Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 250-254.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.03.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Predictive values of platelet count and coagulation index in the 28-day survival of sepsis patients
- Department of Emergency,Wusong Central Hospital,Shanghai 201900,China
-
Received:2022-08-04Online:2023-03-20Published:2023-05-11 -
Contact:Wang Liwei E-mail:2445570931@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Aijun, Wang Liwei. Predictive values of platelet count and coagulation index in the 28-day survival of sepsis patients[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(3): 250-254.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.03.010
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(例) | 年龄 ( | 疾病程度(例) | 感染部位(例) | 合并高血压(例) | 合并糖尿病(例) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 脓毒症 | 脓毒症休克 | 呼吸道 | 腹腔 | 泌尿道或其他 | 有 | 无 | 有 | 无 | ||||||||||||||
| 病死组 | 30 | 14 | 16 | 58.53±3.21 | 25 | 5 | 17 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 24 | 5 | 25 | |||||||||||
| 存活组 | 61 | 34 | 27 | 58.98±3.24 | 52 | 9 | 30 | 24 | 7 | 13 | 48 | 10 | 51 | |||||||||||
| 统计值 | χ2=0.664 | χ2=0.005 | χ2=0.760 | χ2=0.021 | χ2=0.072 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 0.415 | 0.534 | 0.812 | 0.684 | 0.885 | 0.974 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 呼吸频率 ( | PLT [ | PT ( | FIB [ | D-D ( | APTT ( | ||||||||||||||||||
| 病死组 | 20.05±1.35 | 69.10(53.02,87.48) | 18.98±2.78 | 1.96(1.58,2.43) | 11.11±1.69 | 50.66±3.88 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 存活组 | 20.25±1.29 | 101.70(84.97,128.97) | 14.94±1.60 | 2.68(2.18,3.40) | 8.28±1.56 | 46.71±2.56 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.495 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | qSOFA评分 ( | SOFA评分 ( | APACHEⅡ评分 ( | 机械通气时间 ( | 连续性肾脏替代 治疗持续时间 ( | 抗生素使用时间 ( | ||||||||||||||||||
| 病死组 | 1.38±0.37 | 9.57±3.35 | 30.18±7.14 | 4.47±0.73 | 10.63±1.87 | 11.40±2.13 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 存活组 | 1.02±0.29 | 6.21±2.74 | 22.73±6.73 | 4.28±0.66 | 9.89±1.81 | 10.85±1.96 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.222 | 0.070 | 0.227 | |||||||||||||||||||
Tab.1 Comparison of clinical data between the two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(例) | 年龄 ( | 疾病程度(例) | 感染部位(例) | 合并高血压(例) | 合并糖尿病(例) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 脓毒症 | 脓毒症休克 | 呼吸道 | 腹腔 | 泌尿道或其他 | 有 | 无 | 有 | 无 | ||||||||||||||
| 病死组 | 30 | 14 | 16 | 58.53±3.21 | 25 | 5 | 17 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 24 | 5 | 25 | |||||||||||
| 存活组 | 61 | 34 | 27 | 58.98±3.24 | 52 | 9 | 30 | 24 | 7 | 13 | 48 | 10 | 51 | |||||||||||
| 统计值 | χ2=0.664 | χ2=0.005 | χ2=0.760 | χ2=0.021 | χ2=0.072 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 0.415 | 0.534 | 0.812 | 0.684 | 0.885 | 0.974 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 呼吸频率 ( | PLT [ | PT ( | FIB [ | D-D ( | APTT ( | ||||||||||||||||||
| 病死组 | 20.05±1.35 | 69.10(53.02,87.48) | 18.98±2.78 | 1.96(1.58,2.43) | 11.11±1.69 | 50.66±3.88 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 存活组 | 20.25±1.29 | 101.70(84.97,128.97) | 14.94±1.60 | 2.68(2.18,3.40) | 8.28±1.56 | 46.71±2.56 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.495 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | qSOFA评分 ( | SOFA评分 ( | APACHEⅡ评分 ( | 机械通气时间 ( | 连续性肾脏替代 治疗持续时间 ( | 抗生素使用时间 ( | ||||||||||||||||||
| 病死组 | 1.38±0.37 | 9.57±3.35 | 30.18±7.14 | 4.47±0.73 | 10.63±1.87 | 11.40±2.13 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 存活组 | 1.02±0.29 | 6.21±2.74 | 22.73±6.73 | 4.28±0.66 | 9.89±1.81 | 10.85±1.96 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.222 | 0.070 | 0.227 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 项目 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| PLT | -0.075 | 0.016 | 21.489 | 0.000 | 0.928 | 0.899 | 0.958 |
| PT | 0.258 | 0.072 | 13.010 | 0.0001 | 1.294 | 1.125 | 1.489 |
| FIB | -0.906 | 0.307 | 8.698 | 0.003 | 0.404 | 0.221 | 0.738 |
| D-D | 0.350 | 0.103 | 11.496 | 0.001 | 1.419 | 1.159 | 1.737 |
| APTT | 0.307 | 0.059 | 27.361 | 0.000 | 1.360 | 1.212 | 1.525 |
Tab.2 Cox regression analysis of the relationship between main indicators and 28-day survival status of patients with sepsis
| 项目 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| PLT | -0.075 | 0.016 | 21.489 | 0.000 | 0.928 | 0.899 | 0.958 |
| PT | 0.258 | 0.072 | 13.010 | 0.0001 | 1.294 | 1.125 | 1.489 |
| FIB | -0.906 | 0.307 | 8.698 | 0.003 | 0.404 | 0.221 | 0.738 |
| D-D | 0.350 | 0.103 | 11.496 | 0.001 | 1.419 | 1.159 | 1.737 |
| APTT | 0.307 | 0.059 | 27.361 | 0.000 | 1.360 | 1.212 | 1.525 |
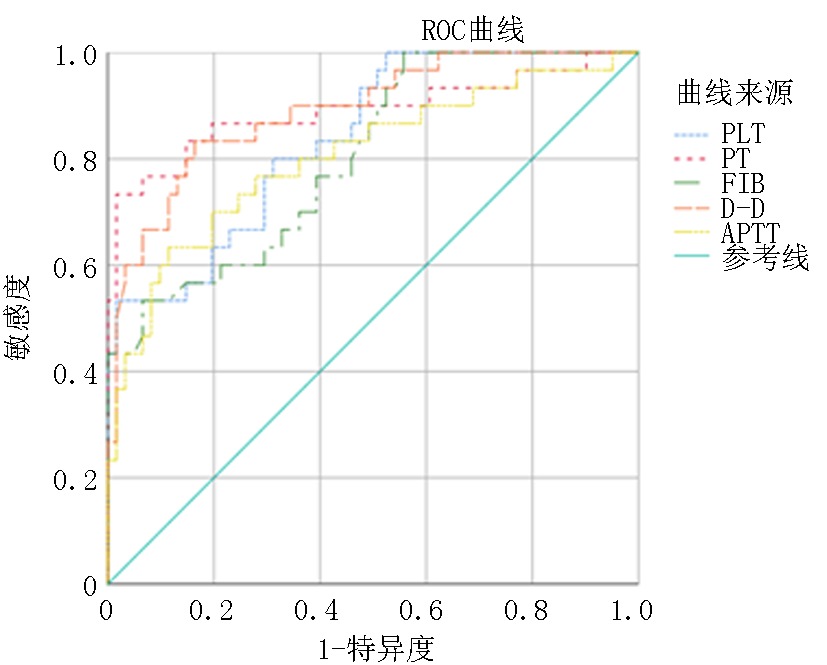
| 指标 | AUC | 标准误 | 95% | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||||
| PLT | 0.838 | 0.043 | 0.755 | 0.922 | 0.533 | 0.984 | 0.517 | 69.455 |
| PT | 0.889 | 0.044 | 0.802 | 0.976 | 0.733 | 0.984 | 0.717 | 17.565 |
| FIB | 0.805 | 0.047 | 0.712 | 0.898 | 0.532 | 0.934 | 0.467 | 1.980 |
| D-D | 0.891 | 0.036 | 0.820 | 0.962 | 0.833 | 0.836 | 0.669 | 9.740 |
| APTT | 0.805 | 0.052 | 0.703 | 0.907 | 0.633 | 0.885 | 0.518 | 49.775 |
Tab.3 Value analysis of PLT and coagulation indexes in predicting the 28-day survival status of patients with sepsis at admission
| 指标 | AUC | 标准误 | 95% | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||||
| PLT | 0.838 | 0.043 | 0.755 | 0.922 | 0.533 | 0.984 | 0.517 | 69.455 |
| PT | 0.889 | 0.044 | 0.802 | 0.976 | 0.733 | 0.984 | 0.717 | 17.565 |
| FIB | 0.805 | 0.047 | 0.712 | 0.898 | 0.532 | 0.934 | 0.467 | 1.980 |
| D-D | 0.891 | 0.036 | 0.820 | 0.962 | 0.833 | 0.836 | 0.669 | 9.740 |
| APTT | 0.805 | 0.052 | 0.703 | 0.907 | 0.633 | 0.885 | 0.518 | 49.775 |
| [1] | Jiang ZM, Yang QH, Zhu CQ. UCP2 in early diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2017, 21(3):549-553. |
| [2] |
Zhu T, Liao X, Feng T, et al. Plasma monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 as a predictive marker for sepsis prognosis: A prospective cohort study[J]. Tohoku J Exp Med, 2017, 241(2):139-147.
doi: 10.1620/tjem.241.139 pmid: 28202856 |
| [3] | 张小军, 蔡俊丹, 吴云, 等. 血清乳酸脱氢酶与脓毒症早期病死率的相关性[J]. 内科急危重症杂志, 2020, 26(5):44-47,52. |
| [4] |
Huang M, Cai S, Su J. The pathogenesis of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(21):5376-5377.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20215376 URL |
| [5] | 陈振华, 江琴. 脓毒症患者凝血功能指标,降钙素原水平与临床预后的关系[J]. 检验医学, 2020, 35(10):93-95. |
| [6] |
Koyama K, Katayama S, Muronoi T, et al. Time course of immature platelet count and its relation to thrombocytopenia and mortality in patients with sepsis[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(1):e0192064.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192064 URL |
| [7] | 徐波. 血小板聚集率,血小板功能在评价脓毒症患者预后的价值[J]. 血栓与止血学, 2020, 26(6):57-59. |
| [8] |
Rather AR, Kasana B. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3)[J]. J Med Sci, 2015, 18(2):162-164.
doi: 10.33883/jms.v18i2.269 URL |
| [9] |
Raith EP, Udy AA, Bailey M, et al. Prognostic accuracy of the SOFA score, SIRS criteria, and qSOFA score for in-hospital mortality among adults with suspected infection admitted to the intensive care unit[J]. JAMA, 2017, 317(3):290-300.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.20328 pmid: 28114553 |
| [10] | 王小军. 炎症反应及细胞内钙浓度异常升高在脓毒症发展中的作用分析[J]. 中南医学科学杂志, 2020, 48(2):103-107. |
| [11] |
Fabbri A, Marchesini G, Benazzi B, et al. Old subjects with sepsis in the emergency department: Trend analysis of case fatality rate[J]. BMC Geriatr, 2019, 19(1):372-373.
doi: 10.1186/s12877-019-1384-8 pmid: 31870317 |
| [12] | 王绪松, 庞春玉, 陈绵平. 血清PCTsTREM-1及D-二聚体水平对脓毒症患者预后评估的价值[J]. 中国急救医学, 2019, 39(10):949-952. |
| [13] |
Sakurai K, Miyashita T, Okazaki M, et al. Role for neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and platelet aggregation in early sepsis-induced hepatic dysfunction[J]. In Vivo, 2017, 31(6):1051-1058.
pmid: 29102925 |
| [14] |
Elisabetta L, Mondrinos MJ, Sun S, et al. Role of protein kinase C-delta in regulating platelet activation and platelet-leukocyte interaction during sepsis[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(4):e0195379.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195379 URL |
| [15] | 廖明喻, 王萌萌, 武免免, 等. 血小板相关参数对脓毒症预测和预后评估价值的研究进展[J]. 山东医药, 2018, 58(46):104-106. |
| [16] | 周亚雄, 李东泽, 姚蓉, 等. 脓毒症相关凝血-炎症评分的构建及其对脓毒症预后评估效能分析[J]. 华西医学, 2018, 33(11):61-67. |
| [17] |
Umemura Y, Yamakawa K, Hayakawa M, et al. Screening itself for disseminated intravascular coagulation may reduce mortality in sepsis: A nationwide multicenter registry in Japan[J]. Thromb Res, 2018, 161(23):60-66.
doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2017.11.023 URL |
| [18] | 郭嘉仲, 陈娟, 万吉云, 等. 脓毒症患者凝血功能指标变化及其对预后的预测效能[J]. 山东医药, 2019, 59(27):60-62. |
| [19] | 徐康立, 周杰, 陈开森. 降钙素原和D-二聚体对老年脓毒症的诊断价值[J]. 热带医学杂志, 2018, 18(4):99-102. |
| [20] | 姜华, 杨健, 罗彬, 等. 脓毒症患者炎性因子,凝血功能与APACHEⅡ评分和预后的关系[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2018, 18(15):128-131. |
| [21] | 李艳秀, 左祥荣, 曹权. 动态监测血小板计数对脓毒症患者预后评价的意义[J]. 内科理论与实践, 2018, 13(6):354-357. |
| [1] | Huang Saihu, Long Zhongjie, Dong Xingqiang, Meng Xiangying, Wu Shuiyan, Bai Zhenjiang. Pathogen and clinical characteristics of children with hematologic neoplasms complicated with sepsis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 38-42. |
| [2] | Zhang Na, Sun Yue, Dong Han, Zhao Peng, Yang Xin, Qi Yuan, Wang Lingling. Correlation between the expression level of SPARC and prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(11): 972-978. |
| [3] | Zhou Lijuan, Zhu Pengwei, Cao Mei, Cheng Zhenmei, Wu Qiaowei, Li Yong. Correlation of serum ferritin, erythrocyte parameters and D-dimer with sepsis in children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(1): 60-63. |
| [4] | Zhou Bin, Zeng Cizheng, Huang Yuge, Zhong Mianling, Wu Jiayuan. Effect of pSOFA score combined with C-reactive protein and procalcitonin in prognosis assessment of sepsis children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(7): 616-622. |
| [5] | Zhang Mengyuan, Zhu Yong. Predictive value of procalcitonin clearance and SOFA score on the prognosis of patients with severe sepsis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 225-229. |
| [6] | Xiao Liuniu, Zhong Yanxia, Li Shusheng. Effect of extracorporeal hemopurification for clinical prognosis and cytokine levels of septic: A meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(1): 5-13. |
| [7] | Hou Wei, Zhang Lijun, Zhang Man, Wang Yakun, Jia Meixuan, Tian Liyuan. Clinical analysis in 84 children with the sepsis of non-elevated peripheral blood leukocytes [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(9): 799-802. |
| [8] | Kang Xiaochun, Zhang Qingqin, Lu Zhihong, Kong Lingli. Correlation between hemoglobin concentration and local control rate and long-term survival rate on radiotherapy for esophageal cancer patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(6): 522-525. |
| [9] | Wang Ai. Effects of Kangai injection combined with bevacizumab and DP scheme on efficacy and serum tumor markers and prognosis of NSCLC [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(6): 517-521. |
| [10] | Eamran Hossain, Tian Ya, Chen Yuan, Zhang Shaodan, Zhang Huifeng. IPEX syndrome concurrent with gut-origin sepsis: A child patient report and literature review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(5): 453-457. |
| [11] | Cheng Li, Huang Wenrong. Effects of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in primary central nervous system lymphoma [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(10): 901-904. |
| [12] | Liu Xitinga, Wu Yuqianga, Chen Zeb. Shortterm and longterm curative effect of pemetrexed combined with carboplatin on advanced NSCLC [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(9): 837-840. |
| [13] | Chao Yangong, Chinese Critical Ultrasound Study Group. Choice of vasoactive drugs in sepsis associated acute kidney injur [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(7): 599-603. |
| [14] | Liu Lixia1, Wang Xiaoting2, Chao Yangong3, Zhang Hongmin2, Wu Jun4, Yin Wanhong5, Zhang Lina6,He Wei7, Zhu Ran8, Ding Xin2, Zhang Qian1, Hu Zhenjie1, Chinese Critical Ultrasound Study Group . Sepsisinduced acute kidney injury: a disease of the microcirculation [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(7): 595-598. |
| [15] | Feng Junshuai, Fu Caihong, Ma Ru, Zhou Qianqian, Zhou Huiru, Zhang Jinzhou, Gao Junlong, Wang Xiandong. Efficacy of plasma diafiltration in treatment of hepatic failure complicated with sepsis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(4): 330-333. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||