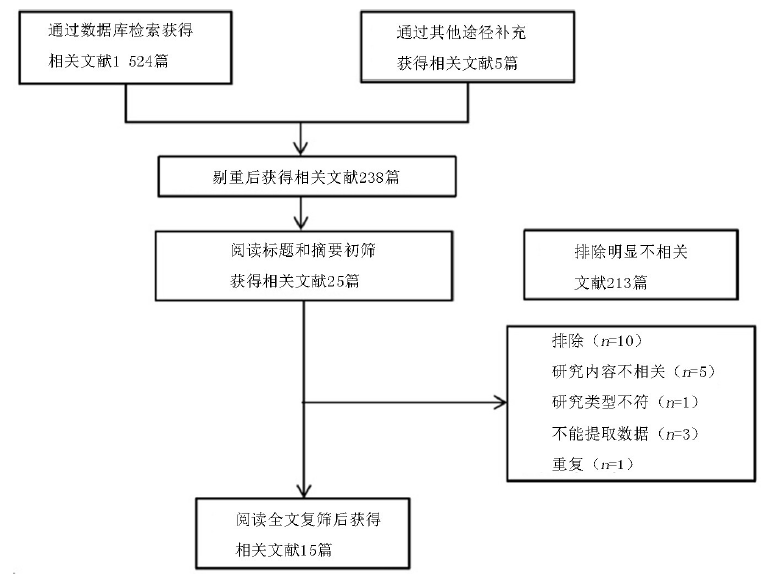
Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (7): 581-590.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.07.001
Meta analysis on correlation between sporadic duodenal neoplasm and colorectal neoplasm
Wang Chengyao, Zhang Zheng, Wu Jing( )
)
- Department of Gastroenterology,Beijing Friendship Hospital,Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050,China
-
Received:2021-11-01Online:2022-07-20Published:2022-08-30 -
Contact:Wu Jing E-mail:wujing36youyi@ccmu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Chengyao, Zhang Zheng, Wu Jing. Meta analysis on correlation between sporadic duodenal neoplasm and colorectal neoplasm[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(7): 581-590.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.07.001
| 纳入文献 | 发表 年份 | 国家/ 地区 | 肿瘤类型 | 样本量 (病例组/对照组) | 对照来源* | 匹配因素* | 主要结局 | 研究类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matsuzaki等[ | 2019 | 日本 | 散发性十二指肠肿瘤 | 157/314 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Kakushima等[ | 2017 | 日本 | 散发性十二指肠腺癌 | 156/468 | 健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
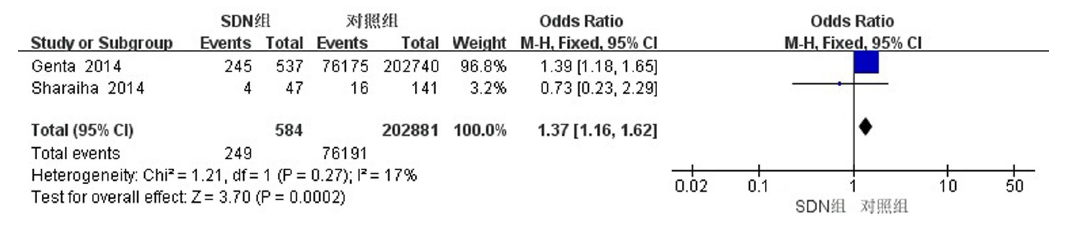
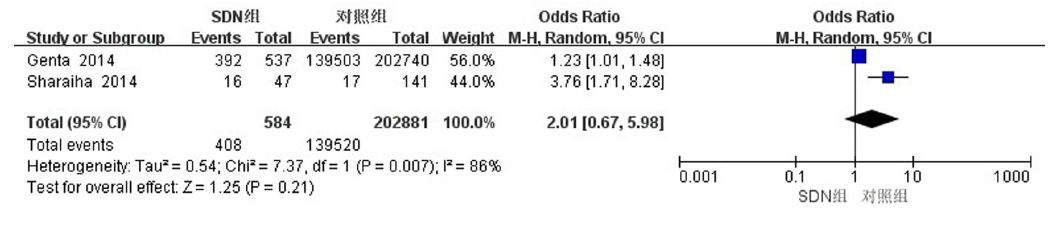
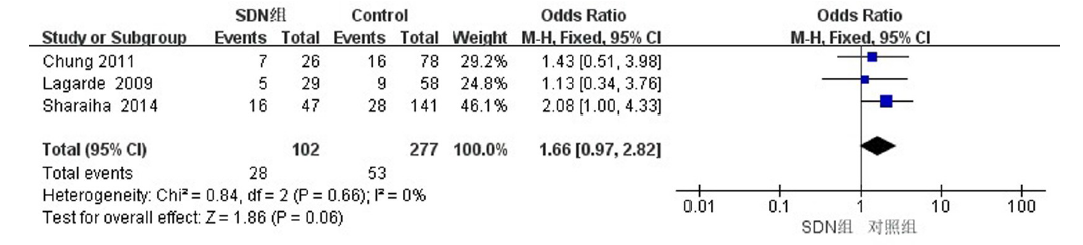
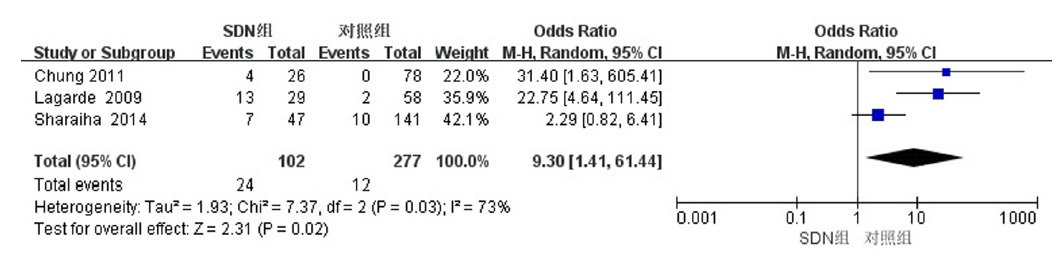
| Sharaiha等[ | 2014 | 美国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 47/141 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Genta等[ | 2014 | 美国 | 散发性十二指肠肿瘤 | 537/202,740 | 非健康人群 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 | |
| Chung等[ | 2011 | 韩国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 45/78 | 健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Dariusz等[ | 2009 | 德国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 48/144 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Lagarde等[ | 2009 | 法国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 29/58 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Ramsoekh等[ | 2008 | 新西兰 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 49/147 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Pequin等[ | 2007 | 法国 | 散发性十二指肠肿瘤 | 35/70 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Schneider等[ | 2005 | 德国 | 散发性十二指肠肿瘤 | 26/104 | 健康人群 | 年龄 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Murray等[ | 2004 | 澳大利亚 | 散发性十二指肠肿瘤 | 56/102 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Panigadi等[ | 2014 | 阿根廷 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 70/140 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别、结直肠癌 家族史 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Pereyra等[ | 2013 | 美国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 34/68 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别、结直肠癌 家族史 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Gonzalez-Ortiz等[ | 2010 | 美国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 21/84 | 非健康人群 | 结直肠腺瘤 | 病例对照研究 | |
| Abbass等[ | 2010 | 美国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 17/15 | 非健康人群 | 结直肠腺瘤 | 横断面研究 |
| 纳入文献 | 发表 年份 | 国家/ 地区 | 肿瘤类型 | 样本量 (病例组/对照组) | 对照来源* | 匹配因素* | 主要结局 | 研究类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matsuzaki等[ | 2019 | 日本 | 散发性十二指肠肿瘤 | 157/314 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Kakushima等[ | 2017 | 日本 | 散发性十二指肠腺癌 | 156/468 | 健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Sharaiha等[ | 2014 | 美国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 47/141 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Genta等[ | 2014 | 美国 | 散发性十二指肠肿瘤 | 537/202,740 | 非健康人群 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 | |
| Chung等[ | 2011 | 韩国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 45/78 | 健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Dariusz等[ | 2009 | 德国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 48/144 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Lagarde等[ | 2009 | 法国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 29/58 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Ramsoekh等[ | 2008 | 新西兰 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 49/147 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Pequin等[ | 2007 | 法国 | 散发性十二指肠肿瘤 | 35/70 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Schneider等[ | 2005 | 德国 | 散发性十二指肠肿瘤 | 26/104 | 健康人群 | 年龄 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Murray等[ | 2004 | 澳大利亚 | 散发性十二指肠肿瘤 | 56/102 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Panigadi等[ | 2014 | 阿根廷 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 70/140 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别、结直肠癌 家族史 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Pereyra等[ | 2013 | 美国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 34/68 | 非健康人群 | 年龄、性别、结直肠癌 家族史 | 结直肠腺瘤 结直肠癌 | 病例对照研究 |
| Gonzalez-Ortiz等[ | 2010 | 美国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 21/84 | 非健康人群 | 结直肠腺瘤 | 病例对照研究 | |
| Abbass等[ | 2010 | 美国 | 散发性十二指肠腺瘤 | 17/15 | 非健康人群 | 结直肠腺瘤 | 横断面研究 |
| 纳入文献 | 发表 年份 | 研究人群选择 | 组间可比性 | 暴露因素的测量 | 总分 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病例的定义和 诊断是否恰当 | 病例的 代表性 | 对照的 选择 | 对照的 定义 | 控制了重要 混杂因素 (年龄、性别) | 控制了其他 混杂因素 | 暴露因素的 确定 | 采用相同的方法确定 病例组和对照组的 暴露因素 | 无应 答率 | ||||||
| Matsuzaki等 | 2019年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 5 | |||||||
| Kakushima等 | 2017年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 5 | |||||||
| Sharaiha等 | 2014年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 8 | ||||
| Genta等 | 2014年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 8 | ||||
| Panigadi等 | 2014年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 8 | ||||
| Pereyra等 | 2013年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 8 | ||||
| Chung等 | 2011年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 8 | ||||
| Gonzalez-Ortiz等 | 2010年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 5 | |||||||
| Dariusz等 | 2009年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 6 | ||||||
| Lagarde等 | 2009年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 7 | |||||
| Ramsoekh等 | 2008年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 7 | |||||
| Pequin等 | 2007年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 7 | |||||
| Schneider等 | 2005年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 7 | |||||
| Murray等 | 2004年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 7 | |||||
| 纳入文献 | 发表 年份 | 研究人群选择 | 组间可比性 | 暴露因素的测量 | 总分 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病例的定义和 诊断是否恰当 | 病例的 代表性 | 对照的 选择 | 对照的 定义 | 控制了重要 混杂因素 (年龄、性别) | 控制了其他 混杂因素 | 暴露因素的 确定 | 采用相同的方法确定 病例组和对照组的 暴露因素 | 无应 答率 | ||||||
| Matsuzaki等 | 2019年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 5 | |||||||
| Kakushima等 | 2017年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 5 | |||||||
| Sharaiha等 | 2014年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 8 | ||||
| Genta等 | 2014年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 8 | ||||
| Panigadi等 | 2014年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 8 | ||||
| Pereyra等 | 2013年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 8 | ||||
| Chung等 | 2011年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 8 | ||||
| Gonzalez-Ortiz等 | 2010年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 5 | |||||||
| Dariusz等 | 2009年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 6 | ||||||
| Lagarde等 | 2009年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 7 | |||||
| Ramsoekh等 | 2008年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 7 | |||||
| Pequin等 | 2007年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 7 | |||||
| Schneider等 | 2005年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 7 | |||||
| Murray等 | 2004年 | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 7 | |||||
| 纳入文献 | 发表年份 | 条目1 | 条目2 | 条目3 | 条目4 | 条目5 | 条目6 | 条目7 | 条目8 | 条目9 | 条目10 | 条目11 | 总分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbass等 | 2010年 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| 纳入文献 | 发表年份 | 条目1 | 条目2 | 条目3 | 条目4 | 条目5 | 条目6 | 条目7 | 条目8 | 条目9 | 条目10 | 条目11 | 总分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbass等 | 2010年 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| 亚组 | 研究数量 | 模型选择 | | Pz* | | Ph* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
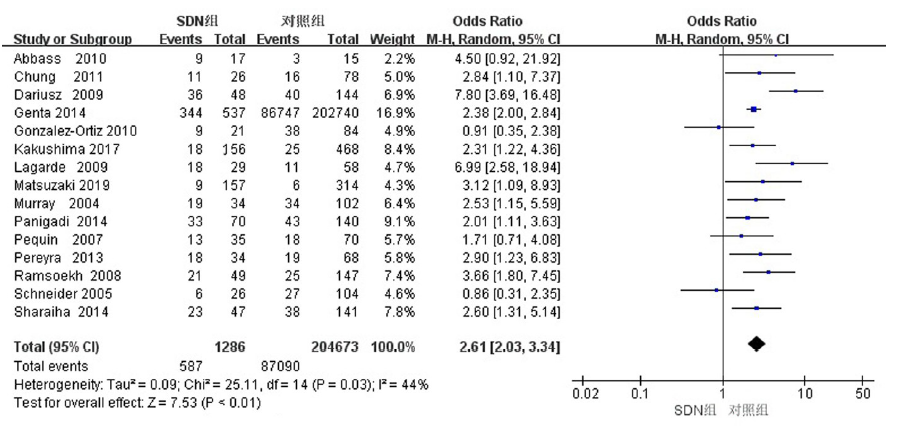
| 全部 | 15 | 随机效应模型 | 2.61[2.03, 3.34] | <0.01 | 44 | 0.03 |
| 研究类型 | ||||||
| 病例对照研究 | 14 | 随机效应模型 | 2.58[1.99-3.33] | <0.01 | 47 | 0.03 |
| 横断面研究 | 1 | - | 4.50[0.92-21.92] | |||
| 国家/地区 | ||||||
| 亚洲 | 3 | 固定效应模型 | 2.59[1.62, 4.15] | <0.01 | 0 | 0.87 |
| 欧洲 | 4 | 随机效应模型 | 3.04[1.07, 8.67] | 0.04 | 82 | 0.001 |
| 美洲 | 5 | 固定效应模型 | 2.33[1.99, 2.73] | <0.01 | 0 | 0.42 |
| 大洋洲 | 2 | 固定效应模型 | 3.08[1.81, 5.24] | <0.01 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 对照组的选择 | ||||||
| 健康人群 | 3 | 固定效应模型 | 1.91[1.20, 3.03] | 0.006 | 42 | 0.18 |
| 非健康人群 | 12 | 随机效应模型 | 2.80[2.11, 3.70] | <0.01 | 47 | 0.04 |
| 样本量 | ||||||
| <100 | 12 | 随机效应模型 | 2.66[1.85, 3.83] | <0.01 | 55 | 0.01 |
| ≥100 | 3 | 固定效应模型 | 2.39[2.02, 2.83] | <0.01 | 0 | 0.88 |
| 结直肠癌家族史 | ||||||
| 有 | 5 | 固定效应模型 | 2.49[1.79, 3.46] | <0.01 | 28 | 0.24 |
| 无 | 10 | 随机效应模型 | 2.62[1.86, 3.69] | <0.01 | 54 | 0.02 |
| SDN组织学类型 | ||||||
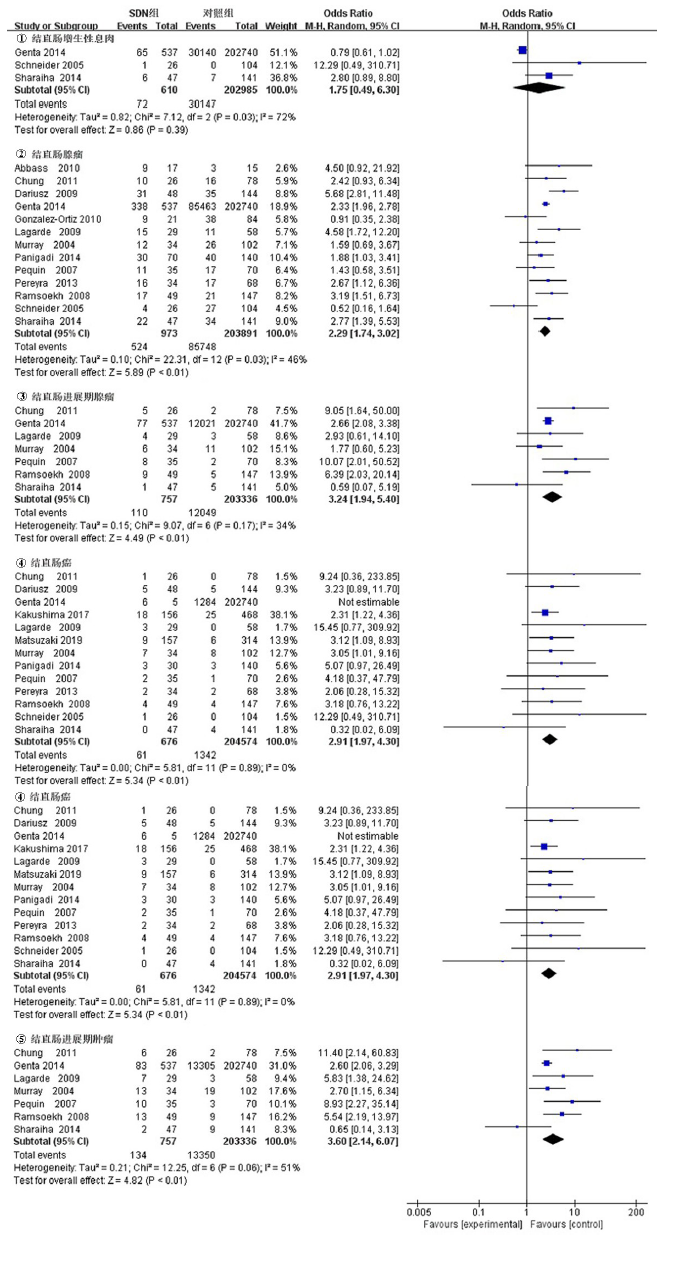
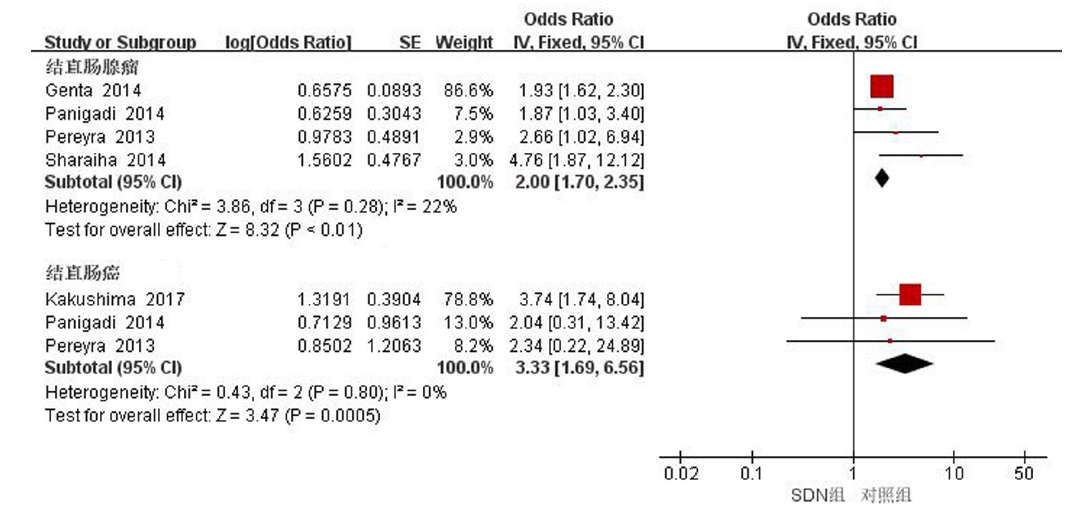
| 十二指肠腺瘤 | 8 | 随机效应模型 | 3.13[2.07, 4.73] | <0.01 | 54 | 0.03 |
| 十二指肠癌 | 1 | - | 2.31[1.22, 4.36] | |||
| 十二指肠腺瘤/腺癌 | 5 | 固定效应模型 | 2.31[1.96, 2.72] | <0.01 | 14 | 0.33 |
| SDN部位 | ||||||
| 非壶腹部 | 8 | 固定效应模型 | 3.56[2.65-4.78] | <0.01 | 36 | 0.14 |
| 壶腹部/非壶腹部 | 7 | 固定效应模型 | 2.27[1.95-2.65] | <0.01 | 25 | 0.24 |
| 亚组 | 研究数量 | 模型选择 | | Pz* | | Ph* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全部 | 15 | 随机效应模型 | 2.61[2.03, 3.34] | <0.01 | 44 | 0.03 |
| 研究类型 | ||||||
| 病例对照研究 | 14 | 随机效应模型 | 2.58[1.99-3.33] | <0.01 | 47 | 0.03 |
| 横断面研究 | 1 | - | 4.50[0.92-21.92] | |||
| 国家/地区 | ||||||
| 亚洲 | 3 | 固定效应模型 | 2.59[1.62, 4.15] | <0.01 | 0 | 0.87 |
| 欧洲 | 4 | 随机效应模型 | 3.04[1.07, 8.67] | 0.04 | 82 | 0.001 |
| 美洲 | 5 | 固定效应模型 | 2.33[1.99, 2.73] | <0.01 | 0 | 0.42 |
| 大洋洲 | 2 | 固定效应模型 | 3.08[1.81, 5.24] | <0.01 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 对照组的选择 | ||||||
| 健康人群 | 3 | 固定效应模型 | 1.91[1.20, 3.03] | 0.006 | 42 | 0.18 |
| 非健康人群 | 12 | 随机效应模型 | 2.80[2.11, 3.70] | <0.01 | 47 | 0.04 |
| 样本量 | ||||||
| <100 | 12 | 随机效应模型 | 2.66[1.85, 3.83] | <0.01 | 55 | 0.01 |
| ≥100 | 3 | 固定效应模型 | 2.39[2.02, 2.83] | <0.01 | 0 | 0.88 |
| 结直肠癌家族史 | ||||||
| 有 | 5 | 固定效应模型 | 2.49[1.79, 3.46] | <0.01 | 28 | 0.24 |
| 无 | 10 | 随机效应模型 | 2.62[1.86, 3.69] | <0.01 | 54 | 0.02 |
| SDN组织学类型 | ||||||
| 十二指肠腺瘤 | 8 | 随机效应模型 | 3.13[2.07, 4.73] | <0.01 | 54 | 0.03 |
| 十二指肠癌 | 1 | - | 2.31[1.22, 4.36] | |||
| 十二指肠腺瘤/腺癌 | 5 | 固定效应模型 | 2.31[1.96, 2.72] | <0.01 | 14 | 0.33 |
| SDN部位 | ||||||
| 非壶腹部 | 8 | 固定效应模型 | 3.56[2.65-4.78] | <0.01 | 36 | 0.14 |
| 壶腹部/非壶腹部 | 7 | 固定效应模型 | 2.27[1.95-2.65] | <0.01 | 25 | 0.24 |
| [1] |
Matsueda K, Kanzaki H, Matsueda K, et al. The clinicopathological differences of sporadic non-ampullary duodenal epithelial neoplasm depending on tumor location[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 34(9):1540-1544.
doi: 10.1111/jgh.14640 URL |
| [2] | Barsouk A, Rawla P, Barsouk A, et al. Epidemiology of cancers of the small intestine: trends, risk factors, and prevention[J]. Med Sci (Basel), 2019, 7(3):46. |
| [3] |
Tokar JL, Higa JT. Capsule endoscopy in persons with duodenal adenomas: Focus on the colon instead?[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2021, 93(3):637-639.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.09.006 pmid: 33583521 |
| [4] |
Kanth P, Samadder NJ, DiSario J. Duodenal adenomas in sporadic and familial adenomatous polyposis patients: Birds of a feather?[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2017, 85(4):813-815.
doi: S0016-5107(16)30896-3 pmid: 28317691 |
| [5] |
Nagtegaal ID, Odze RD, Klimstra D, et al. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system[J]. Histopathology, 2020, 76(2):182-188.
doi: 10.1111/his.13975 pmid: 31433515 |
| [6] |
Sun L, Guzzetta AA, Fu T, Chen J, et al. CpG island methylator phenotype and its association with malignancy in sporadic duodenal adenomas[J]. Epigenetics, 2014, 9(5):738-746.
doi: 10.4161/epi.28082 pmid: 24518818 |
| [7] | Goda K, Kikuchi D, Yamamoto Y, et al. Endoscopic diagnosis of superficial non-ampullary duodenal epithelial tumors in Japan: Multicenter case series[J]. Dig Endosc, 2014 26(Suppl 2):23-29. |
| [8] | Sakaguchi Y, Tsuji Y, Ushiku T, et al. The natural history of sporadic non‐ampullary duodenal epithelial tumors: Can we wait and see?[J]. DEN Open, 2021, 1(1): e9. |
| [9] |
Akahoshi K, Kubokawa M, Inamura K, et al. Current challenge: Endoscopic submucosal dissection of superficial non-ampullary duodenal epithelial tumors[J]. Curr Treat Options Oncol, 2020, 21(12):98.
doi: 10.1007/s11864-020-00796-y URL |
| [10] |
ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Chathadi KV, Khashab MA, et al. The role of endoscopy in ampullary and duodenal adenomas[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2015, 82(5):773-781.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2015.06.027 pmid: 26260385 |
| [11] |
Vanbiervliet G, Strijker M, Arvanitakis M, et al. Endoscopic management of ampullary tumors: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline[J]. Endoscopy, 2021, 53(4):429-448.
doi: 10.1055/a-1397-3198 pmid: 33728632 |
| [12] | Wu ZJ, Lin Y, Xiao J, et al. Clinical significance of colonoscopy in patients with upper gastrointestinal polyps and neoplasms: A meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(3):e91810. |
| [13] |
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2010, 25(9):603-605.
doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z pmid: 20652370 |
| [14] | 曾宪涛, 刘慧, 陈曦, 等. Meta分析系列之四:观察性研究的质量评价工具[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2012, 4(4):297-299. |
|
[ 15 Matsuzaki J, Suzuki H, Shimoda M, et al. Clinical and endoscopic findings to assist the early detection of duodenal adenoma and adenocarcinoma[J]. United European Gastroenterol J, 2019, 7(2):250-260.
doi: 10.1177/2050640618817689 URL |
|
| [16] |
Kakushima N, Ono H, Yoshida M, et al. Characteristics and risk factors for sporadic non-ampullary duodenal adenocarcinoma[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2017, 52(11):1253-1257.
doi: 10.1080/00365521.2017.1369563 URL |
| [17] |
Sharaiha RZ, Cohen MS, Reimers L, et al. Sporadic duodenal adenoma and association with colorectal neoplasia: A case-control study[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2014, 59(10):2523-2528.
doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3188-1 URL |
| [18] |
Genta RM, Hurrell JM, Sonnenberg A. Duodenal adenomas coincide with colorectal neoplasia[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2014, 59(9):2249-2254.
doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3131-5 URL |
| [19] |
Chung WC, Lee BI, Roh SY, et al. Increased prevalence of colorectal neoplasia in korean patients with sporadic duodenal adenomas: A case-control study[J]. Gut Liver, 2011, 5(4):432-436.
doi: 10.5009/gnl.2011.5.4.432 pmid: 22195240 |
| [20] |
Dariusz A, Jochen R. Increased prevalance of colorectal adenoma in patients with sporadic duodenal adenoma[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2009, 21(7):816-818.
doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e328306c7cc URL |
| [21] |
Lagarde S, Dauphin M, Delmas C, et al. Increased risk of colonic neoplasia in patients with sporadic duodenal adenoma[J]. Gastroenterol Clin Biol, 2009, 33(5):441-445.
doi: 10.1016/j.gcb.2008.10.018 URL |
| [22] |
Ramsoekh D, van Leerdam ME, Dekker E, et al. Sporadic duodenal adenoma and the association with colorectal neoplasia: A case-control study[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2008, 103(6):1505-1509.
doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01775.x pmid: 18510617 |
| [23] |
Pequin P, Manfredi S, Quentin V, et al. Patients with sporadic duodenal adenoma are a high-risk group for advanced colorectal neoplasia: Results of a case-control study[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2007, 26(2):277-282.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03359.x URL |
| [24] |
Schneider AR, Seifert H, Trojan J, et al. Frequency of colorectal polyps in patients with sporadic adenomas or adenocarcinomas of the papilla of vater--an age-matched, controlled study[J]. Z Gastroenterol, 2005, 43(10):1123-1127.
pmid: 16220451 |
| [25] |
Murray MA. Sporadic duodenal adenoma is associated with colorectal neoplasia[J]. Gut, 2004, 53(2):261-265.
pmid: 14724161 |
| [26] | Panigadi GN, Pereyra L, R González, et al. Su1243 risk of colonic neoplasia in patients with sporadic duodenal adenomas: A multicenter case-control study[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 146(5):S-412. |
| [27] | Pereyra L, GonzáLez R, Luna P, et al. Increased risk of colonic neoplasia in patients with sporadic duodenal adenomas[J]. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 2013, 77(15s):AB433. |
| [28] |
Gonzalez-Ortiz DI, Torres-Cotto C, Toro DH, et al. Duodenal adenomas in nonpolyposis syndrome patients are not associated to colorectal neoplasia[J]. Bol Asoc Med P R, 2010, 102(4):5-8.
pmid: 21766541 |
| [29] |
Abbass R, Rigaux J, Al-Kawas FH. Nonampullary duodenal polyps: Characteristics and endoscopic management[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2010, 71(4):754-759.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2009.11.043 pmid: 20363416 |
| [30] | Kinugasa H, Kanzaki H, Tanaka T, et al. The impact of KRAS mutation in patients with sporadic nonampullary duodenal epithelial tumors[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2021, 12(11):e00424. |
| [31] |
Ota R, Sawada T, Tsuyama S, et al. Integrated genetic and epigenetic analysis of cancer-related genes in non-ampullary duodenal adenomas and intramucosal adenocarcinomas[J]. J Pathol, 2020, 252(3): 330-342.
doi: 10.1002/path.5529 URL |
| [32] |
Awadie H, Klein A, Tate D, et al. The prevalence of small-bowel polyps on video capsule endoscopy in patients with sporadic duodenal or ampullary adenomas[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2021, 93(3):630-636.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.07.029 pmid: 32717365 |
| [33] |
Das A, Neugut AI, Cooper GS, et al. Association of ampullary and colorectal malignancies[J]. Cancer, 2004, 100(3):524-530.
pmid: 14745868 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||