Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (8): 741-746.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.08.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cardiopulmonary ultrasound-based initial diagnosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome: Literature reviews of nine cases
Zhao Haotian1a, Yan Yaru2,3, Liu Yuanlin1a, Long Ling1b, Li Li1a( )
)
- 1. a Department of Ultrasound; b Department of Intensive Care Unit, Hebei General Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050000,China
2. Graduate School,Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017,China
3. Department of Ultrasound, Shijiazhuang People’s Hospital,Shijiazhuang 050000,China
-
Received:2023-10-05Online:2024-08-20Published:2024-09-03 -
Contact:Li Li,Email: shrmgnk@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Haotian, Yan Yaru, Liu Yuanlin, Long Ling, Li Li. Cardiopulmonary ultrasound-based initial diagnosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome: Literature reviews of nine cases[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(8): 741-746.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.08.010
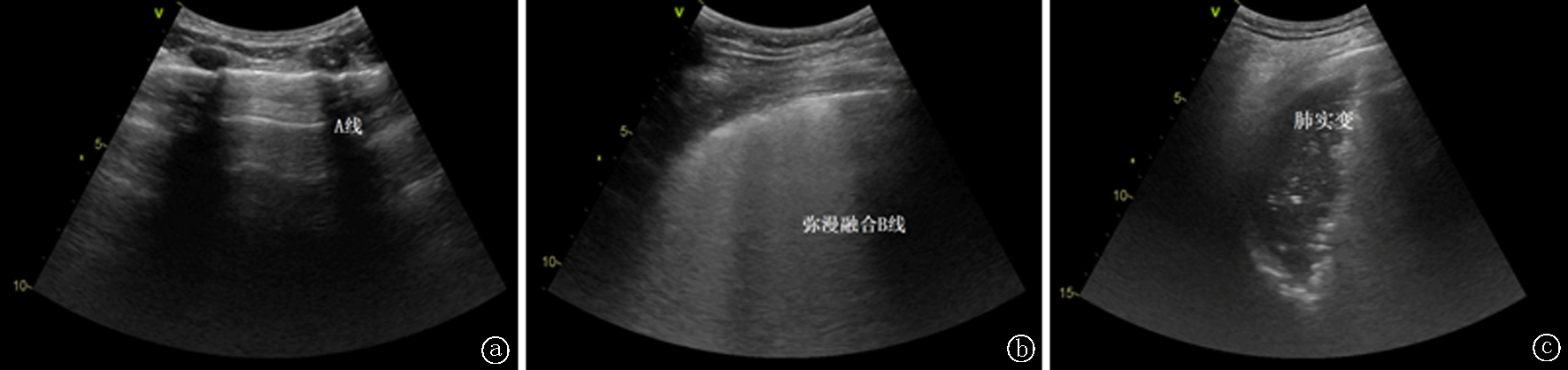
Fig.1 Lung ultrasound manifestations of ARDS a. Lung ultrasound A-line indicates lung ventilation area; b. Diffuse fusion B-line indicates alveolar exudation; c. Lung consolidation indicates collapse of alveoli with loss of ventilation
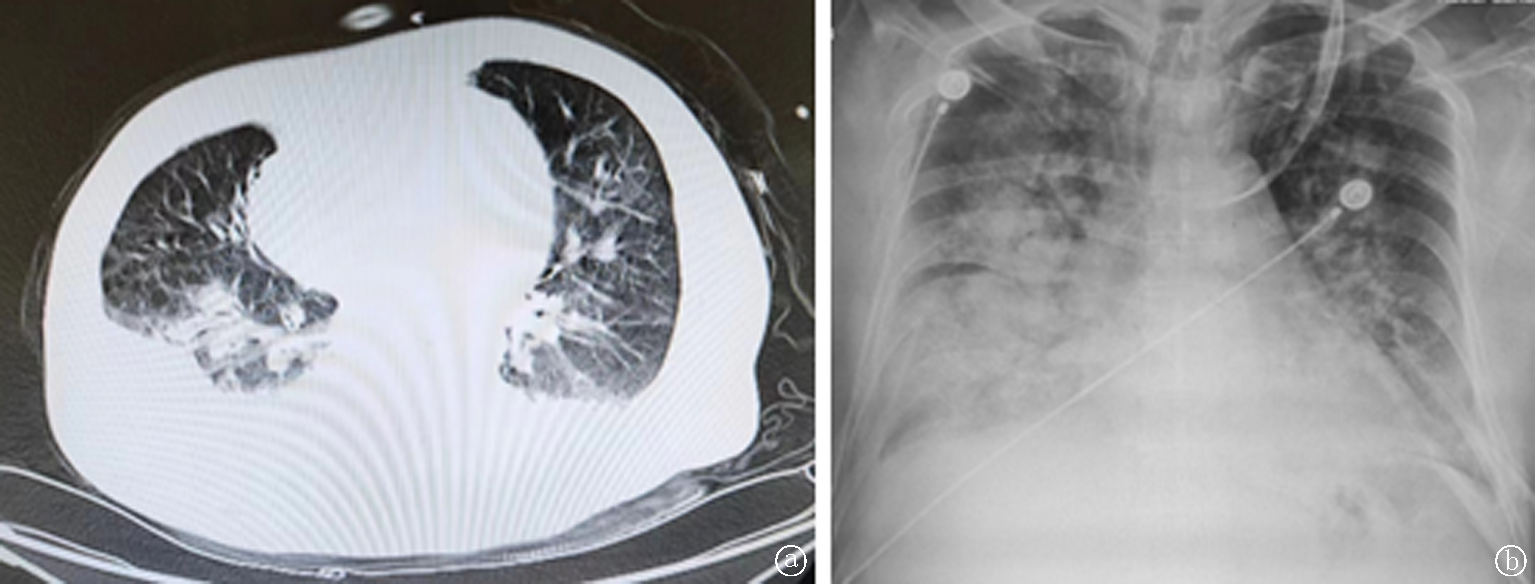
Fig.2 CT and chest X-ray manifestations of ARDS a. CT of ARDS showed multiple exudates in both lungs, consolidation and atelectasis in both lower lungs; b. ARDS chest radiograph shows double lung infiltrates shadows
| 病例 | 性别 | 年龄 (岁) | 来源 | 可能诱因 | 临床表现 | 呼吸频率 (次/min) | 心率 (次/min) | 氧饱和度 (%) | 呼吸支持方式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 男 | 54 | 急诊科 | 异物误吸 | 高热、呼吸困难、憋喘、心率快、低氧血症 | 47 | 126 | 88 | 无创面罩吸氧 |
| 2 | 女 | 79 | 呼吸科 | 肺炎 | 呼吸困难、嗜睡、低氧血症 | 28 | 64 | 95 | 无创面罩吸氧 |
| 3 | 男 | 67 | 胸外科 | 重症肺炎 | 高热、呼吸困难、喘憋、低氧血症 | 24 | 76 | 93 | 鼻导管吸氧 |
| 4 | 男 | 47 | 肾内科 | 脓毒症休克 | 呼吸困难、低血压、意识不清、心率快 | 29 | 110 | 90 | 气管插管+有创通气 |
| 5 | 男 | 85 | 呼吸科 | 重症肺炎 | 高热、呼吸困难、喘憋、心率快、低氧血症 | 31 | 98 | 89 | 鼻导管吸氧 |
| 6 | 女 | 84 | 急诊科 | 重症肺炎 | 高热、呼吸困难、喘憋、烦躁、心率快、低氧血症 | 35 | 99 | 86 | 鼻导管吸氧 |
| 7 | 女 | 52 | 急诊科 | 脓毒症休克 | 呼吸困难、低血压、意识不清、心率快、低氧血症 | 40 | 99 | 83 | 鼻导管吸氧 |
| 8 | 女 | 88 | 急诊科 | 血流感染 | 高热、呼吸困难、喘憋、心率快、低氧血症 | 32 | 101 | 87 | 无创机械通气 |
| 9 | 女 | 66 | 肿瘤科 | 脓毒症休克 | 发热、呼吸困难、低血压、意识不清、心率快、低氧血症 | 47 | 132 | 89 | 无创面罩吸氧 |
Tab.1 General information of nine ARDS patients
| 病例 | 性别 | 年龄 (岁) | 来源 | 可能诱因 | 临床表现 | 呼吸频率 (次/min) | 心率 (次/min) | 氧饱和度 (%) | 呼吸支持方式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 男 | 54 | 急诊科 | 异物误吸 | 高热、呼吸困难、憋喘、心率快、低氧血症 | 47 | 126 | 88 | 无创面罩吸氧 |
| 2 | 女 | 79 | 呼吸科 | 肺炎 | 呼吸困难、嗜睡、低氧血症 | 28 | 64 | 95 | 无创面罩吸氧 |
| 3 | 男 | 67 | 胸外科 | 重症肺炎 | 高热、呼吸困难、喘憋、低氧血症 | 24 | 76 | 93 | 鼻导管吸氧 |
| 4 | 男 | 47 | 肾内科 | 脓毒症休克 | 呼吸困难、低血压、意识不清、心率快 | 29 | 110 | 90 | 气管插管+有创通气 |
| 5 | 男 | 85 | 呼吸科 | 重症肺炎 | 高热、呼吸困难、喘憋、心率快、低氧血症 | 31 | 98 | 89 | 鼻导管吸氧 |
| 6 | 女 | 84 | 急诊科 | 重症肺炎 | 高热、呼吸困难、喘憋、烦躁、心率快、低氧血症 | 35 | 99 | 86 | 鼻导管吸氧 |
| 7 | 女 | 52 | 急诊科 | 脓毒症休克 | 呼吸困难、低血压、意识不清、心率快、低氧血症 | 40 | 99 | 83 | 鼻导管吸氧 |
| 8 | 女 | 88 | 急诊科 | 血流感染 | 高热、呼吸困难、喘憋、心率快、低氧血症 | 32 | 101 | 87 | 无创机械通气 |
| 9 | 女 | 66 | 肿瘤科 | 脓毒症休克 | 发热、呼吸困难、低血压、意识不清、心率快、低氧血症 | 47 | 132 | 89 | 无创面罩吸氧 |
| 病例 | 胸前区(非重力区) | 侧胸壁(中间区域) | 背部(重力依赖区) | 胸腔积液 | 肺超声评分 (分) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 右侧弥漫融合B线, 左侧少量B线 | 双侧局灶性B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 无 | 21 |
| 2 | A线,无异常 | 双侧少量B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 双侧少量 | 11 |
| 3 | A线,无异常 | 右侧少量B线 | 右侧少量B线,左侧弥漫融合B线 | 无 | 8 |
| 4 | 双侧多发B线 | 双侧弥漫融合B线 | 双侧弥漫融合B线 | 仅右侧少量 | 20 |
| 5 | 右侧少量B线 | 右侧肺实变,左侧弥漫性B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 仅右侧少量 | 21 |
| 6 | 双侧少量B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 右侧中量,左侧少量 | 24 |
| 7 | 右侧局部融合B线 | 右侧少量B线,左侧弥漫性B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 无 | 16 |
| 8 | 右侧少量B线 | 双侧多发局灶性B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 无 | 14 |
| 9 | 双侧弥漫B线 | 双侧弥漫性B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 无 | 21 |
Tab.2 Lung ultrasound imaging characteristics of nine ARDS patients
| 病例 | 胸前区(非重力区) | 侧胸壁(中间区域) | 背部(重力依赖区) | 胸腔积液 | 肺超声评分 (分) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 右侧弥漫融合B线, 左侧少量B线 | 双侧局灶性B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 无 | 21 |
| 2 | A线,无异常 | 双侧少量B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 双侧少量 | 11 |
| 3 | A线,无异常 | 右侧少量B线 | 右侧少量B线,左侧弥漫融合B线 | 无 | 8 |
| 4 | 双侧多发B线 | 双侧弥漫融合B线 | 双侧弥漫融合B线 | 仅右侧少量 | 20 |
| 5 | 右侧少量B线 | 右侧肺实变,左侧弥漫性B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 仅右侧少量 | 21 |
| 6 | 双侧少量B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 右侧中量,左侧少量 | 24 |
| 7 | 右侧局部融合B线 | 右侧少量B线,左侧弥漫性B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 无 | 16 |
| 8 | 右侧少量B线 | 双侧多发局灶性B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 无 | 14 |
| 9 | 双侧弥漫B线 | 双侧弥漫性B线 | 双侧肺实变,伴碎片征、支气管征 | 无 | 21 |
| 病例 | 左心结构和功能 | 右心结构和功能 | IVC指标 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVEF (%) | E/e’ | PCWP (mmHg) | RVEDD/ LVEDD | TAPSE (mm) | 肺动脉压力 (mmHg) | “D字征” 表现 | IVCD (mm) | IVCV (%) | |||
| 1 | 73 | 7.37 | 11.03 | 0.80 | 18.7 | 52 | 是 | 17.5 | 46.9 | ||
| 2 | 54 | 12.87 | 17.86 | 0.84 | 15.8 | 69 | 否 | 20.6 | 30.6 | ||
| 3 | 64 | 8.85 | 12.88 | 0.97 | 17.6 | 39 | 否 | 16.5 | 37.0 | ||
| 4 | 71 | 10.21 | 14.56 | 0.79 | 18.4 | 25 | 否 | 18.1 | 17.1 | ||
| 5 | 61 | 16.08 | 21.84 | 1.03 | 19.1 | 50 | 否 | 21.7 | 25.8 | ||
| 6 | 61 | 11.83 | 16.57 | 1.02 | 14.3 | 81 | 是 | 22.0 | 15.9 | ||
| 7 | 76 | 9.15 | 13.25 | 1.28 | 7.2 | 90 | 是 | 30.9 | 10.7 | ||
| 8 | 58 | 6.53 | 10.00 | 1.09 | 19.1 | 52 | 否 | 16.1 | 36.6 | ||
| 9 | 79 | 11.80 | 16.54 | 0.97 | 30 | 56 | 否 | 21.1 | 14.7 | ||
Tab.3 Cardiac ultrasound imaging characteristics of nine ARDS patients
| 病例 | 左心结构和功能 | 右心结构和功能 | IVC指标 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVEF (%) | E/e’ | PCWP (mmHg) | RVEDD/ LVEDD | TAPSE (mm) | 肺动脉压力 (mmHg) | “D字征” 表现 | IVCD (mm) | IVCV (%) | |||
| 1 | 73 | 7.37 | 11.03 | 0.80 | 18.7 | 52 | 是 | 17.5 | 46.9 | ||
| 2 | 54 | 12.87 | 17.86 | 0.84 | 15.8 | 69 | 否 | 20.6 | 30.6 | ||
| 3 | 64 | 8.85 | 12.88 | 0.97 | 17.6 | 39 | 否 | 16.5 | 37.0 | ||
| 4 | 71 | 10.21 | 14.56 | 0.79 | 18.4 | 25 | 否 | 18.1 | 17.1 | ||
| 5 | 61 | 16.08 | 21.84 | 1.03 | 19.1 | 50 | 否 | 21.7 | 25.8 | ||
| 6 | 61 | 11.83 | 16.57 | 1.02 | 14.3 | 81 | 是 | 22.0 | 15.9 | ||
| 7 | 76 | 9.15 | 13.25 | 1.28 | 7.2 | 90 | 是 | 30.9 | 10.7 | ||
| 8 | 58 | 6.53 | 10.00 | 1.09 | 19.1 | 52 | 否 | 16.1 | 36.6 | ||
| 9 | 79 | 11.80 | 16.54 | 0.97 | 30 | 56 | 否 | 21.1 | 14.7 | ||
| 病例 | 条目1:一 周内急性起 病或原有呼 吸症状加重 | 条目2:X线或CT显示不均匀浸润影 | 条目3:肺水肿不能用心源性或容量过负荷解释 | 条目4: 氧合指数 (mmHg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 临床确诊: X线或CT 显示浸润影 | 肺超声 | 临床诊断(体格检查、 实验室检查、血流动力学 监测等) | 心脏超声 | 肺超声 | ||||
| 1 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,背部肺实变 | BNP不高,心脏无增大表现 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 111.00 | |
| 2 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,背部肺实变 | BNP不高,心脏无增大表现 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 134.17 | |
| 3 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线 | BNP不高,心脏无增大表现 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 196.67 | |
| 4 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线 | 血流动力学监测显示PCWP不高 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 53.00 | |
| 5 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,右侧壁、双背部肺实变 | 血流动力学监测显示PCWP不高 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP超出阈值 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 197.09 | |
| 6 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,侧壁、背部肺实变 | 无心衰表现 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 93.49 | |
| 7 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,背部肺实变 | 无心衰表现 | LVEF增高,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 232.97 | |
| 8 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,背部肺实变 | 血流动力学监测显示PCWP不高 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 142.75 | |
| 9 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,背部肺实变 | 血流动力学监测显示PCWP不高 | LVEF增高,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 171.81 | |
Tab.4 Consistency of cardiopulmonary ultrasound characteristics with Berlin Definition in nine ARDS patients
| 病例 | 条目1:一 周内急性起 病或原有呼 吸症状加重 | 条目2:X线或CT显示不均匀浸润影 | 条目3:肺水肿不能用心源性或容量过负荷解释 | 条目4: 氧合指数 (mmHg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 临床确诊: X线或CT 显示浸润影 | 肺超声 | 临床诊断(体格检查、 实验室检查、血流动力学 监测等) | 心脏超声 | 肺超声 | ||||
| 1 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,背部肺实变 | BNP不高,心脏无增大表现 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 111.00 | |
| 2 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,背部肺实变 | BNP不高,心脏无增大表现 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 134.17 | |
| 3 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线 | BNP不高,心脏无增大表现 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 196.67 | |
| 4 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线 | 血流动力学监测显示PCWP不高 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 53.00 | |
| 5 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,右侧壁、双背部肺实变 | 血流动力学监测显示PCWP不高 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP超出阈值 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 197.09 | |
| 6 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,侧壁、背部肺实变 | 无心衰表现 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 93.49 | |
| 7 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,背部肺实变 | 无心衰表现 | LVEF增高,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 232.97 | |
| 8 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,背部肺实变 | 血流动力学监测显示PCWP不高 | LVEF正常,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 142.75 | |
| 9 | 是 | 是 | 双肺多发不均匀B线,背部肺实变 | 血流动力学监测显示PCWP不高 | LVEF增高,E/e’、PCWP不高 | 不符合心源性肺水肿表现 | 171.81 | |
| [1] |
Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, et al. Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(8):788-800.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0291 pmid: 26903337 |
| [2] |
Ferguson ND, Frutos-Vivar F, Esteban A, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: Under recognition by clinicians and diagnostic accuracy of three clinical definitions[J]. Crit Care Med, 2005, 33(10):2228-2234.
doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000181529.08630.49 pmid: 16215375 |
| [3] |
ARDS Definition Task Force, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin definition[J]. JAMA, 2012, 307(23):2526-2533.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.5669 pmid: 22797452 |
| [4] | 黄超, 王凤霞, 冯小倩, 等. 危重症患者左室舒张功能不全与住院死亡率及预后的关系[J]. 中国心血管杂志, 2022, 27(4):319-324. |
| [5] | Matthay MA, Arabi Y, Arroliga AC, et al. A new global definition of acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2024, 209(1):37-47. |
| [6] |
Bos LDJ, Ware LB. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: Causes, pathophysiology, and phenotypes[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400(10358):1145-1156.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01485-4 pmid: 36070787 |
| [7] | Long L, Zhao HT, Zhang ZY, et al. Lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumonia in adults: A meta-analysis[J]. Medicine, 2017, 96(3):e5713. |
| [8] | 赵浩天, 白杨, 燕亚茹, 等. 肺超声—理论与临床诊断规范[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术文献出版社, 2023. |
| [9] |
Chiumello D, Umbrello M, Sferrazza Papa GF, et al. Global and regional diagnostic accuracy of lung ultrasound compared to CT in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Crit Care Med, 2019, 47(11):1599-1606.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003971 pmid: 31464770 |
| [10] | 刘元琳, 赵浩天, 刘奕, 等. 肺超声与胸部CT评价社区获得性肺炎的一致性研究[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2022, 38(8):841-844. |
| [11] |
Deeb MA, Barbic S, Featherstone R, et al. Point-of-care ultrasonography for the diagnosis of acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema in patients presenting with acute dyspnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Acad Emerg Med, 2014, 21(8):843-852.
doi: 10.1111/acem.12435 pmid: 25176151 |
| [12] | 赵浩天, 李丽, 赵鹤龄, 等. 心肺超声在成人急性呼吸困难中的应用:心源性肺水肿与肺炎的鉴别诊断模型构建[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2023, 32(3) : 242-249. |
| [13] | Mojoli F, Bouhemad B, Mongodi S, et al. Lung ultrasound for critically ill patients[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2019, 199(6):701-714. |
| [14] |
Zhou Y, Cheng J, Zhu S, et al. Early pathophysiology-driven airway pressure release ventilation versus low tidal volume ventilation strategy for patients with moderate-severe ARDS: Study protocol for a randomized, multicenter, controlled trial[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2024, 24(1):252.
doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03065-y pmid: 38783268 |
| [15] | Dong LJ, Li J, Liu W, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of lung ultrasound in cardiogenic pulmonary edema: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2023, 27(15):6947-6955. |
| [16] | Merkl T, Astapenko D, Stichhauer R, et al. Exogenous surfactant for lung contusion causing ARDS: A systematic review of clinical and experimental reports[J]. Clin Respir J, 2024, 18(5):e13776. |
| [17] | Casitas R, Galera R, Torres-Vargas M, et al. Medium-term disability and long-term functional impairment persistence in survivors of severe COVID-19 ARDS: Clinical and physiological insights[J]. Arch Bronconeumol, 2024:S0300-2896(24)00185-186. Epub ahead of print. |
| [18] | Tran TK, Tran MC, Joseph A, et al. A systematic review of machine learning models for management, prediction and classification of ARDS[J]. Respir Res, 2024, 25(1):232. |
| [19] |
Huppert LA, Matthay MA, Ware LB. Pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Semin Respir Crit Care Med, 2019, 40(1):31-39.
doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1683996 pmid: 31060086 |
| [20] | 河北省医学会超声分会, 河北省医师协会超声医师分会, 河北省超声医学质量管理与控制中心, 等. 急性呼吸困难床旁肺超声诊断规范专家建议[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2024, 23(3):257-265. |
| [21] | Zochios V, Yusuff H, Schmidt M. Protecting the Right Ventricle Network (PRORVnet). Acute right ventricular injury phenotyping in ARDS[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2023, 49(1):99-102. |
| [22] | Muñoz Moreno JF, Rubio Prieto E, Magro Martín MÁ. Lung ultrasound in ARDS: B-lines pattern and shred sign[J]. Arch Bronconeumol, 2024, 60(3):180. |
| [23] | Dayan RR, Blau M, Taylor J, et al. Lung ultrasound is associated with distinct clinical phenotypes in COVID-19 ARDS: A retrospective observational study[J]. PLoS One, 2024, 19(6):e0304508. |
| [24] | Costamagna A, Steinberg I, Pivetta E, et al. Clinical performance of lung ultrasound in predicting time-dependent changes in lung aeration in ARDS patients[J]. J Clin Monit Comput, 2023, 37(2):473-480. |
| [25] | 曾学英, 尹万红, 周然, 等. 庖丁解牛—重症超声检查融合多元监测掌握重症之肺[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(2):175-180. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||