Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 225-229.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.03.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Predictive value of procalcitonin clearance and SOFA score on the prognosis of patients with severe sepsis
- Department of Critical Care Medicine, Third Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, China
-
Received:2021-10-12Online:2022-03-20Published:2022-04-02 -
Contact:Zhu Yong E-mail:zy19711209@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Mengyuan, Zhu Yong. Predictive value of procalcitonin clearance and SOFA score on the prognosis of patients with severe sepsis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 225-229.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.03.005
| 项目 | 存活组 (n=44) | 死亡组 (n=16) | t/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 30(68.2) 14(31.8) | 9(56.3) 7(43.7) | 0.065 | 0.782 |
| 年龄(岁) | 63.94±12.36 | 68.90±12.91 | -1.986 | 0.009 |
| 体温(℃) | 37.88±0.69 | 37.62±0.75 | 1.236 | 0.675 |
| 收缩压(mm Hg) | 109.64±23.64 | 117.23±24.01 | 2.161 | 0.198 |
| 舒张压(mm Hg) | 79.97±12.05 | 79.31±10.27 | 0.276 | 0.843 |
| 呼吸频率(次/min) | 19.25±3.78 | 21.46±4.87 | -3.725 | 0.421 |
| 感染部位[例(%)] | ||||
| 腹腔 | 19(43.1) | 7(43.7) | 0.009 | 0.941 |
| 肺 | 9(20.4) | 4(25.0) | 0.401 | 0.594 |
| 尿路 | 8(18.1) | 3(18.7) | 1.047 | 0.246 |
| 中枢 | 2(4.6) | 0(0) | 0.371 | 0.500 |
| 血行 | 6(13.6) | 2(12.5) | 1.214 | 0.298 |
| 合并症[例(%)] | ||||
| 糖尿病 | 6(13.6) | 7(43.7) | 5.445 | 0.021 |
| 高血压 | 22(50.8) | 9(56.2) | 3.485 | 0.055 |
| 慢性肺病 | 11(25.0) | 4(27.5) | 0.514 | 0.489 |
| 冠心病 | 8(35.2) | 4(27.5) | 0.024 | 0.864 |
| 肝胆疾病 | 7(16.1) | 3(18.7) | 1.127 | 0.307 |
| 慢性肾病 | 14(34.1) | 5(31.4) | 1.356 | 0.275 |
| 项目 | 存活组 (n=44) | 死亡组 (n=16) | t/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 30(68.2) 14(31.8) | 9(56.3) 7(43.7) | 0.065 | 0.782 |
| 年龄(岁) | 63.94±12.36 | 68.90±12.91 | -1.986 | 0.009 |
| 体温(℃) | 37.88±0.69 | 37.62±0.75 | 1.236 | 0.675 |
| 收缩压(mm Hg) | 109.64±23.64 | 117.23±24.01 | 2.161 | 0.198 |
| 舒张压(mm Hg) | 79.97±12.05 | 79.31±10.27 | 0.276 | 0.843 |
| 呼吸频率(次/min) | 19.25±3.78 | 21.46±4.87 | -3.725 | 0.421 |
| 感染部位[例(%)] | ||||
| 腹腔 | 19(43.1) | 7(43.7) | 0.009 | 0.941 |
| 肺 | 9(20.4) | 4(25.0) | 0.401 | 0.594 |
| 尿路 | 8(18.1) | 3(18.7) | 1.047 | 0.246 |
| 中枢 | 2(4.6) | 0(0) | 0.371 | 0.500 |
| 血行 | 6(13.6) | 2(12.5) | 1.214 | 0.298 |
| 合并症[例(%)] | ||||
| 糖尿病 | 6(13.6) | 7(43.7) | 5.445 | 0.021 |
| 高血压 | 22(50.8) | 9(56.2) | 3.485 | 0.055 |
| 慢性肺病 | 11(25.0) | 4(27.5) | 0.514 | 0.489 |
| 冠心病 | 8(35.2) | 4(27.5) | 0.024 | 0.864 |
| 肝胆疾病 | 7(16.1) | 3(18.7) | 1.127 | 0.307 |
| 慢性肾病 | 14(34.1) | 5(31.4) | 1.356 | 0.275 |
| 组别 | 例数 | PCT0 h | PCT24 h | PCT48 h | PCT72 h | PCT120 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 存活组 | 44 | 0.65±0.07 | 0.74±0.17 | 0.94±0.24 | 0.89±0.24 | 0.64±0.38* | |||
| 死亡组 | 16 | 1.48±0.14 | 1.32±0.36 | 0.89±0.53 | 0.98±0.52 | 0.82±0.74* | |||
| 组间 | F=6.929 P=0.011 | ||||||||
| 不同时点 | F=1.089 P=0.373 | ||||||||
| 组间·不同时点 | F=8.441 P=0.000 | ||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | PCTc24 h | PCTc48 h | PCTc72 h | PCTc120 h | ||||
| 存活组 | 44 | 0.10±0.32# | 0.35±0.22# | 0.64±0.10* | 0.82±0.08# | ||||
| 死亡组 | 16 | -0.59±0.83# | -1.58±2.32# | -0.24±1.02* | -0.11±0.89# | ||||
| 组间 | F=32.027 P=0.000 | ||||||||
| 不同时点 | F=39.449 P=0.000 | ||||||||
| 组间·不同时点 | F=5.781 P=0.002 | ||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | PCT0 h | PCT24 h | PCT48 h | PCT72 h | PCT120 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 存活组 | 44 | 0.65±0.07 | 0.74±0.17 | 0.94±0.24 | 0.89±0.24 | 0.64±0.38* | |||
| 死亡组 | 16 | 1.48±0.14 | 1.32±0.36 | 0.89±0.53 | 0.98±0.52 | 0.82±0.74* | |||
| 组间 | F=6.929 P=0.011 | ||||||||
| 不同时点 | F=1.089 P=0.373 | ||||||||
| 组间·不同时点 | F=8.441 P=0.000 | ||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | PCTc24 h | PCTc48 h | PCTc72 h | PCTc120 h | ||||
| 存活组 | 44 | 0.10±0.32# | 0.35±0.22# | 0.64±0.10* | 0.82±0.08# | ||||
| 死亡组 | 16 | -0.59±0.83# | -1.58±2.32# | -0.24±1.02* | -0.11±0.89# | ||||
| 组间 | F=32.027 P=0.000 | ||||||||
| 不同时点 | F=39.449 P=0.000 | ||||||||
| 组间·不同时点 | F=5.781 P=0.002 | ||||||||
| SOFA评分 (分) | 存活组 (n=44) | 死亡组 (n=16) | t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOFA0 h | 6.43±2.55 | 13.56±2.83 | -8.864 | <0.01 |
| 48 h△SOFA | 1.61±1.63 | -1.31±1.66 | 6.060 | <0.01 |
| SOFA评分 (分) | 存活组 (n=44) | 死亡组 (n=16) | t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOFA0 h | 6.43±2.55 | 13.56±2.83 | -8.864 | <0.01 |
| 48 h△SOFA | 1.61±1.63 | -1.31±1.66 | 6.060 | <0.01 |
| 因素 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | HR | P值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 年龄>65岁 | 0.059 | 0.018 | 11.208 | 1.060 | 0.000 | 1.025 | 1.099 |
| 糖尿病 | 0.216 | 0.150 | 2.058 | 1.241 | 0.851 | 0.924 | 1.665 |
| PCT120 h | 0.070 | 0.044 | 2.563 | 1.072 | 0.109 | 0.984 | 1.168 |
| PCTc24 h | -0.104 | 0.052 | 4.034 | 0.901 | 0.045 | 0.814 | 0.997 |
| PCTc48 h | -0.649 | 0.652 | 0.989 | 0.523 | 0.320 | 0.146 | 1.877 |
| PCTc72 h | |||||||
| PCTc120 h | -0.823 | 0.231 | 12.742 | 0.439 | 0.000 | 0.279 | 0.690 |
| SOFA0 h | 0.620 | 0.134 | 21.455 | 1.859 | 0.000 | 1.430 | 2.417 |
| 48 h△SOFA | -0.254 | 0.107 | 5.616 | 0.766 | 0.018 | 0.629 | 0.957 |
| 因素 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | HR | P值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 年龄>65岁 | 0.059 | 0.018 | 11.208 | 1.060 | 0.000 | 1.025 | 1.099 |
| 糖尿病 | 0.216 | 0.150 | 2.058 | 1.241 | 0.851 | 0.924 | 1.665 |
| PCT120 h | 0.070 | 0.044 | 2.563 | 1.072 | 0.109 | 0.984 | 1.168 |
| PCTc24 h | -0.104 | 0.052 | 4.034 | 0.901 | 0.045 | 0.814 | 0.997 |
| PCTc48 h | -0.649 | 0.652 | 0.989 | 0.523 | 0.320 | 0.146 | 1.877 |
| PCTc72 h | |||||||
| PCTc120 h | -0.823 | 0.231 | 12.742 | 0.439 | 0.000 | 0.279 | 0.690 |
| SOFA0 h | 0.620 | 0.134 | 21.455 | 1.859 | 0.000 | 1.430 | 2.417 |
| 48 h△SOFA | -0.254 | 0.107 | 5.616 | 0.766 | 0.018 | 0.629 | 0.957 |
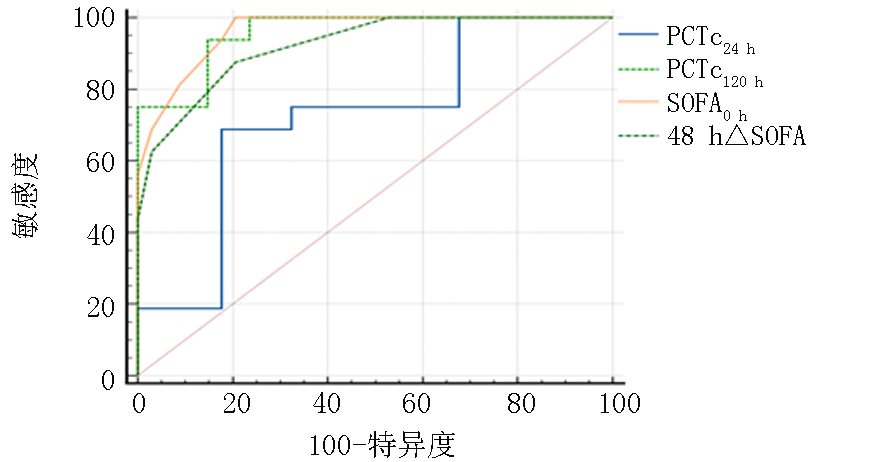
| 指标 | AUC | 标准误 | P值 | 95%CI | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||||
| PCTc24 h | 0.722 | 0.079 | 0.005 | 0.578 | 0.840 | 68.70 | 82.40 | 0.511 | 0.101 |
| PCTc120 h | 0.958 | 0.064 | <0.01 | 0.860 | 0.994 | 93.70 | 85.30 | 0.896 | 0.756 |
| SOFA0 h | 0.962 | 0.0218 | <0.01 | 0.866 | 0.996 | 90.34 | 79.41 | 0.794 | 7.000 |
| 48 h△SOFA | 0.922 | 0.058 | <0.01 | 0.810 | 0.979 | 87.50 | 79.40 | 0.872 | 0.000 |
| 指标 | AUC | 标准误 | P值 | 95%CI | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||||
| PCTc24 h | 0.722 | 0.079 | 0.005 | 0.578 | 0.840 | 68.70 | 82.40 | 0.511 | 0.101 |
| PCTc120 h | 0.958 | 0.064 | <0.01 | 0.860 | 0.994 | 93.70 | 85.30 | 0.896 | 0.756 |
| SOFA0 h | 0.962 | 0.0218 | <0.01 | 0.866 | 0.996 | 90.34 | 79.41 | 0.794 | 7.000 |
| 48 h△SOFA | 0.922 | 0.058 | <0.01 | 0.810 | 0.979 | 87.50 | 79.40 | 0.872 | 0.000 |
| [1] |
Fernando SM, Rochwerg B, Seely AJE. Clinical implications of the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3)[J]. CMAJ, 2018, 190(36):1058-1059.
doi: 10.1503/cmaj.170149 pmid: 30201611 |
| [2] |
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease study[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10219):200-211.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7 URL |
| [3] | 慕婉晴, 周燕南, 胡延妍, 等. 降钙素原(PCT)在脓毒症临床诊断治疗中作用的研究进展[J]. 复旦学报(医学版), 2019, 46(1):103-107. |
| [4] | Hu L, Shi Q, Shi M, et al. Diagnostic value of PCT and CRP for detecting serious bacterial infections in patients with fever of unknown origin: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol, 2017, 25(8):61-69. |
| [5] | 陈真真, 张文祥, 刘志婷, 等. 血乳酸清除率和血清降钙素原清除率对脓毒性休克患儿预后的预测价值[J]. 中国循证儿科杂志, 2019, 14(6):448-452. |
| [6] | 熊庄莉. 血乳酸、D-二聚体、降钙素原动态监测对老年重症肺炎预后的临床价值[D]. 山东中医药大学, 2018. |
| [7] |
Seymour CW, Liu VX, Iwashyna TJ, et al. Assessment of clinical criteria for sepsis: For the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3)[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(8):762-774.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0288 URL |
| [8] | 丁佳, 皋源. PCT清除率与△SOFA在复杂腹腔感染中的预测价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2016, 32(24):4034-4037. |
| [9] | 刘炳炜, 徐燕平, 席绍松, 等. SOFA评分联合PCT检测对脓毒症患者病情及其预后的临床评估价值[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(3):391-393. |
| [10] | 曹钰, 柴艳芬, 邓颖, 等. 中国脓毒症/脓毒性休克急诊治疗指南(2018)[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2018, 19(9):567-588. |
| [11] | 朱美英, 曹鄂洪. 降钙素原的检测和应用——《感染相关生物标志物临床意义解读专家共识》解读[J]. 上海医药, 2018, 39(1):14-18. |
| [12] | 李俊岭, 邓涛, 吴汉聪. 降钙素原清除率对严重脓毒症预后的预测价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2017, 33(2):262-264. |
| [13] |
Karlsson S, Heikkinen M, Alila S, et al. Predictive value of procalcitonin decrease in patients with severe sepsis: A prospective observational study[J]. Crit Care, 2010, 14(6):205.
doi: 10.1186/cc8219 URL |
| [14] | 颜默磊, 蔡国龙, 胡才宝, 等. 降钙素原清除率对老年严重脓毒症/脓毒性休克预后的预测价值[J]. 浙江医学, 2017, 39(9):708-712. |
| [15] |
Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine[J]. Intensive Care Med, 1996, 22(7):707-710.
doi: 10.1007/BF01709751 URL |
| [16] | 魏薇, 夏义琴, 曹钰. 快速序贯器官衰竭评分对脓毒症休克早期预测能力评价[J]. 华西医学, 2017, 32(6):812-818. |
| [17] | 杜斌, 陈德昌, 刘大为, 等. 感染相关的器官衰竭评分对多器官功能障碍综合征预后判断的意义[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2001(2):16-19. |
| [18] | 丁佳, 皋源. PCT清除率与△SOFA在复杂腹腔感染中的预测价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2016, 32(24):4034-4037. |
| [19] | 高磊, 鲍万国, 齐翀, 等. 降钙素原及其变化率联合序贯器官衰竭评分对脓毒症病情与预后判别的临床价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2019, 35(17):2789-2793. |
| [1] | Huang Saihu, Long Zhongjie, Dong Xingqiang, Meng Xiangying, Wu Shuiyan, Bai Zhenjiang. Pathogen and clinical characteristics of children with hematologic neoplasms complicated with sepsis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 38-42. |
| [2] | Liu Lili, Yuan Yuting, Lai Gengliang, Tian Chuan, Lan Xiang, Ye Zhonglv. The relationship between minimal residual disease on day 15 and prognosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 47-52. |
| [3] | Wang Tao, Gao Yuwei, Wang Xinghua, Hu Xiuhong, Cui Hongrui, Xu Baozhen, Yang Hongjuan. Correlation of anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody with idiopathic membranous nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(7): 606-612. |
| [4] | Sun Xingxing, Lin Hai. Changes in immune function and prognostic risk factors for severe pneumonia in children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(6): 521-525. |
| [5] | Gao Qinyu, Bao Beiyan, Jin Yan, Zhao Yu. Analysis of clinical features and prognostic factors of IgA nephropathy complicated with depression [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(6): 510-515. |
| [6] | He Xiangyu, Pan Yan, Zhang Xiaolin. Correlation between serum lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 level and the severity and prognosis of acute ischemic stroke [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(4): 315-318. |
| [7] | Yang Jinqiang, Zhang Renmin. Prognostic value of procalcitonin to platelet ratio in patients with fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(4): 346-351. |
| [8] | Tang Aijun, Wang Liwei. Predictive values of platelet count and coagulation index in the 28-day survival of sepsis patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(3): 250-254. |
| [9] | Zhang Na, Sun Yue, Dong Han, Zhao Peng, Yang Xin, Qi Yuan, Wang Lingling. Correlation between the expression level of SPARC and prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(11): 972-978. |
| [10] | Zhou Lijuan, Zhu Pengwei, Cao Mei, Cheng Zhenmei, Wu Qiaowei, Li Yong. Correlation of serum ferritin, erythrocyte parameters and D-dimer with sepsis in children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(1): 60-63. |
| [11] | Wang Huixin, Zhao Fangqing, Zhang Xinyan, Hou Xiaowen. Relationship between uric acid and prognosis of Chinese patients with acute ischemic stroke: A meta analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(9): 785-790. |
| [12] | Ye Qian, Ling Zhai, Liu Shenxiang, Lu Guotao, Yin Xudong. Meta analysis on effects of glucocorticoid on the immunotherapy of advanced cancer [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(7): 591-598. |
| [13] | Zhou Bin, Zeng Cizheng, Huang Yuge, Zhong Mianling, Wu Jiayuan. Effect of pSOFA score combined with C-reactive protein and procalcitonin in prognosis assessment of sepsis children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(7): 616-622. |
| [14] | Gao Pengli, Chen Lili, Tian Fen, Zhang Jiaqian, Chen Yipeng, Qi Xiaojing, Xing Guangqun. Impact of body mass index in the clinicopathology and prognosis of patients with IgA nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 234-242. |
| [15] | Wang Xiaoqin, Zhou Youfeng, Lin Binrong. Exploring factors influencing adverse prognosis in children with acute encephalitis/ encephalopathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(11): 1017-1020. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||