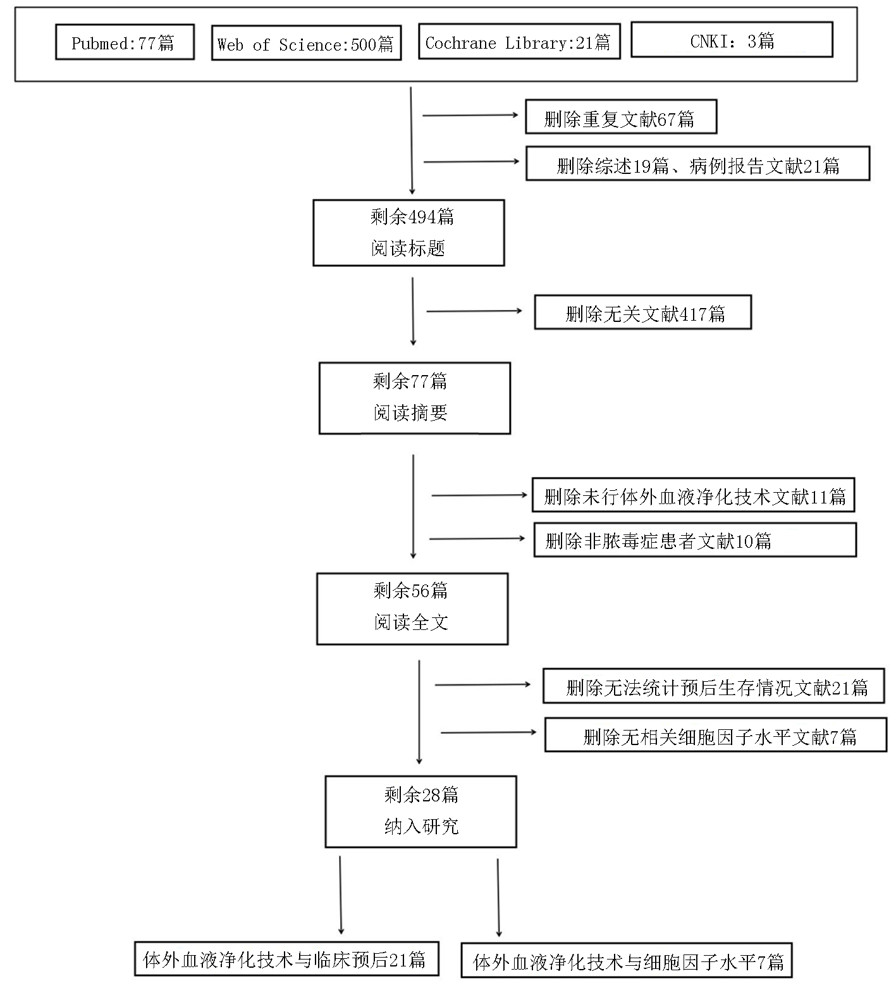
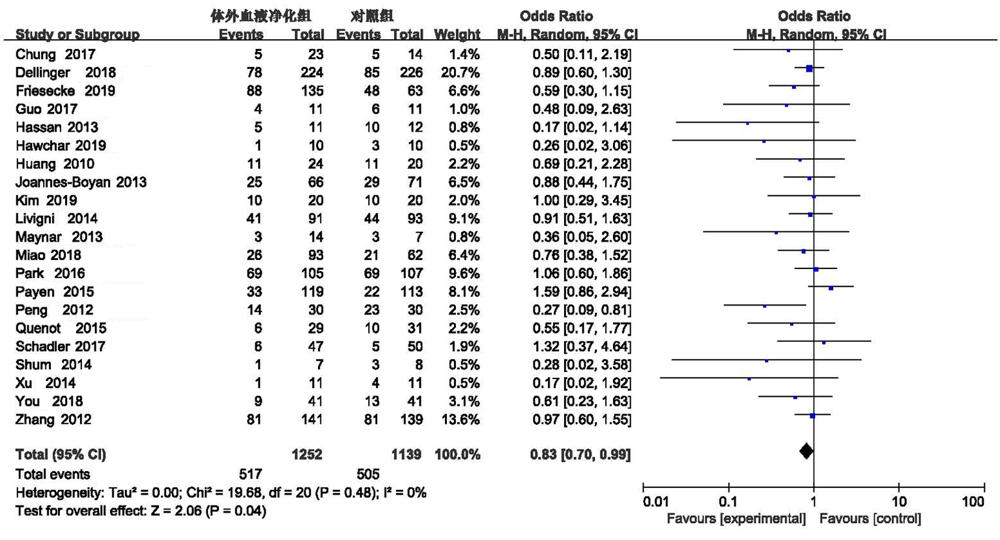
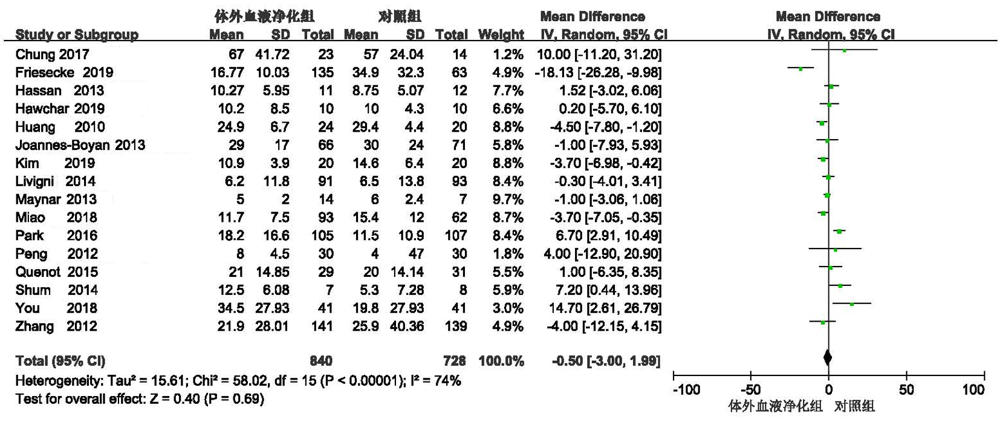
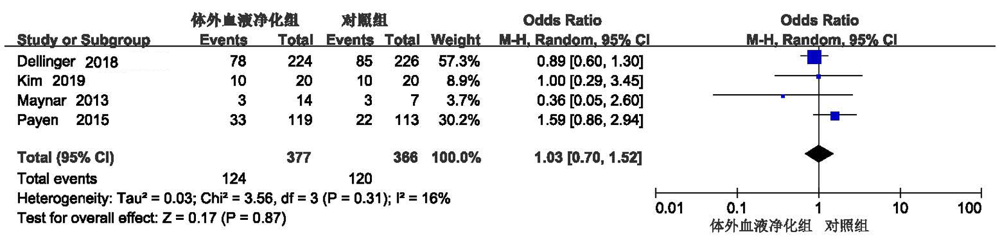
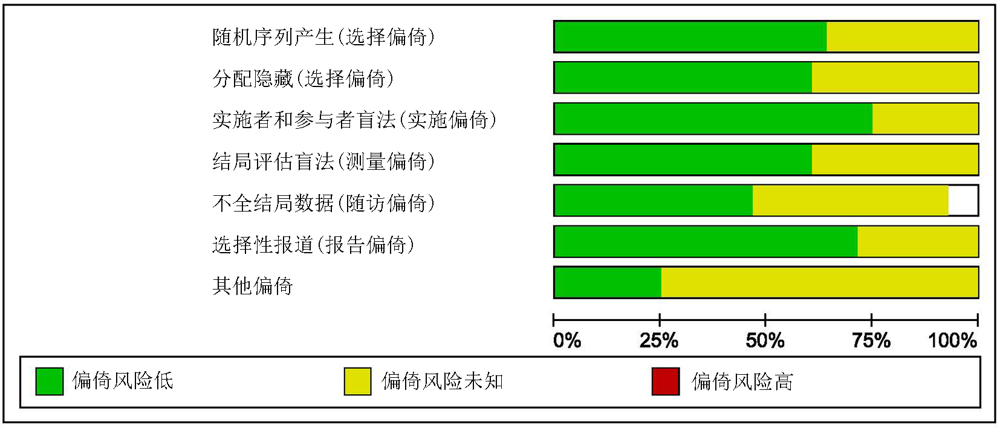
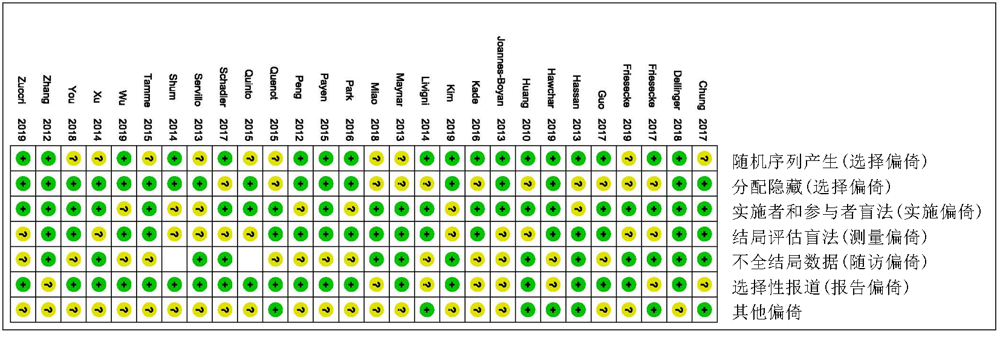
Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 5-13.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.01.001
Effect of extracorporeal hemopurification for clinical prognosis and cytokine levels of septic: A meta-analysis
Xiao Liuniu, Zhong Yanxia, Li Shusheng( )
)
- Department of Intensive Care Unit, Tongji Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College of HUST, Wuhan 430014, China
-
Received:2020-12-05Online:2022-01-20Published:2022-01-20 -
Contact:Li Shusheng E-mail:shushengli16@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xiao Liuniu, Zhong Yanxia, Li Shusheng. Effect of extracorporeal hemopurification for clinical prognosis and cytokine levels of septic: A meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(1): 5-13.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.01.001
| 纳入研究 | 患者 数量 | 平均 年龄(岁) | 性别 | 体外血液净化技术 | 治疗方法(例) | 死亡(例) | 炎症因子下降(例) | ICU住院时间(d) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 血液净化 | 传统治疗 | 血液净化 | 传统治疗 | 血液净化 | 传统治疗 | 血液净化 | 传统治疗 | ||||||||
| Hassan[ | 23 | 61.64 | 16 | 7 | 偶联血浆滤过吸附 | 11 | 12 | 5 | 10 | - | - | 10.27 | 8.75 | ||||
| Maynar[ | 21 | 74.35 | 9 | 12 | 多黏菌素B血液灌注 | 14 | 7 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 5 | 6 | ||||
| Quenot[ | 60 | 66.6 | 42 | 18 | 高容量血液滤过 | 29 | 31 | 6 | 10 | - | - | 21 | 20 | ||||
| Quinto[ | 64 | 63.2 | 43 | 21 | 血液滤过 | 64 | 10 | 54 | 3 | 33 | - | - | |||||
| Schädler[ | 97 | 65.5 | 70 | 27 | 血液吸附 | 47 | 50 | 6 | 5 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| Guo[ | 22 | 54.3 | 15 | 7 | 高容量血液滤过 | 11 | 11 | 4 | 6 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| Huang[ | 44 | 74.8 | 24 | 20 | 血液灌注 | 24 | 20 | 11 | 11 | - | - | 27.9 | 29.4 | ||||
| Kim[ | 40 | 67.25 | 24 | 16 | 多黏菌素B血液灌注 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 10 | - | - | 10.9 | 14.6 | ||||
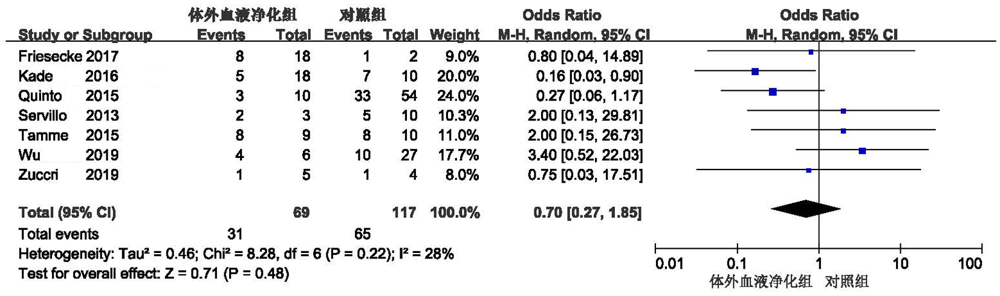
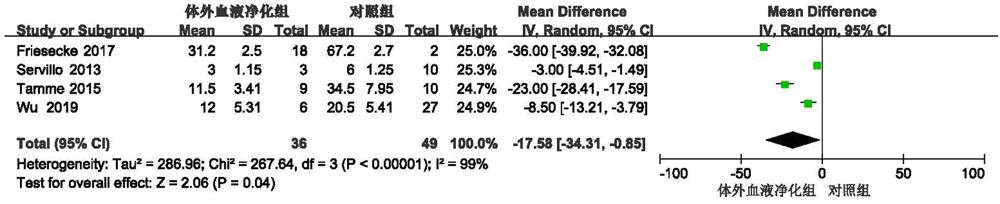
| Friesecke[ | 20 | 60.3 | 16 | 4 | 细胞因子吸附 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 31.2 | 67.2 | |||||
| Servillo[ | 13 | 58.07 | 7 | 6 | 血液滤过 | 13 | 3 | 10 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 4 | |||||
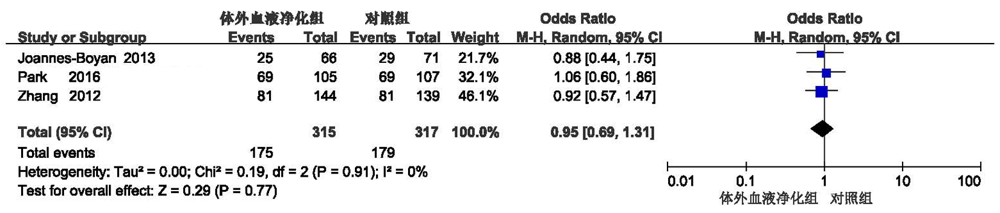
| Joannes-Boyau[ | 137 | 69 | 83 | 54 | 高容量血液滤过 | 66 | 71 | 25 | 29 | - | - | 29 | 30 | ||||
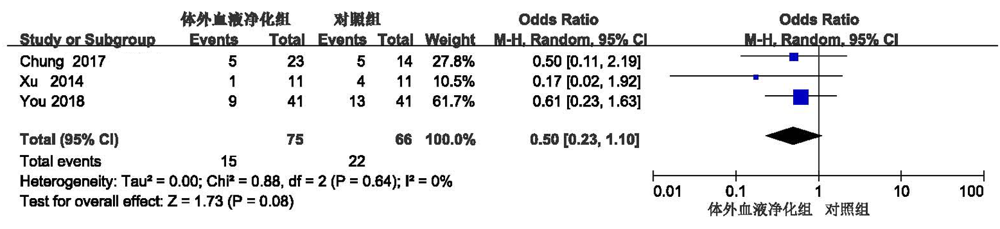
| Chung[ | 37 | 48.5 | 26 | 11 | 高容量血液滤过 | 23 | 14 | 5 | 5 | - | - | 67 | 57 | ||||
| Park[ | 212 | 62.1 | 138 | 74 | 高容量血液滤过 | 105 | 107 | 69 | 69 | - | - | 18.2 | 11.5 | ||||
| Friesecke[ | 198 | 60.12 | - | - | 细胞因子吸附 | 135 | 63 | 88 | 48 | - | - | 16.77 | 34.9 | ||||
| Hawchar[ | 20 | 65.6 | 13 | 7 | 细胞因子吸附 | 10 | 10 | 1 | 3 | - | - | 10.2 | 10.0 | ||||
| Xu[ | 22 | 31.25 | 19 | 3 | 血液透析 | 11 | 11 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 8 | - | - | ||||
| Livigni[ | 184 | 65.25 | 121 | 63 | 偶联血浆滤过吸附 | 91 | 93 | 41 | 44 | - | - | 6.2 | 6.5 | ||||
| Tamme[ | 19 | 65 | 12 | 7 | 高容量血液滤过 | 19 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 11.5 | 34.5 | |||||
| Wu[ | 43 | 46.5 | 31 | 12 | 血液滤过 | 43 | 6 | 27 | 4 | 10 | 12.0 | 20.5 | |||||
| Kade[ | 28 | 60.29 | - | - | 高容量血液滤过 | 28 | 18 | 10 | 5 | 7 | - | - | |||||
| Zhang[ | 280 | 58.29 | 172 | 108 | 高容量血液滤过 | 141 | 139 | 81 | 81 | - | 21.9 | 25.9 | |||||
| Dellinger[ | 450 | 59.85 | 273 | 177 | 多黏菌素B血液灌注 | 224 | 226 | 78 | 85 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| Payen[ | 232 | 71.75 | 134 | 98 | 多黏菌素B血液灌注 | 119 | 113 | 33 | 22 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| You[ | 82 | 40.95 | 65 | 17 | 高容量血液滤过 | 41 | 41 | 9 | 13 | - | - | 34.5 | 28.5 | ||||
| Miao[ | 155 | 56 | 110 | 45 | 高容量血液滤过 | 93 | 62 | 26 | 21 | - | - | 11.7 | 15.4 | ||||
| Zuccrai[ | 9 | - | 5 | 4 | 细胞因子吸附 | 9 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 | - | - | |||||
| Shum[ | 15 | 74.25 | - | - | 血液吸附 | 7 | 8 | 1 | 3 | - | - | 12.5 | 5.3 | ||||
| Peng[ | 60 | - | - | - | 血液灌注 | 30 | 30 | 14 | 23 | 20 | 10 | 8 | 4 | ||||
| 纳入研究 | 患者 数量 | 平均 年龄(岁) | 性别 | 体外血液净化技术 | 治疗方法(例) | 死亡(例) | 炎症因子下降(例) | ICU住院时间(d) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 血液净化 | 传统治疗 | 血液净化 | 传统治疗 | 血液净化 | 传统治疗 | 血液净化 | 传统治疗 | ||||||||
| Hassan[ | 23 | 61.64 | 16 | 7 | 偶联血浆滤过吸附 | 11 | 12 | 5 | 10 | - | - | 10.27 | 8.75 | ||||
| Maynar[ | 21 | 74.35 | 9 | 12 | 多黏菌素B血液灌注 | 14 | 7 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 5 | 6 | ||||
| Quenot[ | 60 | 66.6 | 42 | 18 | 高容量血液滤过 | 29 | 31 | 6 | 10 | - | - | 21 | 20 | ||||
| Quinto[ | 64 | 63.2 | 43 | 21 | 血液滤过 | 64 | 10 | 54 | 3 | 33 | - | - | |||||
| Schädler[ | 97 | 65.5 | 70 | 27 | 血液吸附 | 47 | 50 | 6 | 5 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| Guo[ | 22 | 54.3 | 15 | 7 | 高容量血液滤过 | 11 | 11 | 4 | 6 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| Huang[ | 44 | 74.8 | 24 | 20 | 血液灌注 | 24 | 20 | 11 | 11 | - | - | 27.9 | 29.4 | ||||
| Kim[ | 40 | 67.25 | 24 | 16 | 多黏菌素B血液灌注 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 10 | - | - | 10.9 | 14.6 | ||||
| Friesecke[ | 20 | 60.3 | 16 | 4 | 细胞因子吸附 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 31.2 | 67.2 | |||||
| Servillo[ | 13 | 58.07 | 7 | 6 | 血液滤过 | 13 | 3 | 10 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 4 | |||||
| Joannes-Boyau[ | 137 | 69 | 83 | 54 | 高容量血液滤过 | 66 | 71 | 25 | 29 | - | - | 29 | 30 | ||||
| Chung[ | 37 | 48.5 | 26 | 11 | 高容量血液滤过 | 23 | 14 | 5 | 5 | - | - | 67 | 57 | ||||
| Park[ | 212 | 62.1 | 138 | 74 | 高容量血液滤过 | 105 | 107 | 69 | 69 | - | - | 18.2 | 11.5 | ||||
| Friesecke[ | 198 | 60.12 | - | - | 细胞因子吸附 | 135 | 63 | 88 | 48 | - | - | 16.77 | 34.9 | ||||
| Hawchar[ | 20 | 65.6 | 13 | 7 | 细胞因子吸附 | 10 | 10 | 1 | 3 | - | - | 10.2 | 10.0 | ||||
| Xu[ | 22 | 31.25 | 19 | 3 | 血液透析 | 11 | 11 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 8 | - | - | ||||
| Livigni[ | 184 | 65.25 | 121 | 63 | 偶联血浆滤过吸附 | 91 | 93 | 41 | 44 | - | - | 6.2 | 6.5 | ||||
| Tamme[ | 19 | 65 | 12 | 7 | 高容量血液滤过 | 19 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 11.5 | 34.5 | |||||
| Wu[ | 43 | 46.5 | 31 | 12 | 血液滤过 | 43 | 6 | 27 | 4 | 10 | 12.0 | 20.5 | |||||
| Kade[ | 28 | 60.29 | - | - | 高容量血液滤过 | 28 | 18 | 10 | 5 | 7 | - | - | |||||
| Zhang[ | 280 | 58.29 | 172 | 108 | 高容量血液滤过 | 141 | 139 | 81 | 81 | - | 21.9 | 25.9 | |||||
| Dellinger[ | 450 | 59.85 | 273 | 177 | 多黏菌素B血液灌注 | 224 | 226 | 78 | 85 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| Payen[ | 232 | 71.75 | 134 | 98 | 多黏菌素B血液灌注 | 119 | 113 | 33 | 22 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| You[ | 82 | 40.95 | 65 | 17 | 高容量血液滤过 | 41 | 41 | 9 | 13 | - | - | 34.5 | 28.5 | ||||
| Miao[ | 155 | 56 | 110 | 45 | 高容量血液滤过 | 93 | 62 | 26 | 21 | - | - | 11.7 | 15.4 | ||||
| Zuccrai[ | 9 | - | 5 | 4 | 细胞因子吸附 | 9 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 | - | - | |||||
| Shum[ | 15 | 74.25 | - | - | 血液吸附 | 7 | 8 | 1 | 3 | - | - | 12.5 | 5.3 | ||||
| Peng[ | 60 | - | - | - | 血液灌注 | 30 | 30 | 14 | 23 | 20 | 10 | 8 | 4 | ||||
| [1] |
Rimmele T, Kellum JA. Clinical review: Blood purification for sepsis[J]. Critical Care, 2011, 15(1):205.
doi: 10.1186/cc9411 URL |
| [2] |
Putzu A, Schorer R, Lopez-Delgado JC, et al. Blood purification and mortality in sepsis and septic shock[J]. Anesthesiology, 2019, 131(3):580-593.
doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002820 URL |
| [3] |
Zhou F, Peng Z, Murugan R, et al. Blood purification and mortality in sepsis[J]. Crit Care Med, 2013, 41(9):2209-2220.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31828cf412 URL |
| [4] | Steltzer H, Grieb A, Mostafa K, et al. Use of Cytosorb in traumatic amputation of the forearm and severe septic shock[J]. Case Rep Crit Care, 2017, 2017:8747616. |
| [5] |
Kade G, Literacki S, Rzeszotarska A, et al. Removal of procalcitonin and selected cytokines during continuous veno-venous hemodialysis using high cutoff hemofilters in patients with sepsis and acute kidney injury[J]. Blood Purif, 2018, 46(2):153-159.
doi: 10.1159/000488929 URL |
| [6] |
Chihara S, Masuda Y, Tatsumi H, et al. Evaluation of pre-and post-dilution continuous veno-venous hemofiltration on leukocyte and platelet function in patients with sepsis[J]. Int J Artif Organs, 2019, 42(1):9-16.
doi: 10.1177/0391398818801292 pmid: 30278811 |
| [7] |
Oudemans-Van Straaten HM, Elbers PW. How to explain and exploit the beneficial effects of high-volume hemofiltration on hemodynamics and strong ion gap[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2013, 39(6):1140-1142.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-013-2820-4 pmid: 23361626 |
| [8] |
Hassan J, Cader RA, Kong NC, et al. Original article: Coupled plasma filtration adsorption (CPFA) plus continuous veno-venous haemofiltration (CVVH) versus CVVH alone as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of sepsis[J]. EXCLI J, 2013, 12:681-692.
pmid: 26600735 |
| [9] | Maynar J, Martínez-Sagasti F, Herrera-Gutiérrez M, et al. Direct hemoperfusion with polymyxin B-immobilized cartridge in severe sepsis due to intestinal perforation: hemodynamic findings and clinical considerations in anticoagulation therapy[J]. Rev Esp Quimioter, 2013, 26(2):151-158. |
| [10] |
Quenot JP, Binquet C, Vinsonneau C, et al. Very high volume hemofiltration with the Cascade system in septic shock patients[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2015, 41(12):2111-2120.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-4056-y URL |
| [11] |
Quinto BM, Iizuka IJ, Monte JC, et al. TNF-α depuration is a predictor of mortality in critically ill patients under continuous veno-venous hemodiafiltration treatment[J]. Cytokine, 2015, 71(2):255-260.
doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.10.024 pmid: 25461406 |
| [12] | Schädler D, Pausch C, Heise D, et al. The effect of a novel extracorporeal cytokine hemoadsorption device on IL-6 elimination in septic patients: A randomized controlled trial[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(10):e187015. |
| [13] |
Guo J, Tao W, Tang D, et al. Th17/Regulatory T cell imbalance in sepsis patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome: Attenuated by high-volume hemofiltration[J]. Int J Artif Organs, 2017, 40(11):607-614.
doi: 10.5301/ijao.5000625 URL |
| [14] |
Huang Z, Wang SR, Su W, et al. Removal of humoral mediators and the effect on the survival of septic patients by hemoperfusion with neutral microporous resin column[J]. Ther Apher Dial, 2010, 14(6):596-602.
doi: 10.1111/tap.2010.14.issue-6 URL |
| [15] |
Kim JJ, Park YJ, Moon KY, et al. Polymyxin B hemoperfusion as a feasible therapy after source control in abdominal septic shock[J]. World J Gastrointest Surg, 2019, 11(12):422-432.
doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v11.i12.422 URL |
| [16] |
Friesecke S, Träger K, Schittek GA, et al. International registry on the use of the CytoSorb® adsorber in ICU patients: Study protocol and preliminary results[J]. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed, 2019, 114(8):699-707.
doi: 10.1007/s00063-017-0342-5 pmid: 28871441 |
| [17] | Servillo G, Vargas M, Pastore A, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of continuous venovenous hemofiltration during sepsis: Preliminary data[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2013, 2013:108951. |
| [18] |
Joannes-Boyau O, Honoré PM, Perez P, et al. High-volume versus standard-volume haemofiltration for septic shock patients with acute kidney injury (IVOIRE study): A multicentre randomized controlled trial[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2013, 39(9):1535-1546.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-013-2967-z pmid: 23740278 |
| [19] |
Chung KK, Coates EC, Smith DJ Jr, et al. High-volume hemofiltration in adult burn patients with septic shock and acute kidney injury: A multicenter randomized controlled trial[J]. Crit Care, 2017, 21(1):89.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1678-1 URL |
| [20] |
Park JT, Lee H, Kee YK, et al. High-dose versus conventional-dose continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration and patient and kidney survival and cytokine removal in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2016, 68(4):599-608.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.02.049 URL |
| [21] |
Friesecke S, Stecher SS, Gross S, et al. Extracorporeal cytokine elimination as rescue therapy in refractory septic shock: A prospective single-center study[J]. J Artif Organs, 2017, 20(3):252-259.
doi: 10.1007/s10047-017-0967-4 pmid: 28589286 |
| [22] |
Hawchar F, László I, Öveges N, et al. Extracorporeal cytokine adsorption in septic shock: A proof of concept randomized, controlled pilot study[J]. J Crit Care, 2019, 49:172-178.
doi: S0883-9441(18)30777-9 pmid: 30448517 |
| [23] |
Xu C, Fan K, Xie L, et al. Evaluation of optimized continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration therapy efficiency in severe burn patients with sepsis[J]. Burns Trauma, 2014, 2(3):125-129.
doi: 10.4103/2321-3868.137604 URL |
| [24] | Livigni S, Bertolini G, Rossi C, et al. Efficacy of coupled plasma filtration adsorption (CPFA) in patients with septic shock: A multicenter randomised controlled clinical trial[J]. BMJ Open, 2014, 4(1):e003536. |
| [25] | Tamme K, Maddison L, Kruusat R, et al. Effects of high volume haemodiafiltration on inflammatory response profile and microcirculation in patients with septic shock[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2015, 2015:125615. |
| [26] |
Wu J, Ren J, Liu Q, et al. Effects of changes in the levels of damage-associated molecular patterns following continuous veno-venous hemofiltration therapy on outcomes in acute kidney injury patients with sepsis[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 9:3052.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03052 URL |
| [27] |
Kade G, Lubas A, Rzeszotarska A, et al. Effectiveness of high cut-off hemofilters in the removal of selected cytokines in patients during septic shock accompanied by acute kidney injury-preliminary study[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2016, 22:4338-4344.
doi: 10.12659/MSM.896819 URL |
| [28] |
Zhang P, Yang Y, Lv R, et al. Effect of the intensity of continuous renal replacement therapy in patients with sepsis and acute kidney injury: A single-center randomized clinical trial[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2012, 27(3):967-973.
doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr486 URL |
| [29] |
Dellinger RP, Bagshaw SM, Antonelli M, et al. Effect of targeted polymyxin B hemoperfusion on 28-day mortality in patients with septic shock and elevated endotoxin level[J]. JAMA, 2018, 320(14):1455-1463.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.14618 pmid: 30304428 |
| [30] |
Payen DM, Guilhot J, Launey Y, et al. Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in patients with septic shock due to peritonitis: A multicenter randomized control trial[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2015, 41(6):975-984.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-3751-z URL |
| [31] |
You B, Zhang YL, Luo GX, et al. Early application of continuous high-volume haemofiltration can reduce sepsis and improve the prognosis of patients with severe burns[J]. Crit Care, 2018, 22(1):173.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2095-9 URL |
| [32] |
Miao H, Wang F, Xiong X, et al. Clinical benefits of high-volume hemofiltration in critically Ill pediatric patients with severe sepsis: A retrospective cohort study[J]. Blood Purif, 2018, 45(1-3):18-27.
doi: 10.1159/000481249 URL |
| [33] |
Zuccari S, Damiani E, Domizi R, et al. Changes in cytokines, haemodynamics and microcirculation in patients with sepsis/septic shock undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy and blood purification with cytosorb[J]. Blood Purif, 2020, 49(1-2):107-113.
doi: 10.1159/000502540 URL |
| [34] |
Shum HP, Leung YW, Lam SM, et al. Alteco endotoxin hemoadsorption in gram-negative septic shock patients[J]. Indian J Crit Care Med, 2014, 18(12):783-788.
doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.146305 URL |
| [35] |
Peng ZY, Wang HZ, Carter MJ, et al. Acute removal of common sepsis mediators does not explain the effects of extracorporeal blood purification in experimental sepsis[J]. Kidney Int, 2012, 81(4):363-369.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.320 URL |
| [1] | Huang Saihu, Long Zhongjie, Dong Xingqiang, Meng Xiangying, Wu Shuiyan, Bai Zhenjiang. Pathogen and clinical characteristics of children with hematologic neoplasms complicated with sepsis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 38-42. |
| [2] | Tang Aijun, Wang Liwei. Predictive values of platelet count and coagulation index in the 28-day survival of sepsis patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(3): 250-254. |
| [3] | Zhou Lijuan, Zhu Pengwei, Cao Mei, Cheng Zhenmei, Wu Qiaowei, Li Yong. Correlation of serum ferritin, erythrocyte parameters and D-dimer with sepsis in children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(1): 60-63. |
| [4] | Zhou Bin, Zeng Cizheng, Huang Yuge, Zhong Mianling, Wu Jiayuan. Effect of pSOFA score combined with C-reactive protein and procalcitonin in prognosis assessment of sepsis children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(7): 616-622. |
| [5] | Zhang Mengyuan, Zhu Yong. Predictive value of procalcitonin clearance and SOFA score on the prognosis of patients with severe sepsis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 225-229. |
| [6] | Hou Wei, Zhang Lijun, Zhang Man, Wang Yakun, Jia Meixuan, Tian Liyuan. Clinical analysis in 84 children with the sepsis of non-elevated peripheral blood leukocytes [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(9): 799-802. |
| [7] | Eamran Hossain, Tian Ya, Chen Yuan, Zhang Shaodan, Zhang Huifeng. IPEX syndrome concurrent with gut-origin sepsis: A child patient report and literature review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(5): 453-457. |
| [8] | Chao Yangong, Chinese Critical Ultrasound Study Group. Choice of vasoactive drugs in sepsis associated acute kidney injur [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(7): 599-603. |
| [9] | Liu Lixia1, Wang Xiaoting2, Chao Yangong3, Zhang Hongmin2, Wu Jun4, Yin Wanhong5, Zhang Lina6,He Wei7, Zhu Ran8, Ding Xin2, Zhang Qian1, Hu Zhenjie1, Chinese Critical Ultrasound Study Group . Sepsisinduced acute kidney injury: a disease of the microcirculation [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(7): 595-598. |
| [10] | Feng Junshuai, Fu Caihong, Ma Ru, Zhou Qianqian, Zhou Huiru, Zhang Jinzhou, Gao Junlong, Wang Xiandong. Efficacy of plasma diafiltration in treatment of hepatic failure complicated with sepsis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(4): 330-333. |
| [11] | Xu Ruishana, Zhang Xiaolib. Expression and clinical significance of peripheral blood immune factors in patients with severe sepsis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(7): 579-582,586. |
| [12] | Zhang Yanwei, Zhao Mailiang, Zhang Sheng, Zhou Kuilong, Gao Hui, Wang Junhui, Zhao Xing, Li Chao. Effect of Xuebijing injection combined with ulinastatin on sepsis induced ARDS patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(7): 575-578. |
| [13] | Song Zhonghai1a, Gao Hui1a, Lu Chun1b, Dong Shimin2. Clinical value of serum procalcitonin, T lymphocyte subsets and neutrophil CD64 in evaluating the severity and prognosis of patients with sepsis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(7): 568-574. |
| [14] | Tian Wenlong1, Cheng Hongying1, Dong Shimin2. Meta analysis of levosimendan in treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(7): 562-567. |
| [15] | Li Ruijie1, Chen Lei1, Guo Yanli1, Qi Shifeng1, Ma Xiaoli1, Liu Jiangyan2. Management of hypovolemia in sepsis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(7): 558-561. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||