drugs on the risk of COVID-19 infection and poor prognosis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(10): 869-888. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||