Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (10): 901-908.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.10.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Association of TyG index and its derivatives with the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Li Jiawen1, Liu Yanlan2, Li Yaoshuang3, Qiu Huina2, Li Fang2, Wu Fan2, Lin Chenying3, Lin Jingna2( )
)
- 1. Department of Geriatrics, Tianjin Nankai Hospital, Tianjin 300100, China
2. Department of Endocrinology, Tianjin People's Hospital, Tianjin 300122, China
3. Graduate School, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300203, China
-
Received:2024-07-24Online:2024-10-20Published:2024-10-31 -
Contact:Lin Jingna E-mail:13207628978@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jiawen, Liu Yanlan, Li Yaoshuang, Qiu Huina, Li Fang, Wu Fan, Lin Chenying, Lin Jingna. Association of TyG index and its derivatives with the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(10): 901-908.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.10.006
| 项目 | 非DKD组(n=569) | DKD组(n=326) | t/Z/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 61(56, 66) | 62(55, 67) | -0.172 | 0.864 |
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 266(46.8) 303(53.2) | 178(54.6) 148(45.4) | 5.122 | 0.024 |
| 糖尿病病程(年) | 5(1, 10) | 8(1, 13) | -3.359 | 0.001 |
| 规律运动[例(%)] | 420(73.81) | 240(73.62) | 0.004 | 0.949 |
| 糖尿病饮食管理[例(%)] | 344(60.46) | 195(59.82) | 0.036 | 0.850 |
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 130(120, 140) | 132(127, 140) | -3.147 | 0.002 |
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 80(74, 8) | 80(73, 8) | -0.289 | 0.773 |
| 目前吸烟[例(%)] | 214(37.6) | 152(46.6) | 6.970 | 0.008 |
| 目前饮酒[例(%)] | 174(30.6) | 107(32.8) | 0.484 | 0.487 |
| 合并高血压病[例(%)] | 352(61.9) | 227(69.6) | 5.477 | 0.019 |
| 使用降压药[例(%)] | 193(60.1) | 468(52.9) | 10.439 | 0.001 |
| 使用降脂药[例(%)] | 53(9.3) | 51(15.6) | 8.085 | 0.004 |
| 糖尿病药物使用[例(%)] | ||||
| 未使用药物 | 195(34.3) | 73(22.4) | ||
| 只用口服降糖药 | 252(44.3) | 135(41.4) | 28.880 | 0.000 |
| 只用胰岛素 | 13(2.3) | 7(2.2) | ||
| 口服药胰岛素联合 | 109(19.1) | 111(34.0) | ||
| FPG(mmol/L) | 8.350(6.800, 10.200) | 8.700(7.200, 10.800) | -1.967 | 0.049 |
| HbA1c(%) | 8.800(7.400, 10.700) | 9.100(7.800, 10.900) | -1.831 | 0.067 |
| FINS(mU/L) | 10.710(6.900, 15.900) | 11.900(7.500, 16.300) | -1.834 | 0.067 |
| SCr(μmol/L) | 57.000(48.000, 65.200) | 59.000(49.200, 72.000) | -2.675 | 0.007 |
| UA(μmol/L) | 278.980(231.000, 330.000) | 298.255(247.800, 361.900) | -3.853 | 0.000 |
| ALT(U/L) | 20.520(14.600, 30.300) | 18.645(13.400, 29.700) | -1.624 | 0.104 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 4.880(4.300, 5.600) | 4.885(4.200, 5.600) | -0.141 | 0.888 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 1.490(1.100, 2.200) | 1.775(1.200, 2.500) | -3.565 | 0.000 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.190(1.000, 1.300) | 1.145(1.000, 1.300) | -1.686 | 0.092 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 3.050(2.500, 3.600) | 3.000(2.500, 3.600) | -0.971 | 0.331 |
| eGFR[ml/(min×1.73 m2)] | 121.320(104.900, 140.400) | 116.520(97.100, 138.300) | -2.863 | 0.004 |
| UACR(mg/mmol) | 1.015(0.500, 1.900) | 3.985(1.300, 8.100) | -12.325 | 0.000 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 25.447(23.700, 28.300) | 25.837(23.600, 28.300) | -1.030 | 0.303 |
| WC(cm) | 90.000(84.100, 97.000) | 91.000(85.000, 99.000) | -2.163 | 0.031 |
| TyG指数 | 7.618(7.300, 8.100) | 7.837(7.400, 8.300) | -4.122 | 0.000 |
| TyG-WC | 688.945(629.800, 754.600) | 721.013(643.700, 788.600) | -3.723 | 0.000 |
| TyG-BMI | 197.301(178.200, 219.700) | 204.966(182.100, 229.200) | -2.368 | 0.018 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.919(2.500, 6.200) | 4.697(2.700, 6.900) | -2.424 | 0.015 |
Tab. 1 Clinical data and alternative indicators of IR between the two groups
| 项目 | 非DKD组(n=569) | DKD组(n=326) | t/Z/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 61(56, 66) | 62(55, 67) | -0.172 | 0.864 |
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 266(46.8) 303(53.2) | 178(54.6) 148(45.4) | 5.122 | 0.024 |
| 糖尿病病程(年) | 5(1, 10) | 8(1, 13) | -3.359 | 0.001 |
| 规律运动[例(%)] | 420(73.81) | 240(73.62) | 0.004 | 0.949 |
| 糖尿病饮食管理[例(%)] | 344(60.46) | 195(59.82) | 0.036 | 0.850 |
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 130(120, 140) | 132(127, 140) | -3.147 | 0.002 |
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 80(74, 8) | 80(73, 8) | -0.289 | 0.773 |
| 目前吸烟[例(%)] | 214(37.6) | 152(46.6) | 6.970 | 0.008 |
| 目前饮酒[例(%)] | 174(30.6) | 107(32.8) | 0.484 | 0.487 |
| 合并高血压病[例(%)] | 352(61.9) | 227(69.6) | 5.477 | 0.019 |
| 使用降压药[例(%)] | 193(60.1) | 468(52.9) | 10.439 | 0.001 |
| 使用降脂药[例(%)] | 53(9.3) | 51(15.6) | 8.085 | 0.004 |
| 糖尿病药物使用[例(%)] | ||||
| 未使用药物 | 195(34.3) | 73(22.4) | ||
| 只用口服降糖药 | 252(44.3) | 135(41.4) | 28.880 | 0.000 |
| 只用胰岛素 | 13(2.3) | 7(2.2) | ||
| 口服药胰岛素联合 | 109(19.1) | 111(34.0) | ||
| FPG(mmol/L) | 8.350(6.800, 10.200) | 8.700(7.200, 10.800) | -1.967 | 0.049 |
| HbA1c(%) | 8.800(7.400, 10.700) | 9.100(7.800, 10.900) | -1.831 | 0.067 |
| FINS(mU/L) | 10.710(6.900, 15.900) | 11.900(7.500, 16.300) | -1.834 | 0.067 |
| SCr(μmol/L) | 57.000(48.000, 65.200) | 59.000(49.200, 72.000) | -2.675 | 0.007 |
| UA(μmol/L) | 278.980(231.000, 330.000) | 298.255(247.800, 361.900) | -3.853 | 0.000 |
| ALT(U/L) | 20.520(14.600, 30.300) | 18.645(13.400, 29.700) | -1.624 | 0.104 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 4.880(4.300, 5.600) | 4.885(4.200, 5.600) | -0.141 | 0.888 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 1.490(1.100, 2.200) | 1.775(1.200, 2.500) | -3.565 | 0.000 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.190(1.000, 1.300) | 1.145(1.000, 1.300) | -1.686 | 0.092 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 3.050(2.500, 3.600) | 3.000(2.500, 3.600) | -0.971 | 0.331 |
| eGFR[ml/(min×1.73 m2)] | 121.320(104.900, 140.400) | 116.520(97.100, 138.300) | -2.863 | 0.004 |
| UACR(mg/mmol) | 1.015(0.500, 1.900) | 3.985(1.300, 8.100) | -12.325 | 0.000 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 25.447(23.700, 28.300) | 25.837(23.600, 28.300) | -1.030 | 0.303 |
| WC(cm) | 90.000(84.100, 97.000) | 91.000(85.000, 99.000) | -2.163 | 0.031 |
| TyG指数 | 7.618(7.300, 8.100) | 7.837(7.400, 8.300) | -4.122 | 0.000 |
| TyG-WC | 688.945(629.800, 754.600) | 721.013(643.700, 788.600) | -3.723 | 0.000 |
| TyG-BMI | 197.301(178.200, 219.700) | 204.966(182.100, 229.200) | -2.368 | 0.018 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.919(2.500, 6.200) | 4.697(2.700, 6.900) | -2.424 | 0.015 |
| 变量 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 0.315 | 0.139 | 5.099 | 0.024 | 1.370 | 1.042~1.800 |
| 年龄 | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.197 | 0.657 | 1.004 | 0.986~1.022 |
| 规律运动 | -0.010 | 0.158 | 0.004 | 0.949 | 0.990 | 0.727~1.349 |
| 糖尿病饮食管理 | 0.027 | 0.142 | 0.036 | 0.850 | 1.027 | 0.778~1.356 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 0.033 | 0.009 | 12.464 | 0.000 | 1.034 | 1.015~1.053 |
| 收缩压 | 0.015 | 0.005 | 8.128 | 0.004 | 1.015 | 1.005~1.026 |
| 舒张压 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.358 | 0.549 | 1.005 | 0.989~1.021 |
| 目前吸烟 | 0.371 | 0.141 | 6.945 | 0.008 | 1.449 | 1.100~1.910 |
| 目前饮酒 | 0.104 | 0.149 | 0.484 | 0.487 | 1.109 | 0.828~1.485 |
| 合并高血压病 | 0.346 | 0.148 | 5.456 | 0.020 | 1.414 | 1.057~1.890 |
| 使用降压药 | 0.457 | 0.142 | 10.382 | 0.001 | 1.579 | 1.196~2.085 |
| 使用降脂药 | 0.591 | 0.210 | 7.926 | 0.005 | 1.806 | 1.197~2.724 |
| 糖尿病药物使用 | 0.327 | 0.062 | 27.770 | 0.000 | 1.387 | 1.228~1.566 |
| FPG | 0.002 | 0.001 | 2.958 | 0.085 | 1.002 | 1.000~1.005 |
| HbA1c | 0.056 | 0.033 | 2.981 | 0.084 | 1.058 | 0.992~1.128 |
| FINS | 0.004 | 0.003 | 1.521 | 0.217 | 1.004 | 0.998~1.010 |
| UA | 0.004 | 0.001 | 17.302 | 0.000 | 1.004 | 1.002~1.005 |
| ALT | -0.005 | 0.004 | 1.491 | 0.222 | 0.995 | 0.987~1.003 |
| TC | 0.045 | 0.056 | 0.664 | 0.415 | 1.046 | 0.938~1.167 |
| TG | 0.006 | 0.002 | 7.697 | 0.006 | 1.006 | 1.002~1.010 |
| HDL-C | -0.495 | 0.247 | 4.001 | 0.045 | 0.610 | 0.375~0.990 |
| LDL-C | -0.050 | 0.080 | 0.391 | 0.532 | 0.951 | 0.813~1.113 |
| BMI | 0.028 | 0.02 | 1.891 | 0.169 | 1.028 | 0.988~1.069 |
| WC | 0.019 | 0.007 | 6.392 | 0.011 | 1.019 | 1.004~1.033 |
| TyG指数 | 0.394 | 0.100 | 15.620 | 0.000 | 1.482 | 1.219~1.802 |
| TyG-WC | 0.027 | 0.007 | 16.052 | 0.000 | 1.027 | 1.014~1.041 |
| TyG-BMI | 0.054 | 0.020 | 7.336 | 0.007 | 1.056 | 1.015~1.098 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.015 | 0.008 | 2.996 | 0.083 | 1.015 | 0.998~1.031 |
Tab.2 Univariate logistic regression analysis of the influencing factors of DKD in T2DM patients
| 变量 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 0.315 | 0.139 | 5.099 | 0.024 | 1.370 | 1.042~1.800 |
| 年龄 | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.197 | 0.657 | 1.004 | 0.986~1.022 |
| 规律运动 | -0.010 | 0.158 | 0.004 | 0.949 | 0.990 | 0.727~1.349 |
| 糖尿病饮食管理 | 0.027 | 0.142 | 0.036 | 0.850 | 1.027 | 0.778~1.356 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 0.033 | 0.009 | 12.464 | 0.000 | 1.034 | 1.015~1.053 |
| 收缩压 | 0.015 | 0.005 | 8.128 | 0.004 | 1.015 | 1.005~1.026 |
| 舒张压 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.358 | 0.549 | 1.005 | 0.989~1.021 |
| 目前吸烟 | 0.371 | 0.141 | 6.945 | 0.008 | 1.449 | 1.100~1.910 |
| 目前饮酒 | 0.104 | 0.149 | 0.484 | 0.487 | 1.109 | 0.828~1.485 |
| 合并高血压病 | 0.346 | 0.148 | 5.456 | 0.020 | 1.414 | 1.057~1.890 |
| 使用降压药 | 0.457 | 0.142 | 10.382 | 0.001 | 1.579 | 1.196~2.085 |
| 使用降脂药 | 0.591 | 0.210 | 7.926 | 0.005 | 1.806 | 1.197~2.724 |
| 糖尿病药物使用 | 0.327 | 0.062 | 27.770 | 0.000 | 1.387 | 1.228~1.566 |
| FPG | 0.002 | 0.001 | 2.958 | 0.085 | 1.002 | 1.000~1.005 |
| HbA1c | 0.056 | 0.033 | 2.981 | 0.084 | 1.058 | 0.992~1.128 |
| FINS | 0.004 | 0.003 | 1.521 | 0.217 | 1.004 | 0.998~1.010 |
| UA | 0.004 | 0.001 | 17.302 | 0.000 | 1.004 | 1.002~1.005 |
| ALT | -0.005 | 0.004 | 1.491 | 0.222 | 0.995 | 0.987~1.003 |
| TC | 0.045 | 0.056 | 0.664 | 0.415 | 1.046 | 0.938~1.167 |
| TG | 0.006 | 0.002 | 7.697 | 0.006 | 1.006 | 1.002~1.010 |
| HDL-C | -0.495 | 0.247 | 4.001 | 0.045 | 0.610 | 0.375~0.990 |
| LDL-C | -0.050 | 0.080 | 0.391 | 0.532 | 0.951 | 0.813~1.113 |
| BMI | 0.028 | 0.02 | 1.891 | 0.169 | 1.028 | 0.988~1.069 |
| WC | 0.019 | 0.007 | 6.392 | 0.011 | 1.019 | 1.004~1.033 |
| TyG指数 | 0.394 | 0.100 | 15.620 | 0.000 | 1.482 | 1.219~1.802 |
| TyG-WC | 0.027 | 0.007 | 16.052 | 0.000 | 1.027 | 1.014~1.041 |
| TyG-BMI | 0.054 | 0.020 | 7.336 | 0.007 | 1.056 | 1.015~1.098 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.015 | 0.008 | 2.996 | 0.083 | 1.015 | 0.998~1.031 |
| 变量 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |||
| TyG指数 | 1.516(1.240~1.854) | 0.000 | 1.534(1.240~1.897) | 0.000 | 1.373(1.090~1.728) | 0.007 | ||
| TyG-WC | 1.027(1.013~1.040) | 0.000 | 1.025(1.010~1.040) | 0.001 | 1.017(1.001~1.032) | 0.036 | ||
| TyG-BMI | 1.064(1.021~1.107) | 0.003 | 1.056(1.011~1.104) | 0.015 | 1.029(0.982~1.078) | 0.238 | ||
| HOMA-IR | 1.016(0.999~1.033) | 0.074 | 1.005(0.989~1.022) | 0.524 | 1.003(0.987~1.020) | 0.696 | ||
Tab.3 Binary logistic regression analysis of IR alternative indicators and DKD
| 变量 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |||
| TyG指数 | 1.516(1.240~1.854) | 0.000 | 1.534(1.240~1.897) | 0.000 | 1.373(1.090~1.728) | 0.007 | ||
| TyG-WC | 1.027(1.013~1.040) | 0.000 | 1.025(1.010~1.040) | 0.001 | 1.017(1.001~1.032) | 0.036 | ||
| TyG-BMI | 1.064(1.021~1.107) | 0.003 | 1.056(1.011~1.104) | 0.015 | 1.029(0.982~1.078) | 0.238 | ||
| HOMA-IR | 1.016(0.999~1.033) | 0.074 | 1.005(0.989~1.022) | 0.524 | 1.003(0.987~1.020) | 0.696 | ||
| 指标 | 例数(范围) | 未校正 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |||||
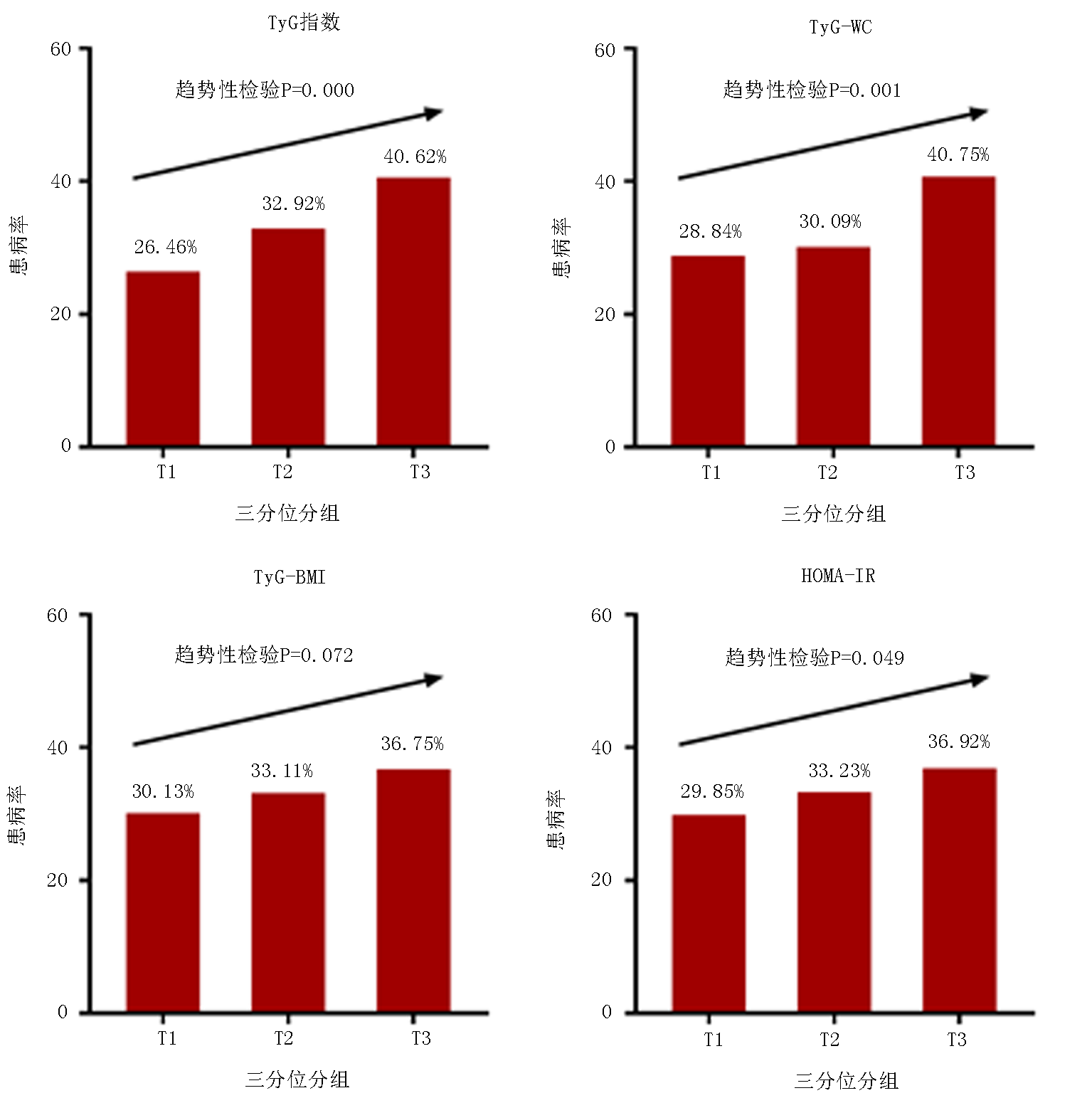
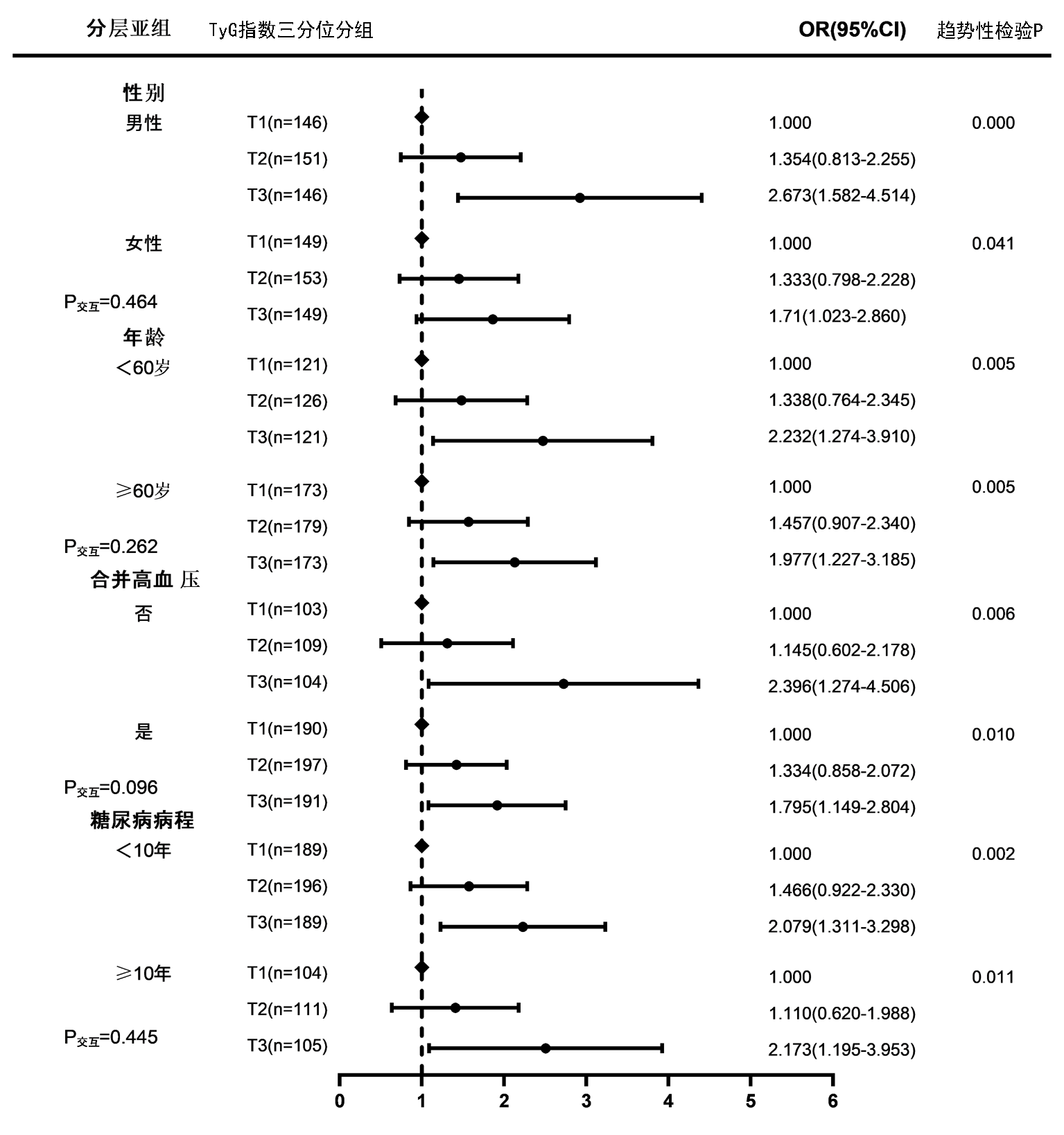
| TyG指数 | ||||||||||||
| T1 | 295(≤7.444) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| T2 | 304(7.444~7.990) | 1.320(0.936~1.862) | 0.114 | 1.365(0.965~1.930) | 0.079 | 1.386(0.966~1.989) | 0.077 | 1.254(0.865~1.819) | 0.232 | |||
| T3 | 295(≥7.990) | 1.968(1.401~2.765) | 0.000 | 2.079(1.468~2.945) | 0.000 | 2.117(1.472~3.047) | 0.000 | 1.763(1.195~2.600) | 0.004 | |||
| 趋势性检验P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | ||||||||
| TyG-WC | ||||||||||||
| T1 | 287(≤657.709) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| T2 | 297(657.709~744.502) | 1.012(0.715~1.433) | 0.945 | 0.986(0.696~1.399) | 0.938 | 0.944(0.654~1.360) | 0.756 | 0.820(0.561~1.197) | 0.304 | |||
| T3 | 287(≥744.502) | 1.780(1.267~2.500) | 0.001 | 1.738(1.233~2.450) | 0.002 | 1.638(1.131~2.372) | 0.009 | 1.291(0.872~1.911) | 0.202 | |||
| 趋势性检验P | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.009 | 0.169 | ||||||||
| TyG-BMI | ||||||||||||
| T1 | 261(≤186.559) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| T2 | 268(186.559~214.183) | 1.112(0.780~1.586) | 0.558 | 1.135(0.794~1.623) | 0.488 | 1.134(0.780~1.650) | 0.509 | 0.966(0.654~1.426) | 0.860 | |||
| T3 | 261(≥214.183) | 1.382(0.971~1.969) | 0.073 | 1.463(1.019~2.099) | 0.039 | 1.374(0.934~2.020) | 0.107 | 1.094(0.727~1.645) | 0.666 | |||
| 趋势性检验P | 0.072 | 0.039 | 0.106 | 0.652 | ||||||||
| HOMA-IR | ||||||||||||
| T1 | 294(≤3.102) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| T2 | 304(3.102~5.459) | 1.119(0.798~1.569) | 0.514 | 1.150(0.819~1.616) | 0.420 | 1.051(0.738~1.496) | 0.784 | 0.956(0.665~1.374) | 0.808 | |||
| T3 | 294(≥5.459) | 1.401(1.000~1.961) | 0.050 | 1.491(1.060~2.098) | 0.022 | 1.199(0.833~1.725) | 0.329 | 1.029(0.706~1.500) | 0.881 | |||
| 趋势性检验P | 0.072 | 0.022 | 0.328 | 0.875 | ||||||||
Tab.4 Binary logistic regression analysis of the tertiles of IR alternative indicators and DKD
| 指标 | 例数(范围) | 未校正 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | OR(95%CI) | P值 | |||||
| TyG指数 | ||||||||||||
| T1 | 295(≤7.444) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| T2 | 304(7.444~7.990) | 1.320(0.936~1.862) | 0.114 | 1.365(0.965~1.930) | 0.079 | 1.386(0.966~1.989) | 0.077 | 1.254(0.865~1.819) | 0.232 | |||
| T3 | 295(≥7.990) | 1.968(1.401~2.765) | 0.000 | 2.079(1.468~2.945) | 0.000 | 2.117(1.472~3.047) | 0.000 | 1.763(1.195~2.600) | 0.004 | |||
| 趋势性检验P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | ||||||||
| TyG-WC | ||||||||||||
| T1 | 287(≤657.709) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| T2 | 297(657.709~744.502) | 1.012(0.715~1.433) | 0.945 | 0.986(0.696~1.399) | 0.938 | 0.944(0.654~1.360) | 0.756 | 0.820(0.561~1.197) | 0.304 | |||
| T3 | 287(≥744.502) | 1.780(1.267~2.500) | 0.001 | 1.738(1.233~2.450) | 0.002 | 1.638(1.131~2.372) | 0.009 | 1.291(0.872~1.911) | 0.202 | |||
| 趋势性检验P | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.009 | 0.169 | ||||||||
| TyG-BMI | ||||||||||||
| T1 | 261(≤186.559) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| T2 | 268(186.559~214.183) | 1.112(0.780~1.586) | 0.558 | 1.135(0.794~1.623) | 0.488 | 1.134(0.780~1.650) | 0.509 | 0.966(0.654~1.426) | 0.860 | |||
| T3 | 261(≥214.183) | 1.382(0.971~1.969) | 0.073 | 1.463(1.019~2.099) | 0.039 | 1.374(0.934~2.020) | 0.107 | 1.094(0.727~1.645) | 0.666 | |||
| 趋势性检验P | 0.072 | 0.039 | 0.106 | 0.652 | ||||||||
| HOMA-IR | ||||||||||||
| T1 | 294(≤3.102) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| T2 | 304(3.102~5.459) | 1.119(0.798~1.569) | 0.514 | 1.150(0.819~1.616) | 0.420 | 1.051(0.738~1.496) | 0.784 | 0.956(0.665~1.374) | 0.808 | |||
| T3 | 294(≥5.459) | 1.401(1.000~1.961) | 0.050 | 1.491(1.060~2.098) | 0.022 | 1.199(0.833~1.725) | 0.329 | 1.029(0.706~1.500) | 0.881 | |||
| 趋势性检验P | 0.072 | 0.022 | 0.328 | 0.875 | ||||||||
| [1] |
Rabkin R. Diabetic nephropathy[J]. Clin Cornerstone, 2003, 5(2):1-11.
doi: 10.1016/s1098-3597(03)90014-7 pmid: 12800476 |
| [2] | Hsu CC, Chang HY, Huang MC, et al. Association between insulin resistance and development of microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2011, 34(4):982-987. |
| [3] | Rizvi A, Varasteh B, Chen YD, et al. Lack of a relationship between urinary albumin excretion rate and insulin resistance in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus[J]. Metabolism, 1996, 45(9):1062-1064. |
| [4] |
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, et al. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man[J]. Diabetologia, 1985, 28(7):412-419.
doi: 10.1007/BF00280883 pmid: 3899825 |
| [5] |
Hong S, Han K, Park CY. The insulin resistance by triglyceride glucose index and risk for dementia: Population-based study[J]. Alzheimers Res Ther, 2021, 13(1):9.
doi: 10.1186/s13195-020-00758-4 pmid: 33402193 |
| [6] |
Brahimaj A, Rivadeneira F, Muka T, et al. Novel metabolic indices and incident type 2 diabetes among women and men: The Rotterdam Study[J]. Diabetologia, 2019, 62(9):1581-1590.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4921-2 pmid: 31183505 |
| [7] |
Park B, Lee HS, Lee YJ. Triglyceride glucose (TyG) index as a predictor of incident type 2 diabetes among nonobese adults: A 12-year longitudinal study of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study cohort[J]. Transl Res, 2021, 228:42-51.
doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2020.08.003 pmid: 32827706 |
| [8] |
Simental-Mendía LE, Rodríguez-Morán M, Guerrero-Romero F. The product of fasting glucose and triglycerides as surrogate for identifying insulin resistance in apparently healthy subjects[J]. Metab Syndr Relat Disord, 2008, 6(4):299-304.
doi: 10.1089/met.2008.0034 pmid: 19067533 |
| [9] |
Guerrero-Romero F, Simental-Mendía LE, González-Ortiz M, et al. The product of triglycerides and glucose, a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2010, 95(7):3347-3351.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0288 pmid: 20484475 |
| [10] | Vasques AC, Novaes FS, de Oliveira Mda S, et al. TyG index performs better than HOMA in a Brazilian population: A hyperglycemic clamp validated study[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2011, 93(3):e98-e100. |
| [11] | Er LK, Wu S, Chou HH, et al. Triglyceride glucose-body mass index is a simple and clinically useful surrogate marker for insulin resistance in nondiabetic individuals[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(3):e0149731. |
| [12] | Yang S, Shi X, Liu W, et al. Association between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and heart failure in subjects with diabetes mellitus or prediabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14:1294909. |
| [13] | Peng N, Kuang M, Peng Y, et al. Associations between TyG-BMI and normal-high blood pressure values and hypertension: Cross-sectional evidence from a non-diabetic population[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2023, 10:1129112. |
| [14] |
Dang K, Wang X, Hu J, et al. The association between triglyceride-glucose index and its combination with obesity indicators and cardiovascular disease: NHANES 2003-2018[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2024, 23(1):8.
doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02115-9 pmid: 38184598 |
| [15] | Srinivasan S, Singh P, Kulothungan V, et al. Relationship between triglyceride glucose index, retinopathy and nephropathy in type 2 diabetes[J]. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab, 2020, 4(1):e00151. |
| [16] | Gowda S, Desai PB, Kulkarni SS, et al. Markers of renal function tests[J]. N Am J Med Sci, 2010, 2(4):170-173. |
| [17] | Ji W, Gao L, Sun P, et al. Association of the triglyceride-glucose index and vascular target organ damage in a Beijing community-based population[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9:948402. |
| [18] | Liu L, Xia R, Song X, et al. Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study[J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2021, 12(4):557-565. |
| [19] | Xu X, Tang X, Che H, et al. Triglyceride-glucose product is an independent risk factor for predicting chronic kidney disease in middle-aged and elderly population: A prospective cohort study[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 2021, 41(11):1600-1608. |
| [20] | Shang J, Yu D, Cai Y, et al. The triglyceride glucose index can predict newly diagnosed biopsy-proven diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: A nested case control study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98(46):e17995. |
| [21] | Lim J, Kim J, Koo SH, et al. Comparison of triglyceride glucose index, and related parameters to predict insulin resistance in Korean adults: An analysis of the 2007-2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(3):e0212963. |
| [22] |
Malek M, Khamseh ME, Chehrehgosha H, et al. Triglyceride glucose-waist to height ratio: A novel and effective marker for identifying hepatic steatosis in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Endocrine, 2021, 74(3):538-545.
doi: 10.1007/s12020-021-02815-w pmid: 34355342 |
| [23] | Cho YK, Lee J, Kim HS, et al. Triglyceride glucose-waist circumference better predicts coronary calcium progression compared with other indices of insulin resistance: A longitudinal observational study[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 10(1):92. |
| [24] |
Kuang M, Yang R, Huang X, et al. Assessing temporal differences in the predictive power of baseline TyG-related parameters for future diabetes: An analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21(1):299.
doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04159-7 pmid: 37138277 |
| [25] | Li X, Sun M, Yang Y, et al. Predictive Effect of triglyceride glucose-related parameters, obesity indices, and lipid ratios for diabetes in a Chinese population: A prospective cohort study[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2022, 13:862919. |
| [26] | Jiang Y, Lai X. Association between the triglyceride glucose index, triglyceride-glucose body mass index and diabetic kidney disease in adults with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2024, 11:1328601. |
| [27] |
Da Silva AA, Do Carmo JM, Li X, et al. Role of hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in hypertension: Metabolic syndrome revisited[J]. Can J Cardiol 2020, 36(5): 671-682.
doi: S0828-282X(20)30169-0 pmid: 32389340 |
| [28] | Hill MA, Yang Y, Zhang L, et al. Insulin resistance, cardiovascular stiffening and cardiovascular disease[J]. Metabolism, 2021, 119:154766. |
| [29] | 陈映群, 张卫星, 李智, 等. 高尿酸通过氧化应激诱导心肌细胞胰岛素抵抗[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2022, 57(3): 418-424. |
| [30] |
Zhang Y, Wang R, Fu X, et al. Non-insulin-based insulin resistance indexes in predicting severity for coronary artery disease[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2022, 14(1):191.
doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00967-x pmid: 36528713 |
| [31] | Carreau AM, Xie D, Garcia-Reyes Y, et al. Good agreement between hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp and 2 hours oral minimal model assessed insulin sensitivity in adolescents[J]. Pediatr Diabetes, 2020, 21(7):1159-1168. |
| [32] | Fritz J, Brozek W, Concin H, et al. The triglyceride-glucose index and obesity-related risk of end-stage kidney disease in Austrian adults[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2021, 4(3):e212612. |
| [33] |
Sasson AN, Cherney DZ. Renal hyperfiltration related to diabetes mellitus and obesity in human disease[J]. World J Diabetes, 2012, 3(1):1-6.
doi: 10.4239/wjd.v3.i1.1 pmid: 22253940 |
| [34] | Gupta J, Mitra N, Kanetsky PA, et al. Association between albuminuria, kidney function, and inflammatory biomarker profile in CKD in CRIC[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012; 7(12):1938-1946. |
| [35] |
Marunaka Y. Roles of interstitial fluid pH in diabetes mellitus: Glycolysis and mitochondrial function[J]. World J Diabetes, 2015, 6(1):125-135.
doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.125 pmid: 25685283 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||