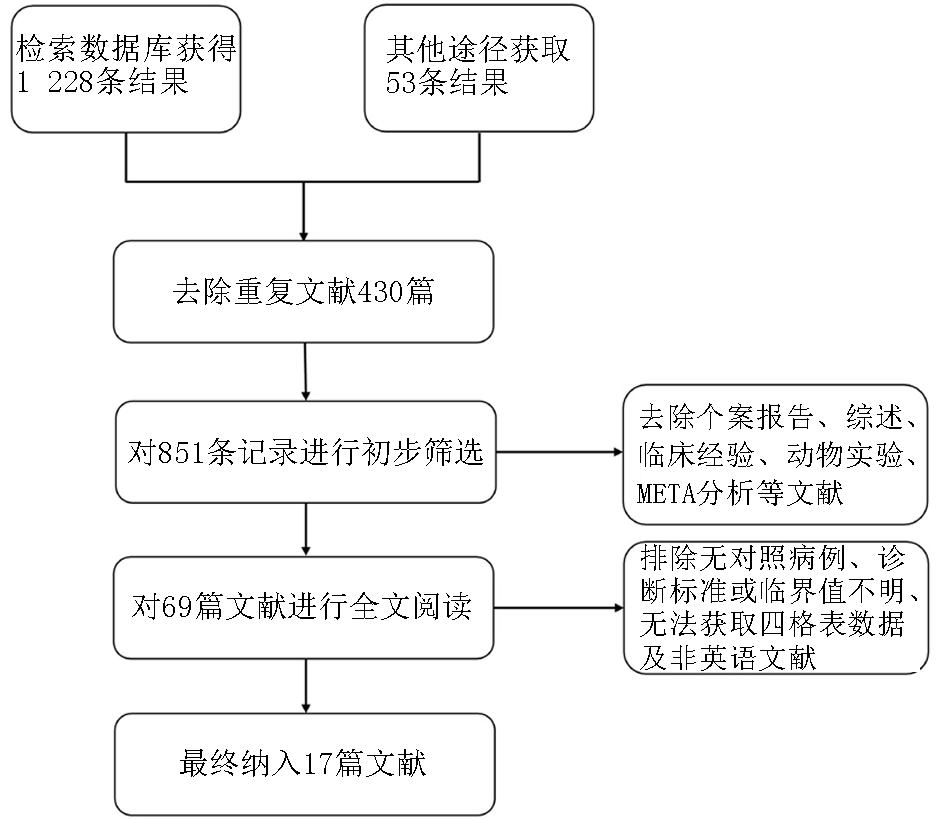
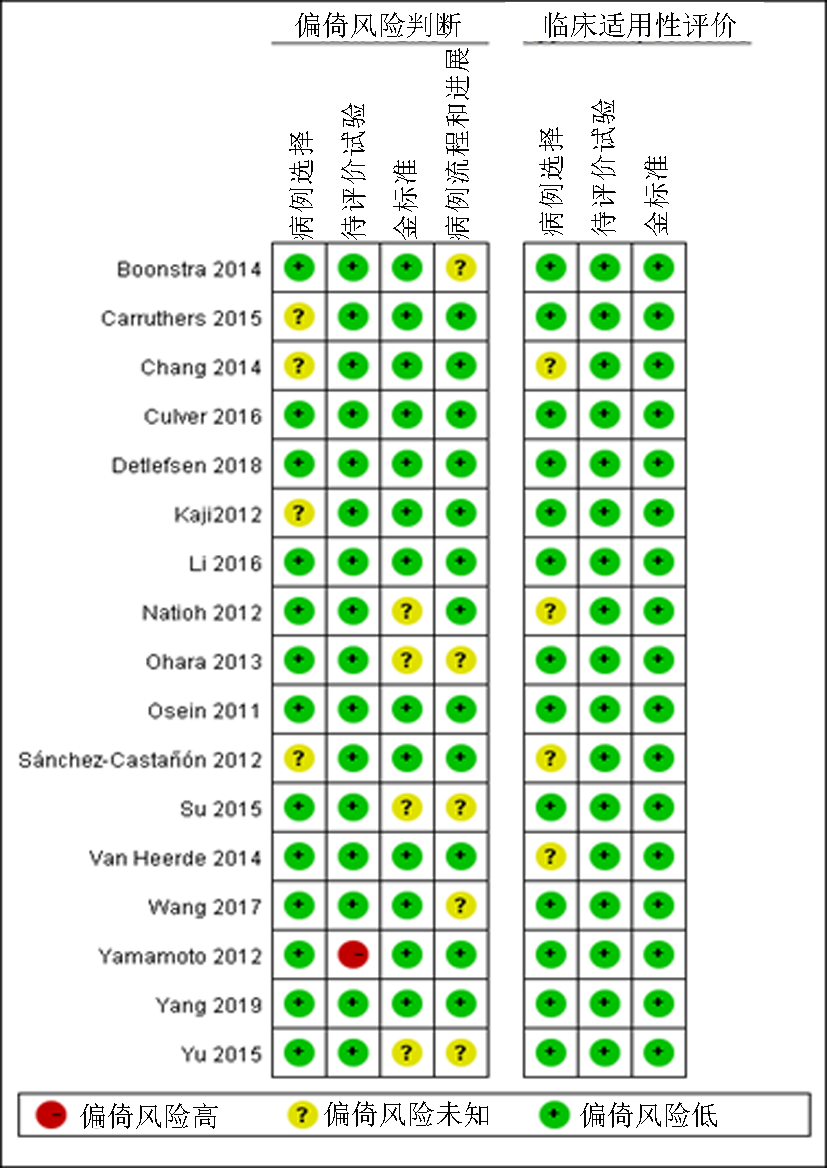
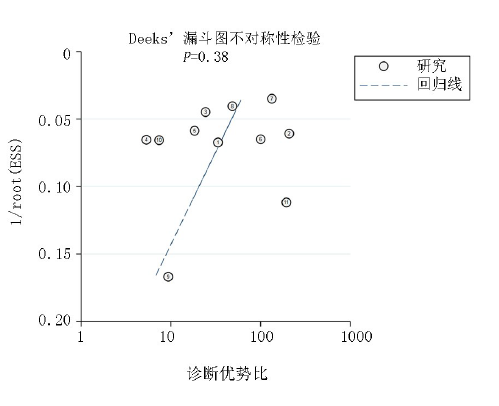
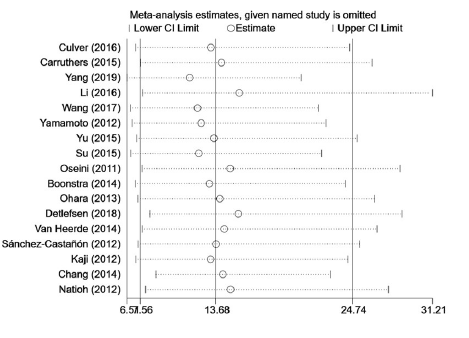
Clinical Focus ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (7): 587-594.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.07.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Diagnostic value of serum IgG4 for IgG4-related diseases: A meta-analysis
Ding Hang, Liu Yuan, Zhang Lianfeng, Zhou Lin( )
)
- Department of Gastroenterology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
-
Received:2020-11-05Online:2021-07-20Published:2021-08-02 -
Contact:Zhou Lin E-mail:zl372@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ding Hang, Liu Yuan, Zhang Lianfeng, Zhou Lin. Diagnostic value of serum IgG4 for IgG4-related diseases: A meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(7): 587-594.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.07.002
| 作者 | 年份 | 国家 | 疾病类型 | IgG4-RD (例) | 对照组主要疾病 | 对照组 (例) | 诊断标准 | IgGA 临界值 (g/L) | 纳入及排除(例) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | FP | FN | TN | |||||||||
| Natioh[ | 2012 | 日本 | AIP | 30 | PC | 19 | JPS2006标准或HISORt 标准 | 1.35 2.8 | 26 23 | 4 1 | 4 7 | 15 59 |
| Wang[ | 2017 | 中国 | IgG4-RD | 25 | AID;PC;AP;CCA;胆道结石;胆道狭窄;十二指肠乳头癌 | 298 | IgG4-RD病理诊断共识 | 1.35 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 298 |
| Su[ | 2015 | 中国 | IgG4-RD | 12 | AID;消化系统疾病;肾脏疾病;感染性疾病;肾脏疾病;心血管及呼吸系统疾病 | 945 | IgG4-RD综合诊断标准 | 1.35 | 12 | 32 | 0 | 913 |
| Yu[ | 2015 | 中国 | IgG4-RD | 161 | AID;恶性肿瘤;胰腺炎;过敏性疾病等 | 2 740 | IgG4-RD综合诊断标准 | 1.35 2.7 | 138 121 | 635 161 | 23 40 | 2 105 2 579 |
| Carruthers[ | 2015 | 美国 | IgG4-RD | 72 | AID;免疫缺陷病;感染性疾病;肺炎;胰胆管疾病;白血病 | 308 | IgG4-RD病理诊断共识 | 1.35 2.7 | 65 25 | 125 28 | 7 47 | 183 280 |
| Sánchez Castañón[ | 2012 | 西班牙 | AIP | 12 | PC | 175 | HISORt标准 | 1.3 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 165 |
| Yang[ | 2019 | 中国 | IgG4-RD | 68 | 风湿性疾病;肾脏疾病;肝胆管及胰腺、胃肠道疾病;造血系统疾病;呼吸系统及心血管疾病;恶性肿瘤 | 8 097 | IgG4-RD综合诊断标准;IgG4-RD病理诊断共识 | 1.4 2.8 | 67 58 | 846 219 | 1 10 | 7 251 7 878 |
| Culver[ | 2016 | 英国 | IgG4-RD | 58 | 恶性肿瘤;PSC;PBC;胰腺炎;肝炎;AIH;AID;IBD | 1 082 | IgG4-RD综合诊断标准;HISORt标准;ICDC | 1.4 2.8 | 48 33 | 166 41 | 10 25 | 916 1041 |
| Li[ | 2016 | 中国 | IgG4-RD | 242 | AID;肾脏疾病;恶性肿瘤;胰腺炎以及健康人群 | 255 | IgG4-RD综合诊断标准 | 1.35 2.7 | 196 150 | 39 16 | 46 92 | 216 239 |
| Ohara[ | 2013 | 日本 | IgG4-SC | 344 | PSC;CCA;PC | 504 | 2012日本IgG4-SC诊断标准;ICDC | 1.35 2.7 | 309 235 | 41 8 | 35 109 | 463 496 |
| Chang[ | 2014 | 中国 | AIP | 162 | PC | 90 | 亚洲标准或ICDC或 HISORt标准 | 1.4 2.8 | 105 49 | 18 5 | 57 113 | 72 85 |
| Boonstra[ | 2014 | 荷兰 | IgG4-SC | 73 | PSC | 310 | HISORt标准 | 1.4 2.8 | 66 51 | 45 7 | 7 22 | 265 303 |
| Kaji[ | 2012 | 日本 | AIP | 35 | PC | 71 | ICDC;亚洲标准 | 1.35 | 32 | 2 | 3 | 69 |
| Van Heerde[ | 2014 | 荷兰 | AIP | 33 | PC | 53 | ICDC或亚洲标准或 HISORt标准 | 1.4 | 28 | 10 | 5 | 43 |
| Oseini[ | 2011 | 美国 | IgG4-SC | 97 | CCA | 287 | HISORt标准 | 1.4 2.8 | 69 41 | 37 11 | 28 56 | 250 276 |
| Detlefsen[ | 2018 | 丹麦 | AIP | 19 | PC | 17 | ICDC | 1.4 2.8 | 11 7 | 2 1 | 8 12 | 15 16 |
| Yamamoto[ | 2012 | 日本 | IgG4-RD | 102 | 风湿性疾病;支气管哮喘;IPF;肝硬化;慢性肝炎;恶性肿瘤;MCD以及健康组 | 299 | HISORt标准 | 1.44 | 97 | 28 | 5 | 271 |
| 作者 | 年份 | 国家 | 疾病类型 | IgG4-RD (例) | 对照组主要疾病 | 对照组 (例) | 诊断标准 | IgGA 临界值 (g/L) | 纳入及排除(例) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | FP | FN | TN | |||||||||
| Natioh[ | 2012 | 日本 | AIP | 30 | PC | 19 | JPS2006标准或HISORt 标准 | 1.35 2.8 | 26 23 | 4 1 | 4 7 | 15 59 |
| Wang[ | 2017 | 中国 | IgG4-RD | 25 | AID;PC;AP;CCA;胆道结石;胆道狭窄;十二指肠乳头癌 | 298 | IgG4-RD病理诊断共识 | 1.35 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 298 |
| Su[ | 2015 | 中国 | IgG4-RD | 12 | AID;消化系统疾病;肾脏疾病;感染性疾病;肾脏疾病;心血管及呼吸系统疾病 | 945 | IgG4-RD综合诊断标准 | 1.35 | 12 | 32 | 0 | 913 |
| Yu[ | 2015 | 中国 | IgG4-RD | 161 | AID;恶性肿瘤;胰腺炎;过敏性疾病等 | 2 740 | IgG4-RD综合诊断标准 | 1.35 2.7 | 138 121 | 635 161 | 23 40 | 2 105 2 579 |
| Carruthers[ | 2015 | 美国 | IgG4-RD | 72 | AID;免疫缺陷病;感染性疾病;肺炎;胰胆管疾病;白血病 | 308 | IgG4-RD病理诊断共识 | 1.35 2.7 | 65 25 | 125 28 | 7 47 | 183 280 |
| Sánchez Castañón[ | 2012 | 西班牙 | AIP | 12 | PC | 175 | HISORt标准 | 1.3 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 165 |
| Yang[ | 2019 | 中国 | IgG4-RD | 68 | 风湿性疾病;肾脏疾病;肝胆管及胰腺、胃肠道疾病;造血系统疾病;呼吸系统及心血管疾病;恶性肿瘤 | 8 097 | IgG4-RD综合诊断标准;IgG4-RD病理诊断共识 | 1.4 2.8 | 67 58 | 846 219 | 1 10 | 7 251 7 878 |
| Culver[ | 2016 | 英国 | IgG4-RD | 58 | 恶性肿瘤;PSC;PBC;胰腺炎;肝炎;AIH;AID;IBD | 1 082 | IgG4-RD综合诊断标准;HISORt标准;ICDC | 1.4 2.8 | 48 33 | 166 41 | 10 25 | 916 1041 |
| Li[ | 2016 | 中国 | IgG4-RD | 242 | AID;肾脏疾病;恶性肿瘤;胰腺炎以及健康人群 | 255 | IgG4-RD综合诊断标准 | 1.35 2.7 | 196 150 | 39 16 | 46 92 | 216 239 |
| Ohara[ | 2013 | 日本 | IgG4-SC | 344 | PSC;CCA;PC | 504 | 2012日本IgG4-SC诊断标准;ICDC | 1.35 2.7 | 309 235 | 41 8 | 35 109 | 463 496 |
| Chang[ | 2014 | 中国 | AIP | 162 | PC | 90 | 亚洲标准或ICDC或 HISORt标准 | 1.4 2.8 | 105 49 | 18 5 | 57 113 | 72 85 |
| Boonstra[ | 2014 | 荷兰 | IgG4-SC | 73 | PSC | 310 | HISORt标准 | 1.4 2.8 | 66 51 | 45 7 | 7 22 | 265 303 |
| Kaji[ | 2012 | 日本 | AIP | 35 | PC | 71 | ICDC;亚洲标准 | 1.35 | 32 | 2 | 3 | 69 |
| Van Heerde[ | 2014 | 荷兰 | AIP | 33 | PC | 53 | ICDC或亚洲标准或 HISORt标准 | 1.4 | 28 | 10 | 5 | 43 |
| Oseini[ | 2011 | 美国 | IgG4-SC | 97 | CCA | 287 | HISORt标准 | 1.4 2.8 | 69 41 | 37 11 | 28 56 | 250 276 |
| Detlefsen[ | 2018 | 丹麦 | AIP | 19 | PC | 17 | ICDC | 1.4 2.8 | 11 7 | 2 1 | 8 12 | 15 16 |
| Yamamoto[ | 2012 | 日本 | IgG4-RD | 102 | 风湿性疾病;支气管哮喘;IPF;肝硬化;慢性肝炎;恶性肿瘤;MCD以及健康组 | 299 | HISORt标准 | 1.44 | 97 | 28 | 5 | 271 |
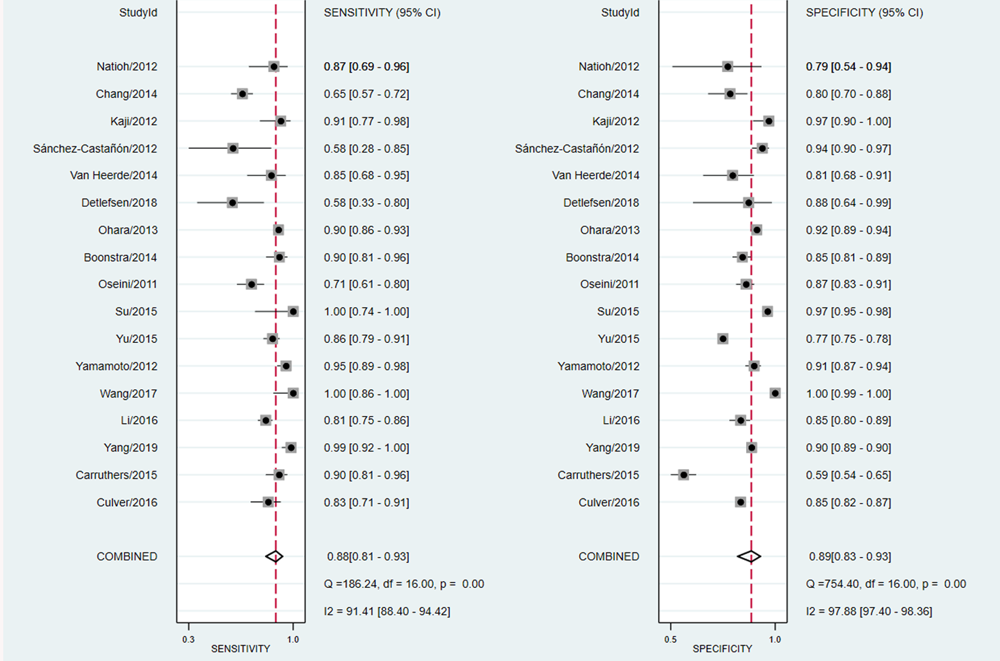
| 分组 | 篇数 | 敏感度(95%CI) | P值 | 特异度(95%CI) | P值 | DOR(95%CI) | AUC(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
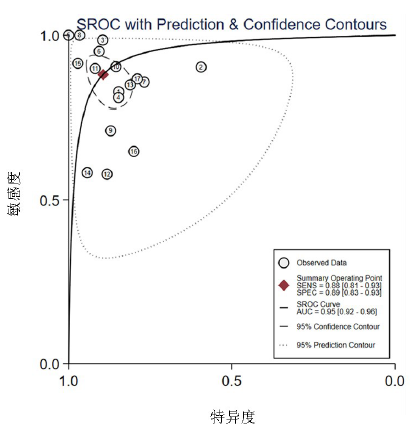
| 总体 | 17 | 0.88(0.81-0.93) | 0.89(0.83-0.93) | 62(25-153) | 0.95(0.92-0.96) | ||
| 地区 | |||||||
| 亚洲 欧美 | 10 7 | 0.93(0.83-0.97) 0.8(0.69-0.87) | <0.05 | 0.92(0.84-0.96) 0.85(0.77-0.91) | <0.05 | 156(30-816) 23(15-34) | 0.97(0.96-0.98) 0.89(0.86-0.92) |
| 疾病谱 | |||||||
| IgG4-RD AIP | 11 6 | 0.92(0.84-0.96) 0.77(0.64-0.86) | <0.05 | 0.90(0.81-0.95) 0.89(0.81-0.94) | 0.09 | 101(26-388) 27(10-75) | 0.96(0.94-0.98) 0.91(0.88-0.93) |
| 样本量(例) | |||||||
| <100 >100 | 5 12 | 0.89(0.79-0.95) 0.85(0.75-0.92) | 0.05 | 0.91(0.83-0.96) 0.86(0.79-0.9) | <0.05 | 85(24-304) 34(12-95) | 0.96(0.94-0.97) 0.92(0.89-0.94) |
| 分组 | 篇数 | 敏感度(95%CI) | P值 | 特异度(95%CI) | P值 | DOR(95%CI) | AUC(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体 | 17 | 0.88(0.81-0.93) | 0.89(0.83-0.93) | 62(25-153) | 0.95(0.92-0.96) | ||
| 地区 | |||||||
| 亚洲 欧美 | 10 7 | 0.93(0.83-0.97) 0.8(0.69-0.87) | <0.05 | 0.92(0.84-0.96) 0.85(0.77-0.91) | <0.05 | 156(30-816) 23(15-34) | 0.97(0.96-0.98) 0.89(0.86-0.92) |
| 疾病谱 | |||||||
| IgG4-RD AIP | 11 6 | 0.92(0.84-0.96) 0.77(0.64-0.86) | <0.05 | 0.90(0.81-0.95) 0.89(0.81-0.94) | 0.09 | 101(26-388) 27(10-75) | 0.96(0.94-0.98) 0.91(0.88-0.93) |
| 样本量(例) | |||||||
| <100 >100 | 5 12 | 0.89(0.79-0.95) 0.85(0.75-0.92) | 0.05 | 0.91(0.83-0.96) 0.86(0.79-0.9) | <0.05 | 85(24-304) 34(12-95) | 0.96(0.94-0.97) 0.92(0.89-0.94) |
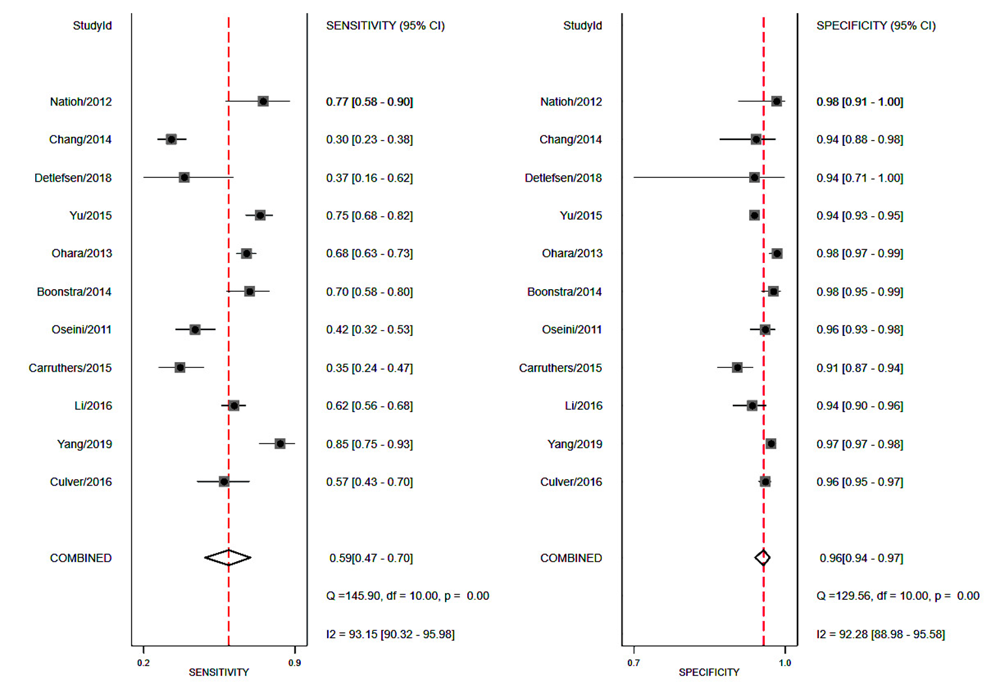
| 分组 | 篇数 | 敏感度(95%CI) | P值 | 特异度(95%CI) | P值 | DOR(95%CI) | AUC(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
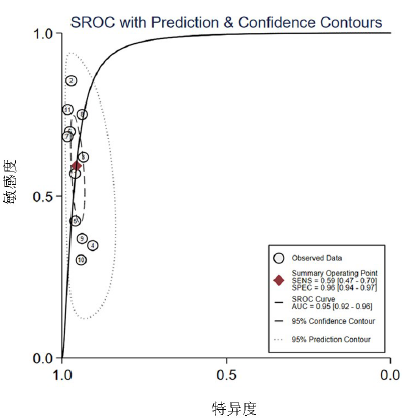
| 总体 | 11 | 0.59(0.47-0.7) | 0.96(0.94-0.97) | 34(17-69) | 0.95(0.92-0.96) | ||
| 地区 | |||||||
| 亚洲 欧美 | 6 5 | 0.67(0.52-0.80) 0.49(0.36-0.61) | 0.1 | 0.96(0.94-0.98) 0.95(0.93-0.97) | <0.05 | 53(21-135) 20(8-51) | 0.96(0.94-0.97) 0.89(0.86-0.92) |
| 样本量(例) | |||||||
| <100 >100 | 7 4 | 0.59(0.43-0.73) 0.6(0.42-0.75) | 0.72 | 0.96(0.94-0.97) 0.96(0.92-0.98) | <0.05 | 33(13-83) 32(12-87) | 0.95(0.93-0.97) 0.94(0.91-0.96) |
| 分组 | 篇数 | 敏感度(95%CI) | P值 | 特异度(95%CI) | P值 | DOR(95%CI) | AUC(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体 | 11 | 0.59(0.47-0.7) | 0.96(0.94-0.97) | 34(17-69) | 0.95(0.92-0.96) | ||
| 地区 | |||||||
| 亚洲 欧美 | 6 5 | 0.67(0.52-0.80) 0.49(0.36-0.61) | 0.1 | 0.96(0.94-0.98) 0.95(0.93-0.97) | <0.05 | 53(21-135) 20(8-51) | 0.96(0.94-0.97) 0.89(0.86-0.92) |
| 样本量(例) | |||||||
| <100 >100 | 7 4 | 0.59(0.43-0.73) 0.6(0.42-0.75) | 0.72 | 0.96(0.94-0.97) 0.96(0.92-0.98) | <0.05 | 33(13-83) 32(12-87) | 0.95(0.93-0.97) 0.94(0.91-0.96) |
| [1] |
Takahashi H, Yamamoto M, Suzuki C, et al. The birthday of a new syndrome: IgG4-related diseases constitute a clinical entity[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2010,9(9):591-594.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.05.003 pmid: 20457280 |
| [2] |
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Nakamura T, et al. Current approach to the diagnosis of IgG4-related disease-Combination of comprehensive diagnostic and organ-specific criteria[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2017,27(3):381-391.
doi: 10.1080/14397595.2017.1290911 URL |
| [3] |
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2001,344(10):732-738.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM200103083441005 URL |
| [4] |
Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Mattoo H, et al. IgG4-related disease: Clinical and laboratory features in one hundred twenty-five patients[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2015,67(9):2466-2475.
doi: 10.1002/art.39205 URL |
| [5] |
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2011,155(8):529-536.
doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009 pmid: 22007046 |
| [6] |
Naitoh I, Nakazawa T, Hayashi K, et al. Clinical differences between mass-forming autoimmune pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2012,47(5):607-613.
doi: 10.3109/00365521.2012.667147 URL |
| [7] |
Wang L, Chu X, Ma Y, et al. A Comparative analysis of serum IgG4 levels in patients with IgG4-related disease and other disorders[J]. Am J Med Sci, 2017,354(3):252-256.
doi: S0002-9629(17)30278-1 pmid: 28918831 |
| [8] |
Su Y, Sun W, Wang C, et al. Detection of serum IgG4 levels in patients with IgG4-related disease and other disorders[J]. PLoS One, 2015,10(4):e0124233.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124233 URL |
| [9] |
Yu KH, Chan TM, Tsai PH, et al. Diagnostic performance of serum IgG4 levels in patients with IgG4-related disease[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2015,94(41):e1707.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001707 URL |
| [10] |
Carruthers MN, Khosroshahi A, Augustin T, et al. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2015,74(1):14-18.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204907 pmid: 24651618 |
| [11] | Sanchez-Castanon M, de Las Heras-Castano G, Gomez C, et al. Differentiation of autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreas cancer: Utility of anti-amylase and anti-carbonic anhydrase II autoantibodies[J]. Auto Immun Highlights, 2012,3(1):11-17. |
| [12] |
Yang H, Li J, Wang Y, et al. Distribution characteristics of elevated serum immunoglobulin G4(IgG4) and its relationship with IgG4-related disease[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2019,48(6):497-504.
doi: 10.1080/03009742.2019.1602882 pmid: 31354076 |
| [13] |
Culver EL, Sadler R, Simpson D, et al. Elevated serum IgG4 levels in diagnosis, treatment response, organ involvement, and relapse in a prospective IgG4-related disease UK cohort[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2016,111(5):733-743.
doi: 10.1038/ajg.2016.40 pmid: 27091321 |
| [14] |
Li P, Chen H, Deng C, et al. Establishment of a serum IgG4 cut-off value for the differential diagnosis of IgG4-related disease in Chinese population[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2016,26(4):583-587.
doi: 10.3109/14397595.2015.1117171 URL |
| [15] |
Ohara H, Nakazawa T, Kawa S, et al. Establishment of a serum IgG4 cut-off value for the differential diagnosis of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis: A Japanese cohort[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013,28(7):1247-1251.
doi: 10.1111/jgh.12248 URL |
| [16] |
Chang MC, Liang PC, Jan S, et al. Increase diagnostic accuracy in differentiating focal type autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer with combined serum IgG4 and CA19-9 levels[J]. Pancreatology, 2014,14(5):366-372.
doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2014.07.010 URL |
| [17] |
Boonstra K, Culver EL, de Buy Wenniger LM, et al. Serum immunoglobulin G4 and immunoglobulin G1 for distinguishing immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis from primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Hepatology, 2014,59(5):1954-1963.
doi: 10.1002/hep.26977 pmid: 24375491 |
| [18] |
Kaji R, Takedatsu H, Okabe Y, et al. Serum immunoglobulin G4 associated with number and distribution of extrapancreatic lesions in type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis patients[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012,27(2):268-272.
doi: 10.1111/jgh.2012.27.issue-2 URL |
| [19] | van Heerde MJ, Buijs J, Hansen BE, et al. Serum level of Ca 19-9 increases ability of IgG4 test to distinguish patients with autoimmune pancreatitis from those with pancreatic carcinoma[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2014,59(6):1322-1329. |
| [20] |
Oseini AM, Chaiteerakij R, Shire AM, et al. Utility of serum immunoglobulin G4 in distinguishing immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis from cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2011 54(3):940-948.
doi: 10.1002/hep.24487 pmid: 21674559 |
| [21] |
Detlefsen S, de Vos JD, Tanassi JT, et al. Value of anti-plasminogen binding peptide, anti-carbonic anhydrase II, immunoglobulin G4, and other serological markers for the differentiation of autoimmune pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2018,97(31):e11641.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011641 URL |
| [22] |
Yamamoto M, Tabeya T, Naishiro Y, et al. Value of serum IgG4 in the diagnosis of IgG4-related disease and in differentiation from rheumatic diseases and other diseases[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2012,22(3):419-425.
doi: 10.3109/s10165-011-0532-6 URL |
| [23] |
Bledsoe JR, Della-Torre E, Rovati L, et al. IgG4-related disease: review of the histopathologic features, differential diagnosis, and therapeutic approach[J]. APMIS, 2018,126(6):459-476.
doi: 10.1111/apm.12845 pmid: 29924455 |
| [24] |
Varghese JL, Fung AWS, Mattman A, et al. Clinical utility of serum IgG4 measurement[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2020,506:228-235.
doi: S0009-8981(20)30147-9 pmid: 32272158 |
| [25] | 蒋晓涵, 胡乃中, 陈丽红. 免疫球蛋白G4鉴别诊断自身免疫性胰腺炎与胰腺癌价值的荟萃分析[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2016,16(2):119-123. |
| [26] | 乔敏, 董丽娜, 王俊平. 血清IgG4在鉴别自身免疫性胰腺炎与胰腺癌中应用价值的Meta分析[J]. 中国临床实用医学, 2017,11(5):30-34, 39. |
| [27] | Wallace ZS, Naden RP, Chari S, et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020,79(1):77-87. |
| [28] |
Shimosegawa T, Chari ST, Frulloni L, et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: Guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology[J]. Pancreas, 2011,40(3):352-358.
doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182142fd2 URL |
| [29] |
Yamada K, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. New clues to the nature of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: A retrospective Japanese multicenter study of baseline clinical features of 334 cases[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2017,19(1):262.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1467-x URL |
| [30] |
Harkness T, Fu X, Zhang Y, et al. Immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin G subclass concentrations differ according to sex and race[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2020,125(2):190-195.
doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.03.018 URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||