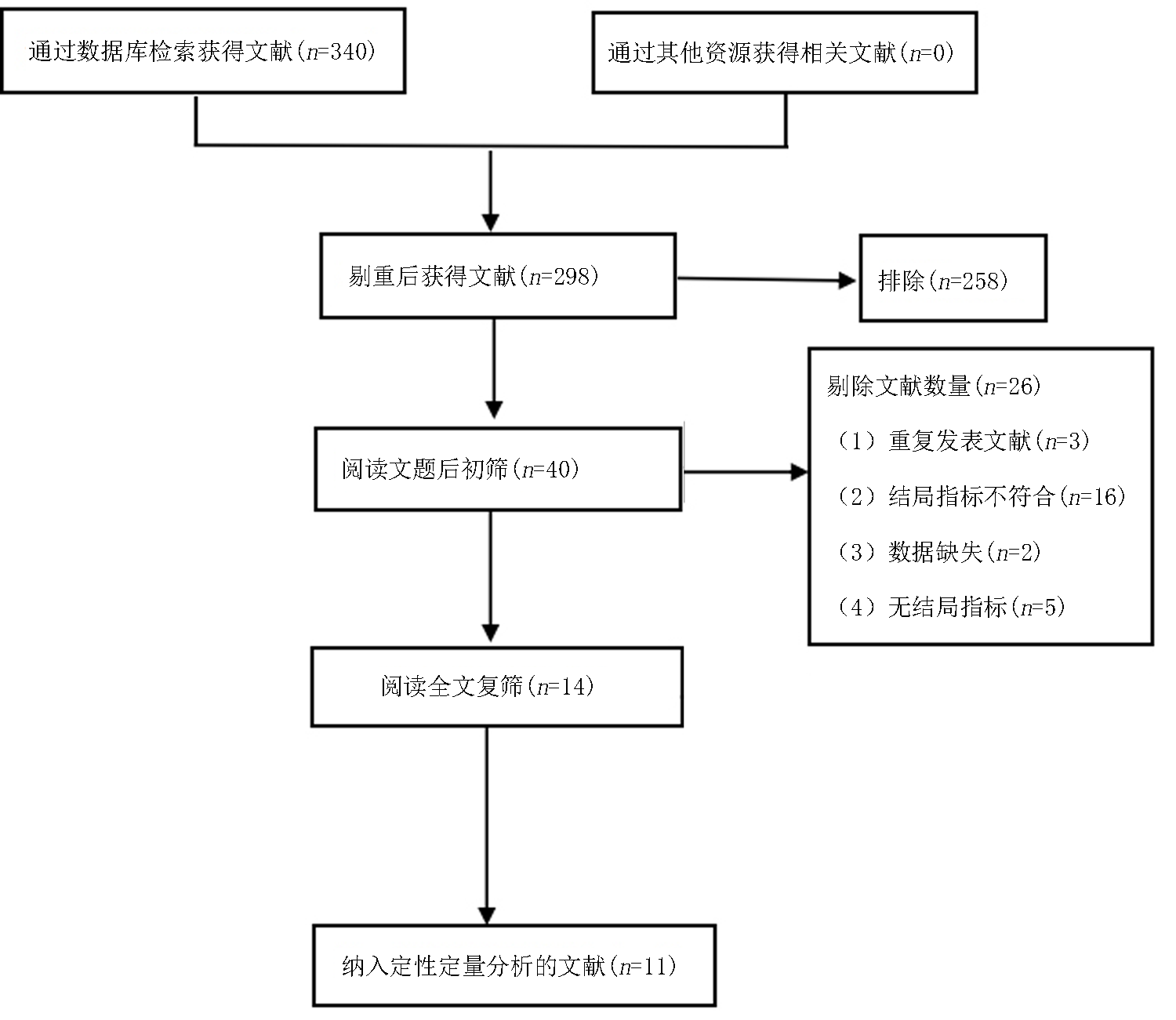
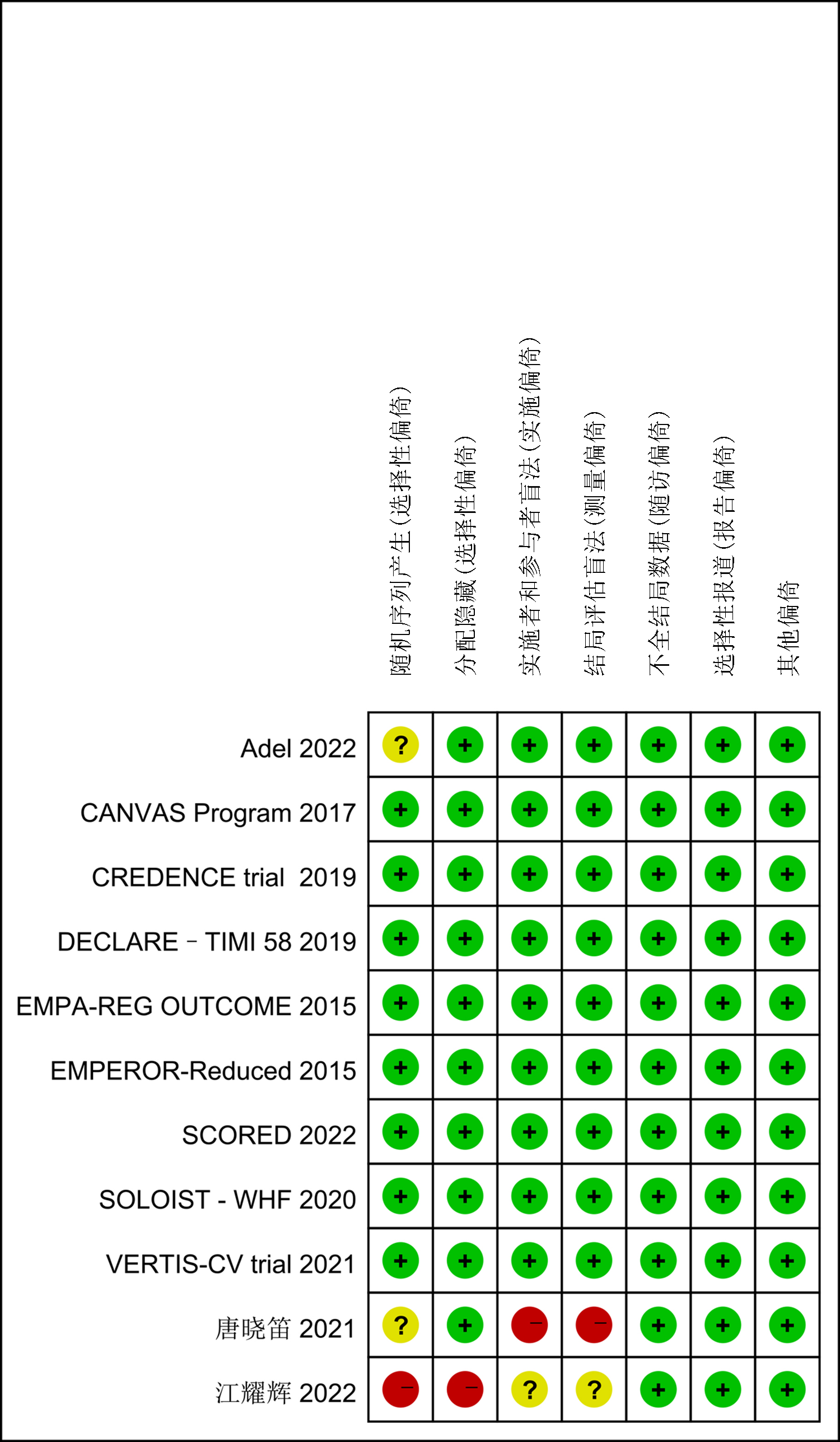
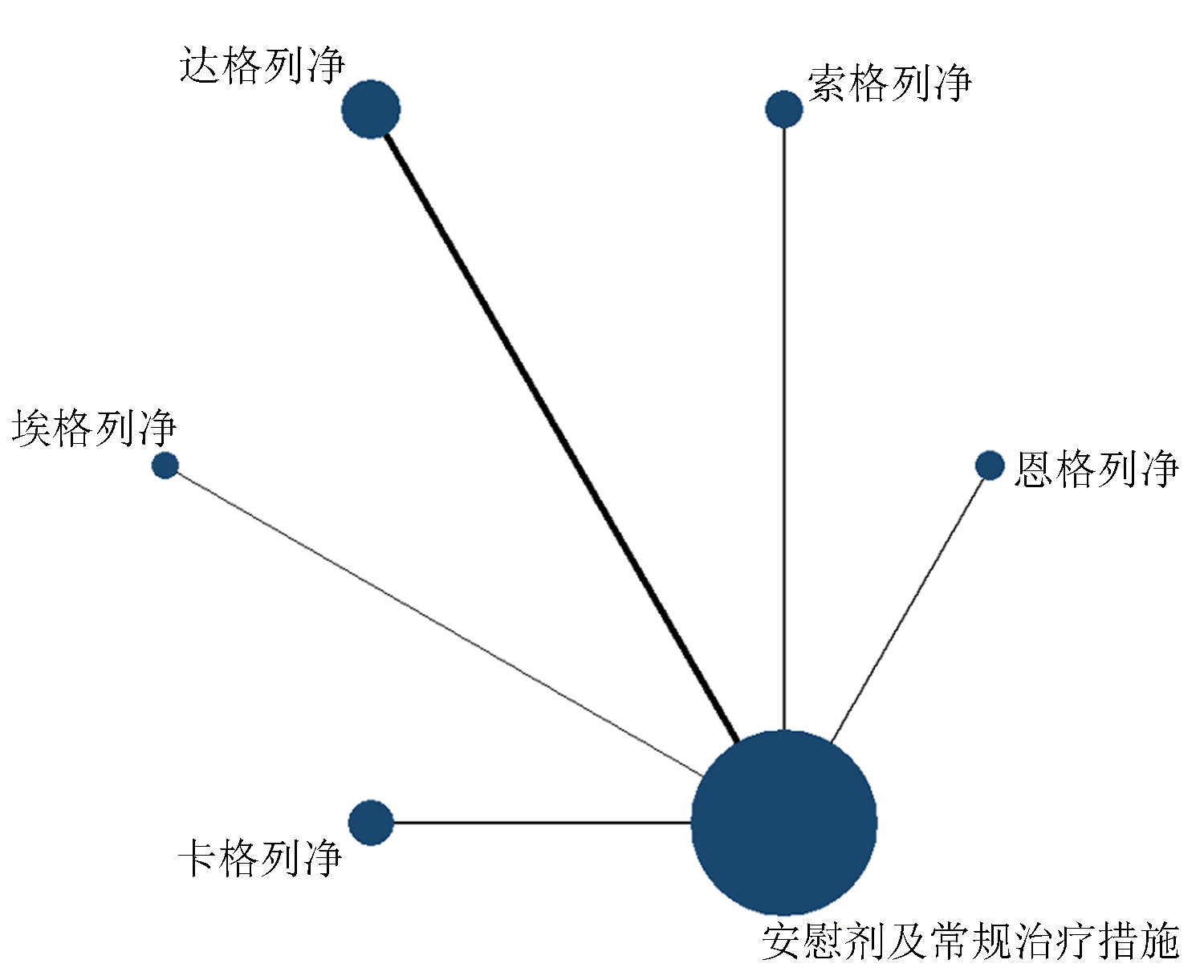
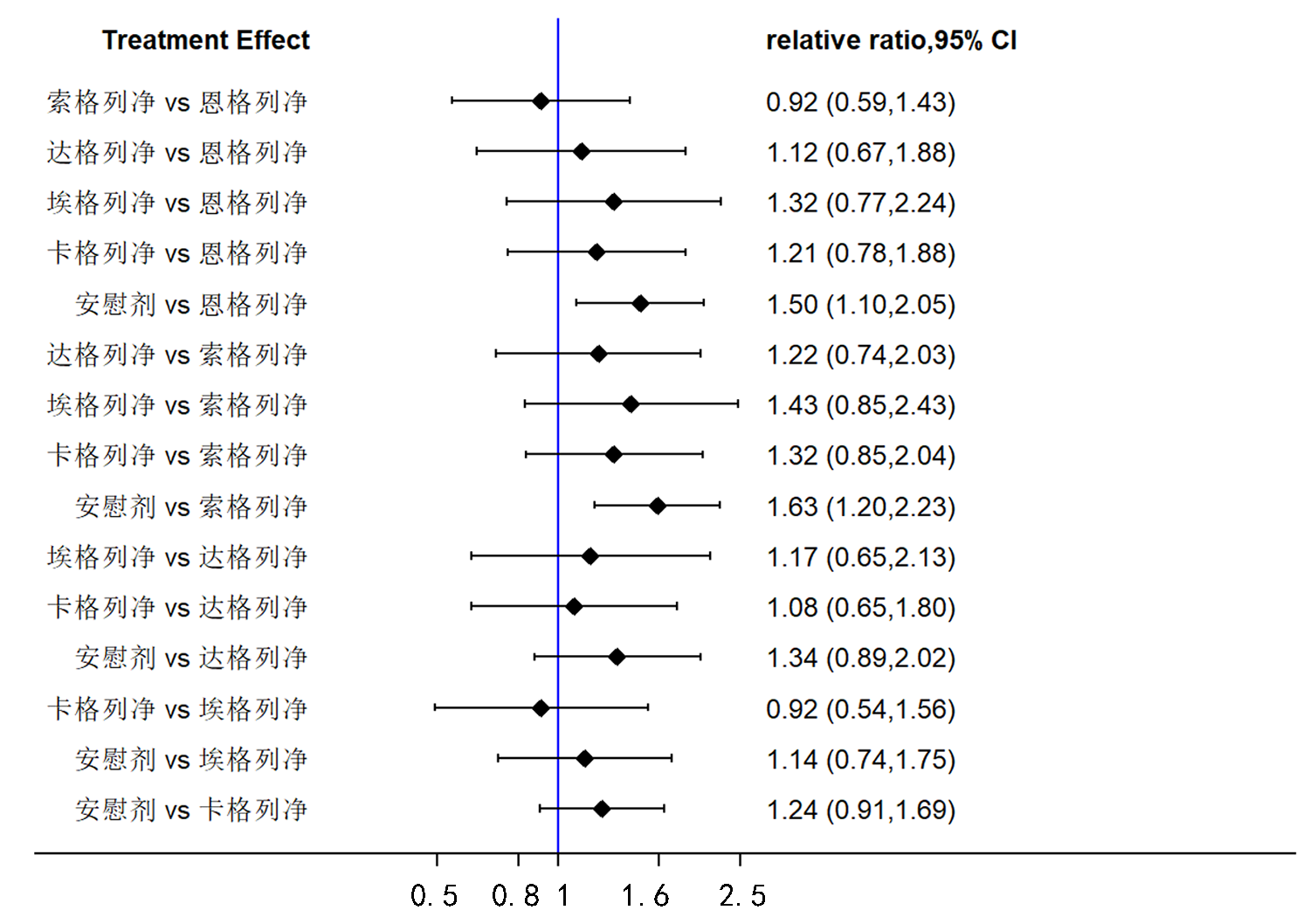
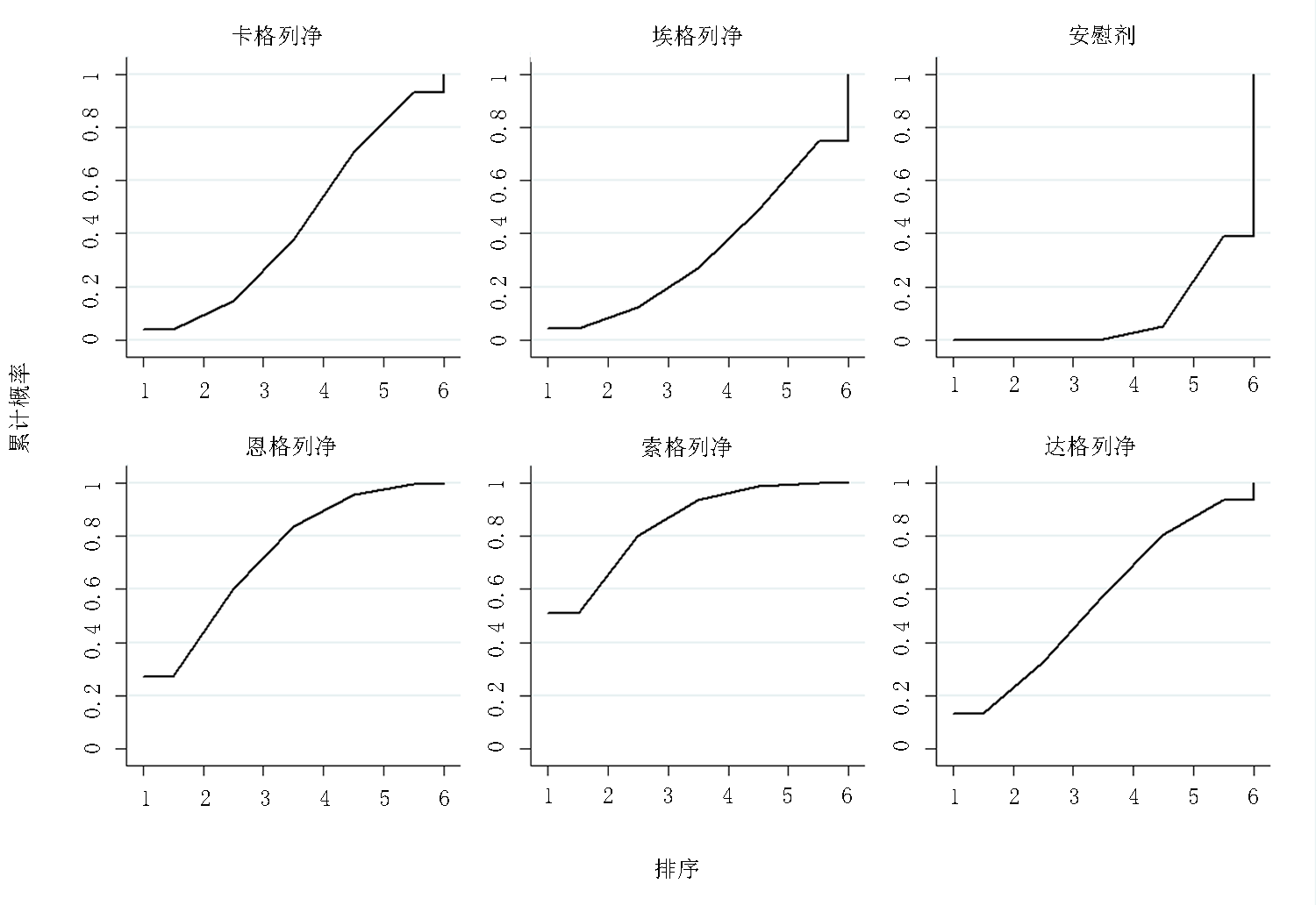
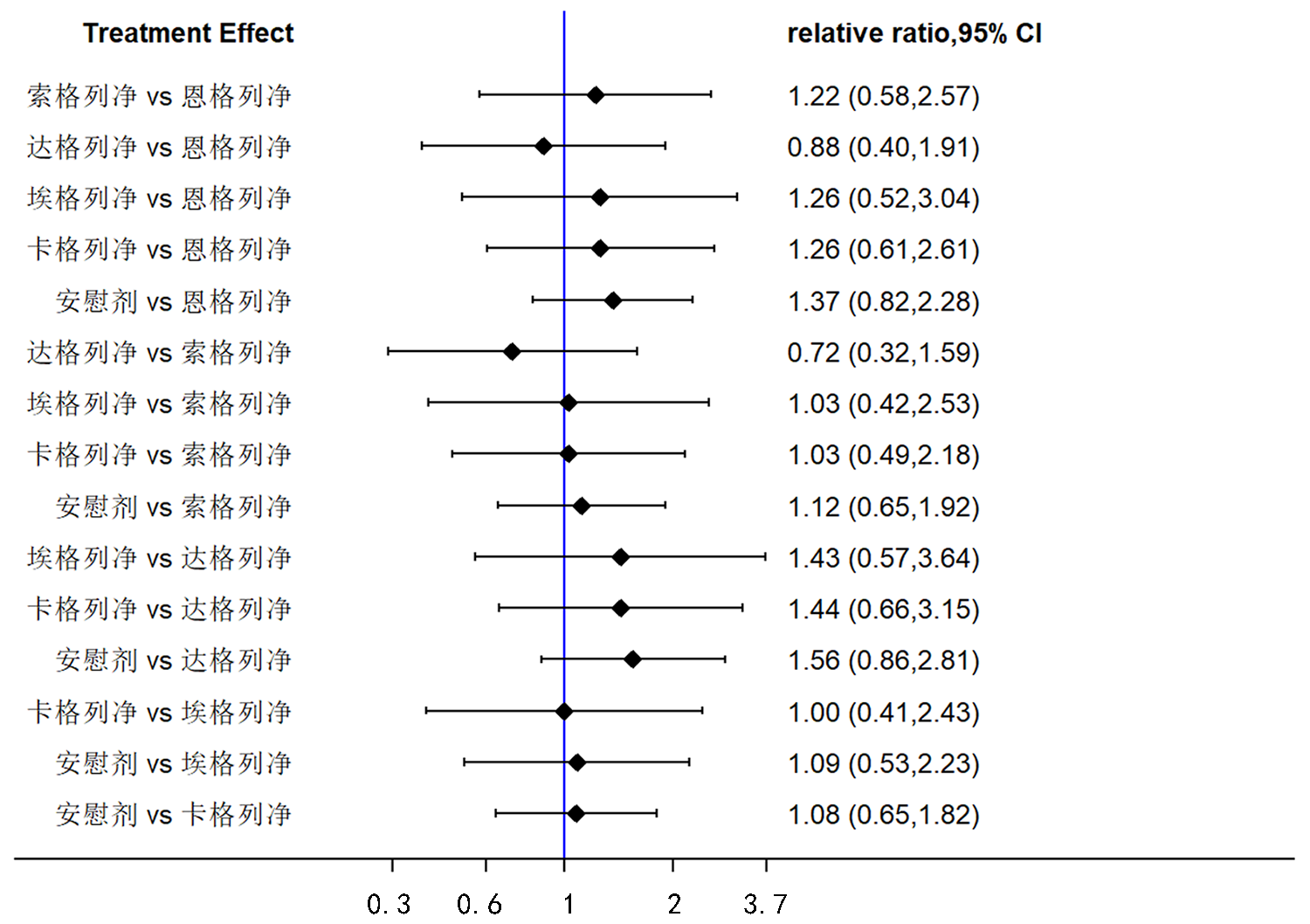
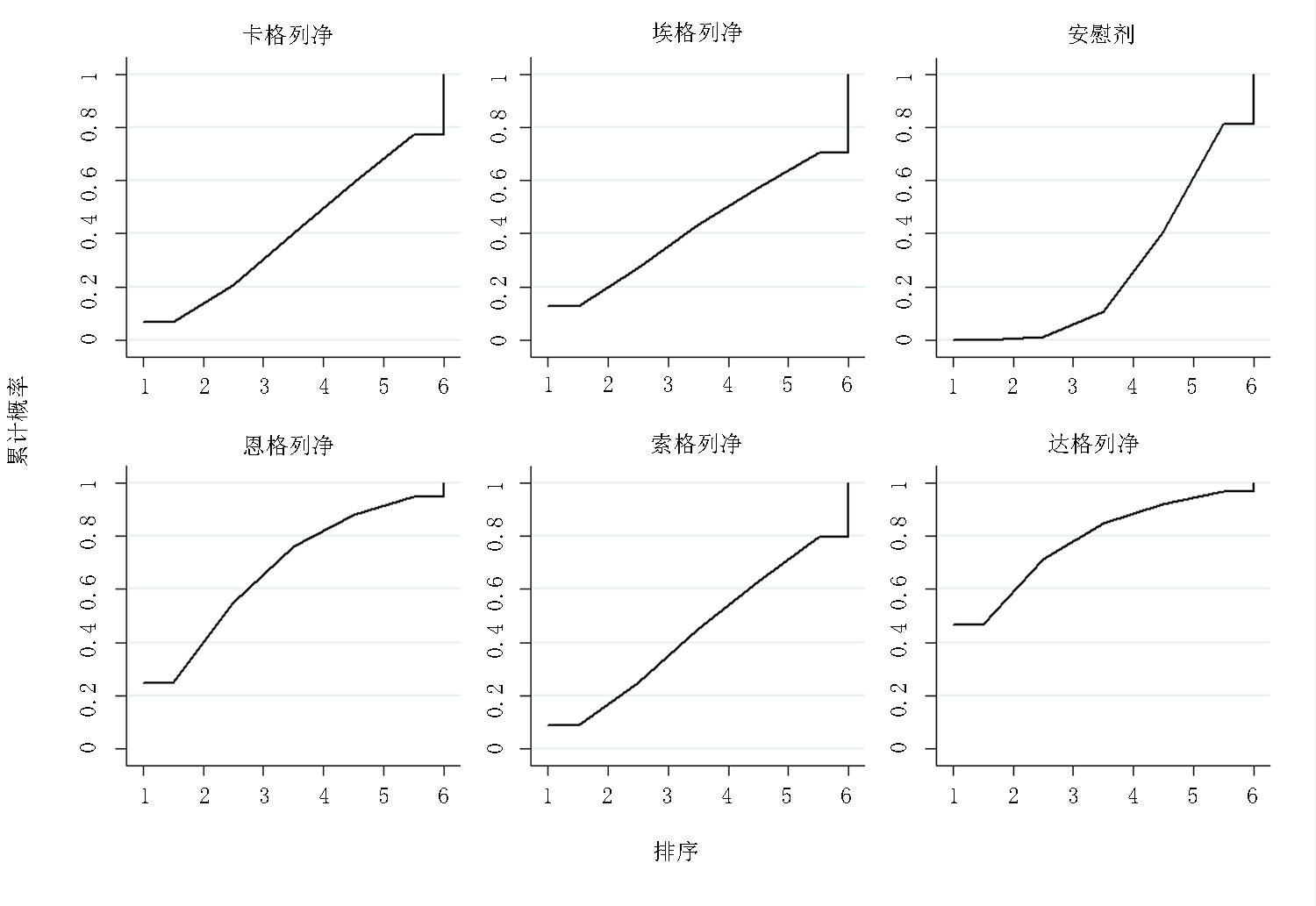
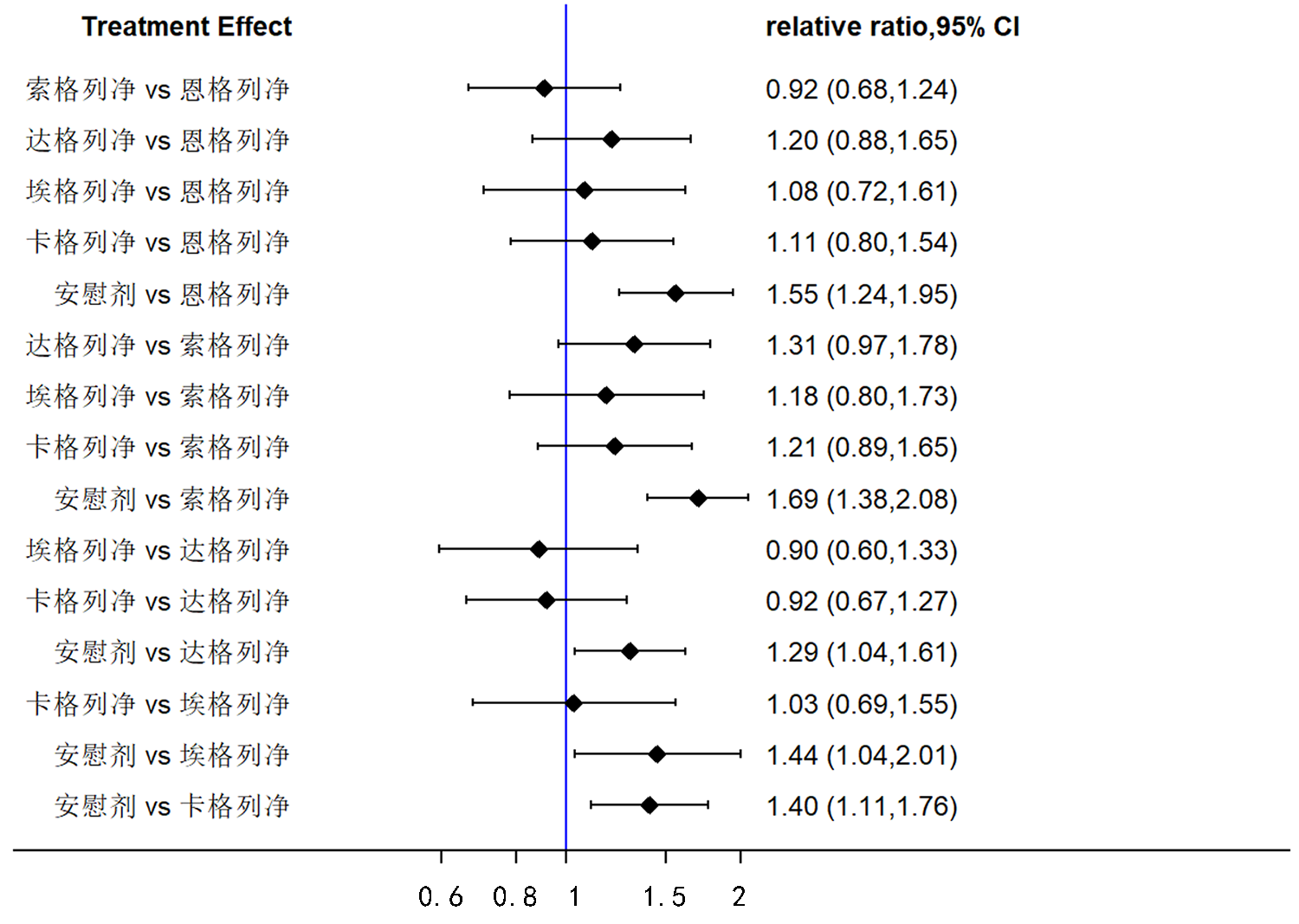
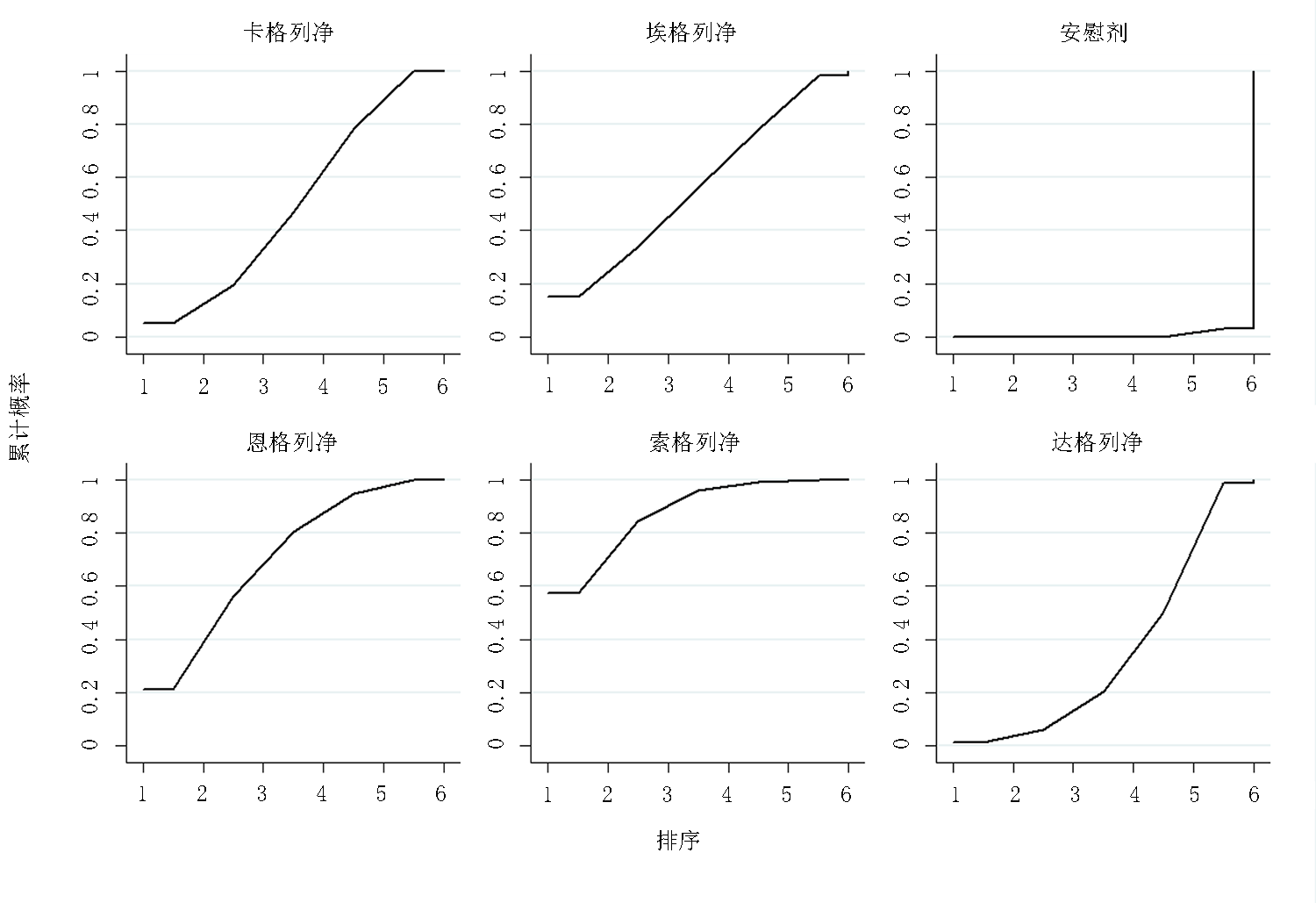
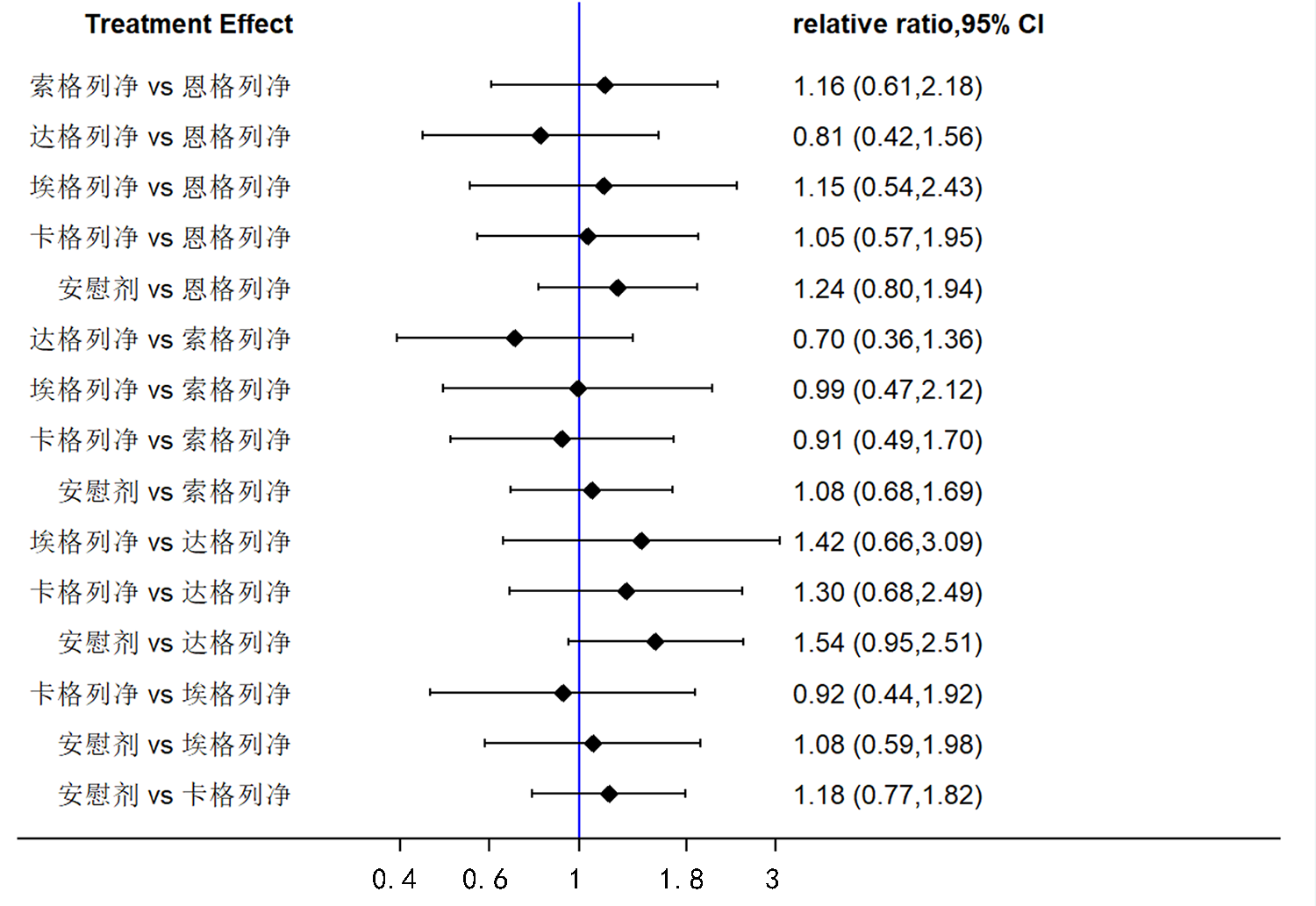
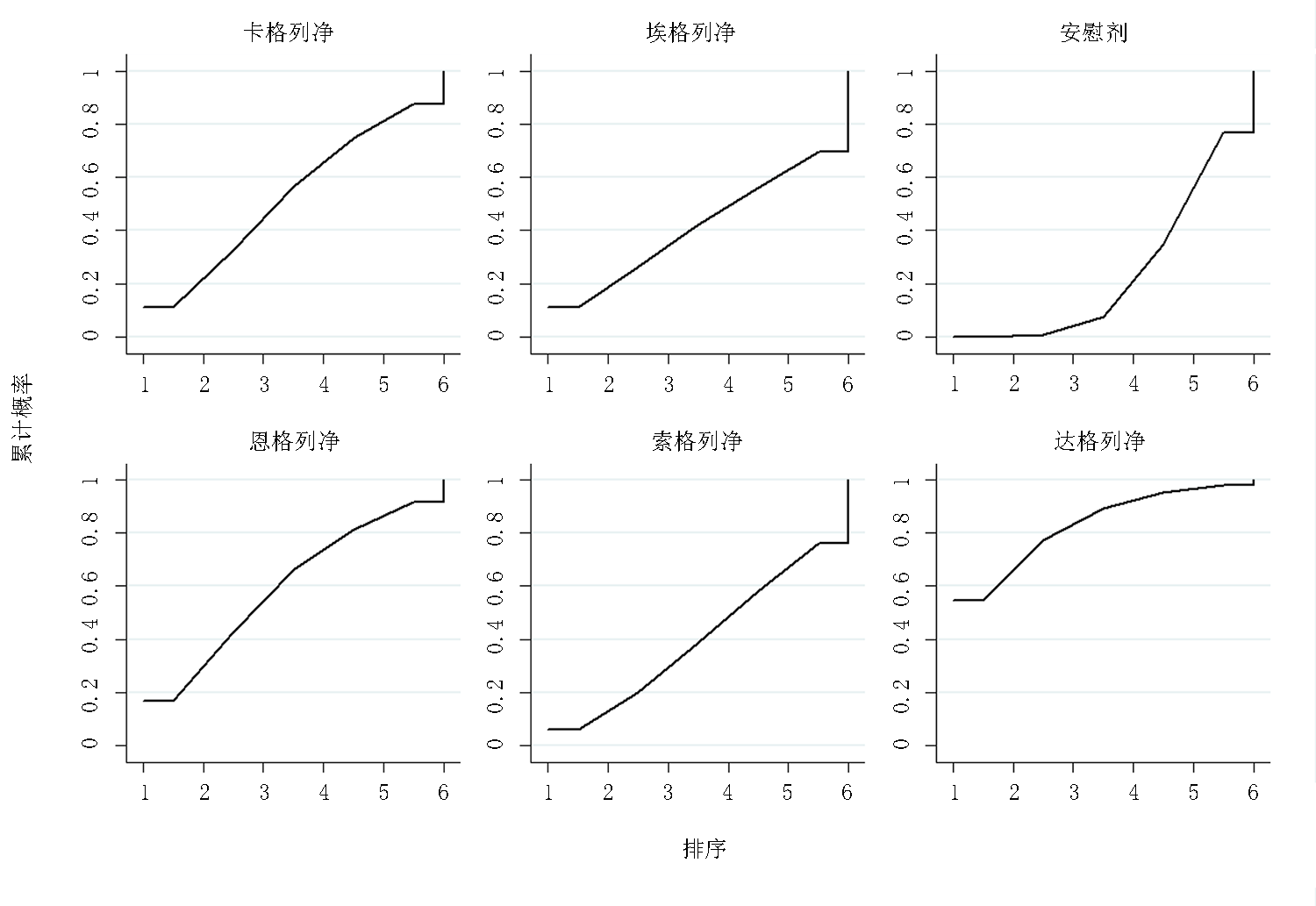
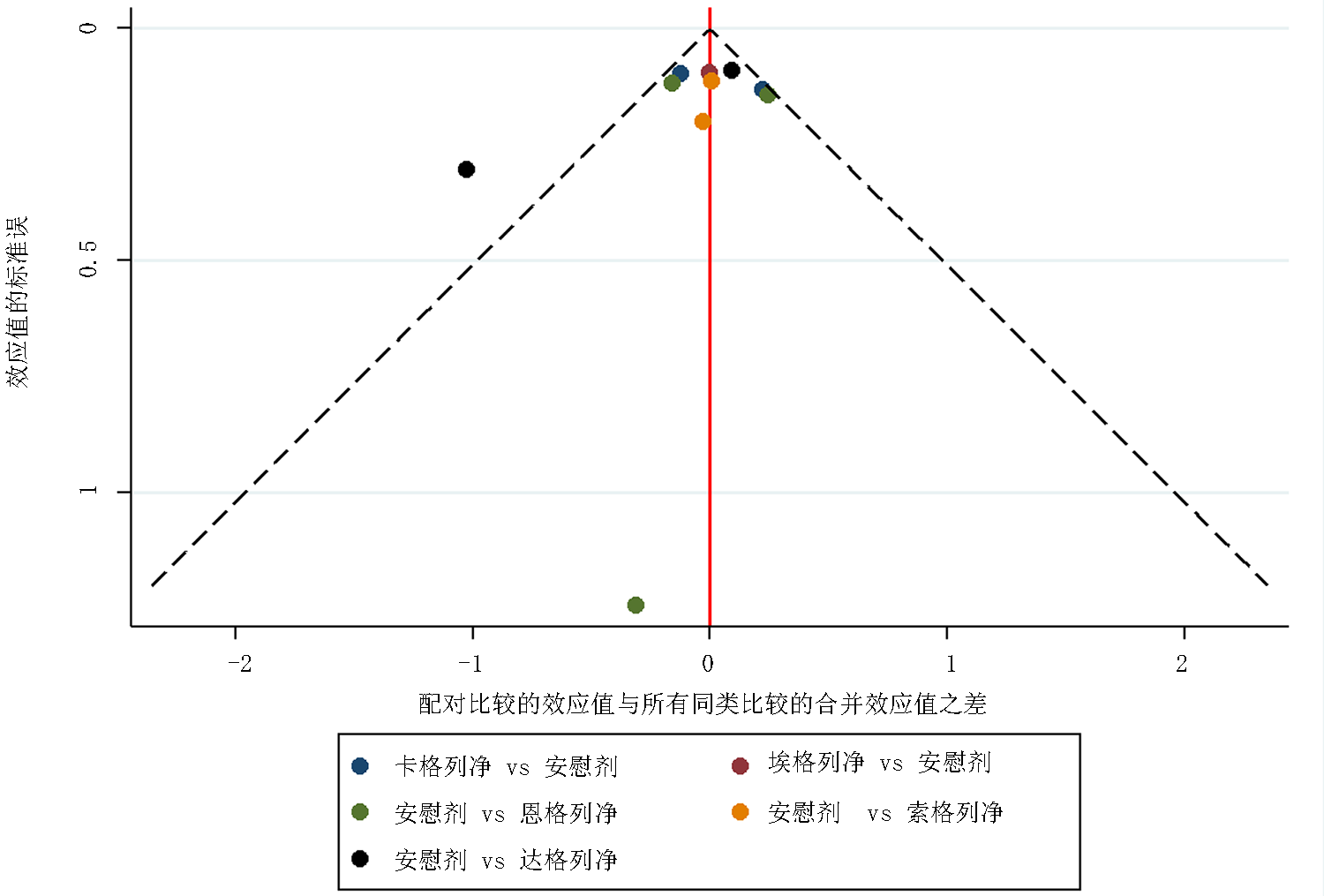
Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 1061-1073.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.12.001
A network meta-analysis of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes
Wang Runqing1( ), Wang Qian2, Liao Jianxiong1
), Wang Qian2, Liao Jianxiong1
- 1. The Sixth Clinical College of Guangzhou Medical University,Guangzhou 510182,China
2. The Second Clinical College of Guangdong Medical University,Dongguan 523808,China
-
Received:2022-07-26Online:2022-12-20Published:2023-01-18 -
Contact:Wang Runqing E-mail:wrq010914@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Runqing, Wang Qian, Liao Jianxiong. A network meta-analysis of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(12): 1061-1073.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.12.001
| 纳入研究 | 年份 | 样本量(例) | 干预措施 | 结局指标 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||
| 江耀辉[ | 2022 | 671 | 1 310 | 达格列净 | 安慰剂和其他常规治疗 | ①②③④ | |
| 唐晓笛[ | 2021 | 100 | 100 | 达格列净 | 其他常规治疗 | ①④ | |
| Adel[ | 2022 | 45 | 48 | 恩格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①② | |
| EMPEROR-Reduced[ | 2021 | 927 | 929 | 恩格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| SCORED[ | 2021 | 5 292 | 5 292 | 索格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| VERTIS-CV trial[ | 2020 | 5 499 | 2 747 | 埃格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| CANVAS Program[ | 2017 | 5 795 | 4 347 | 卡格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| EMPA-REG[ | 2015 | 4 680 | 2 340 | 恩格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| DECLARE-TIMI 58[ | 2019 | 8 585 | 8 575 | 达格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| SOLOIST-WHF[ | 2021 | 608 | 614 | 索格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| CREDENCE trial[ | 2020 | 2 202 | 2 199 | 卡格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①③④ | |
| 纳入研究 | 年份 | 样本量(例) | 干预措施 | 结局指标 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||
| 江耀辉[ | 2022 | 671 | 1 310 | 达格列净 | 安慰剂和其他常规治疗 | ①②③④ | |
| 唐晓笛[ | 2021 | 100 | 100 | 达格列净 | 其他常规治疗 | ①④ | |
| Adel[ | 2022 | 45 | 48 | 恩格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①② | |
| EMPEROR-Reduced[ | 2021 | 927 | 929 | 恩格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| SCORED[ | 2021 | 5 292 | 5 292 | 索格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| VERTIS-CV trial[ | 2020 | 5 499 | 2 747 | 埃格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| CANVAS Program[ | 2017 | 5 795 | 4 347 | 卡格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| EMPA-REG[ | 2015 | 4 680 | 2 340 | 恩格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| DECLARE-TIMI 58[ | 2019 | 8 585 | 8 575 | 达格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| SOLOIST-WHF[ | 2021 | 608 | 614 | 索格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①②③④ | |
| CREDENCE trial[ | 2020 | 2 202 | 2 199 | 卡格列净 | 安慰剂 | ①③④ | |
| [1] | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2021, 13(4): 315-409. |
| [2] | 郑刚. 心力衰竭发病机制研究新进展[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2018, 20(4): 428-431. |
| [3] |
Abdul-Ghani MA, Norton L, Defronzo RA. Role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT 2) inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J]. Endocr Rev, 2011, 32(4): 515-531.
doi: 10.1210/er.2010-0029 pmid: 21606218 |
| [4] |
O'meara E, Mcdonald M, Chan M, et al. CCS/CHFS heart failure guidelines: Clinical trial update on functional mitral regurgitation, SGLT2 inhibitors, ARNI in HFpEF, and tafamidis in amyloidosis[J]. Can J Cardiol, 2020, 36(2): 159-169.
doi: S0828-282X(19)31514-4 pmid: 32036861 |
| [5] |
Hutton B, Catalá-López F, Moher D. The PRISMA statement extension for systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analysis: PRISMA-NMA[J]. Med Clin (Barc), 2016, 147(6): 262-266.
doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2016.02.025 URL |
| [6] | 江耀辉, 王喆, 郑汝杰, 等. 达格列净对冠心病合并2型糖尿病患者临床结局的影响[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2022, 37(3): 250-255. |
| [7] | 唐晓笛, 樊瑛. 钠-葡萄糖协同转运蛋白抑制剂对合并射血分数保留型心力衰竭的2型糖尿病患者的心血管保护作用研究[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2021, 37(1): 68-72. |
| [8] |
Adel SMH, Jorfi F, Mombeini H, et al. Effect of a low dose of empagliflozin on short-term outcomes in type 2 diabetics with acute coronary syndrome after percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Saudi Med J, 2022, 43(5): 458-464.
doi: 10.15537/smj.2022.43.5.20220018 pmid: 35537720 |
| [9] |
Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, et al. Effect of empagliflozin on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in patients with heart failure by baseline diabetes status: Results from the EMPEROR-reduced trial[J]. Circulation, 2021, 143(4): 337-349.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.051824 pmid: 33175585 |
| [10] |
Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Pitt B, et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(2): 129-139.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2030186 URL |
| [11] |
Cannon CP, Pratley R, Dagogo-Jack S, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with ertugliflozin in type 2 diabetes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 383(15): 1425-1435.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2004967 URL |
| [12] | Neal B, Perkovic V, Matthews DR. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(21): 2099. |
| [13] |
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 373(22): 2117-2128.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504720 URL |
| [14] |
Kato ET, Silverman MG, Mosenzon O, et al. Effect of dapagliflozin on heart failure and mortality in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Circulation, 2019, 139(22): 2528-2536.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.040130 pmid: 30882238 |
| [15] |
Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Steg PG, et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and recent worsening heart failure[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(2): 117-128.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2030183 URL |
| [16] |
Jardine MJ, Zhou Z, Mahaffey KW, et al. Renal, cardiovascular, and safety outcomes of canagliflozin by baseline kidney function: A secondary analysis of the CREDENCE randomized trial[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2020, 31(5): 1128-1139.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019111168 pmid: 32354987 |
| [17] |
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Magliano DJ, et al. Diabetes mellitus statistics on prevalence and mortality: Facts and fallacies[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2016, 12(10): 616-622.
doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.105 pmid: 27388988 |
| [18] | Javeed N, Matveyenko AV. Circadian etiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Physiology (Bethesda), 2018, 33(2): 138-150. |
| [19] |
Kannel WB, Mcgee DL. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Framingham study[J]. JAMA, 1979, 241(19): 2035-2038.
doi: 10.1001/jama.1979.03290450033020 URL |
| [20] |
Iribarren C, Karter AJ, Go AS, et al. Glycemic control and heart failure among adult patients with diabetes[J]. Circulation, 2001, 103(22): 2668-2673.
doi: 10.1161/01.cir.103.22.2668 pmid: 11390335 |
| [21] |
Marwick TH, Ritchie R, Shaw JE, et al. Implications of underlying mechanisms for the recognition and management of diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2018, 71(3): 339-351.
doi: S0735-1097(17)41633-0 pmid: 29348027 |
| [22] |
Qin CX, Sleaby R, Davidoff AJ, et al. Insights into the role of maladaptive hexosamine biosynthesis and O-GlcNAcylation in development of diabetic cardiac complications[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2017, 116: 45-56.
doi: S1043-6618(16)31338-X pmid: 27988387 |
| [23] |
Diamant M, Lamb HJ, Smit JW, et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy in uncomplicated type 2 diabetes is associated with the metabolic syndrome and systemic inflammation[J]. Diabetologia, 2005, 48(8): 1669-1670.
pmid: 15988579 |
| [24] |
Tschöpe C, Walther T, Escher F, et al. Transgenic activation of the kallikrein-kinin system inhibits intramyocardial inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. FASEB J, 2005, 19(14): 2057-2059.
pmid: 16129698 |
| [25] |
Westermann D, Rutschow S, Van Linthout S, et al. Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase attenuates left ventricular dysfunction by mediating pro-inflammatory cardiac cytokine levels in a mouse model of diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetologia, 2006, 49(10): 2507-2513.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0385-2 pmid: 16937126 |
| [26] |
Rajesh M, Bátkai S, Kechrid M, et al. Cannabinoid 1 receptor promotes cardiac dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. Diabetes, 2012, 61(3): 716-727.
doi: 10.2337/db11-0477 pmid: 22315315 |
| [27] |
Li J, Zhu H, Shen E, et al. Deficiency of rac1 blocks NADPH oxidase activation, inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress, and reduces myocardial remodeling in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes[J]. Diabetes, 2010, 59(8): 2033-2042.
doi: 10.2337/db09-1800 pmid: 20522592 |
| [28] |
Thomas MC. Type 2 diabetes and heart failure: challenges and solutions[J]. Curr Cardiol Rev, 2016, 12(3): 249-255.
doi: 10.2174/1573403x12666160606120254 pmid: 27280301 |
| [29] |
Parati G, Esler M. The human sympathetic nervous system: Its relevance in hypertension and heart failure[J]. Eur Heart J, 2012, 33(9): 1058-1066.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs041 pmid: 22507981 |
| [30] |
Zoccali C, Mallamaci F, Parlongo S, et al. Plasma norepinephrine predicts survival and incident cardiovascular events in patients with end-stage renal disease[J]. Circulation, 2002, 105(11): 1354-1359.
doi: 10.1161/hc1102.105261 pmid: 11901048 |
| [31] |
Nitenberg A, Ledoux S, Valensi P, et al. Impairment of coronary microvascular dilation in response to cold pressor--induced sympathetic stimulation in type 2 diabetic patients with abnormal stress thallium imaging[J]. Diabetes, 2001, 50(5): 1180-1185.
pmid: 11334424 |
| [32] |
Huynh K, Bernardo BC, Mcmullen JR, et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms and new treatment strategies targeting antioxidant signaling pathways[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2014, 142(3): 375-415.
doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.01.003 URL |
| [33] |
Bolinder J, Ljunggren Ö, Kullberg J, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on body weight, total fat mass, and regional adipose tissue distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control on metformin[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2012, 97(3): 1020-1031.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-2260 pmid: 22238392 |
| [34] |
Lambers Heerspink H J, De Zeeuw D, Wie L, et al. Dapagliflozin a glucose-regulating drug with diuretic properties in subjects with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2013, 15(9): 853-862.
doi: 10.1111/dom.12127 pmid: 23668478 |
| [35] |
Abdul-Ghani M, Del Prato S, Chilton R, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors and cardiovascular risk: Lessons learned from the EMPA-REG outcome study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2016, 39(5): 717-725.
doi: 10.2337/dc16-0041 pmid: 27208375 |
| [36] |
Abdul-Ghani MA, Norton L, Defronzo RA. Renal sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibition in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2015, 309(11): F889-900.
doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00267.2015 URL |
| [37] |
Odden MC, Amadu AR, Smit E, et al. Uric acid levels, kidney function, and cardiovascular mortality in US adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1988-1994 and 1999-2002[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2014, 64(4): 550-557.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.04.024 pmid: 24906981 |
| [38] | 许藏丹, 赵新, 顾文元. 钠-葡萄糖共转运蛋白2抑制剂对伴有严重肾功能不全的2型糖尿病患者心血管保护作用的Meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(1):14-19. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||