

临床荟萃 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 84-88.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.01.018
张立愔1,2, 许龙1a, 吕冬云1a( ), 孙睿1a, 张国超1b, 盛雪1b
), 孙睿1a, 张国超1b, 盛雪1b
收稿日期:2020-06-25
出版日期:2021-01-20
发布日期:2021-01-16
通讯作者:
吕冬云
E-mail:110526551@qq.com
Received:2020-06-25
Online:2021-01-20
Published:2021-01-16
摘要:
通过整理当前的关键发现并对当前研究中面临的问题进行归纳。叙述了肠道菌群对阿尔兹海默症(Alzheimer's disease,AD)发病机制及影响。实验研究结果发现,微生物细菌分泌物对AD发病产生相关影响,如脆弱拟杆菌释放的脂多糖(BF-LPS),暴露于人体中枢神经系统后,促进AD病程的进一步发展,对机体免疫反应和认知功能产生显著改变。其次通过益生菌治疗影响人体肠道微生态平衡以及饮食方面的自主改变等外界干预,对逆转AD病程具有重要作用。
中图分类号:
张立愔, 许龙, 吕冬云, 孙睿, 张国超, 盛雪. 肠道微生物菌群对阿尔兹海默症的相关作用机制[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(1): 84-88.
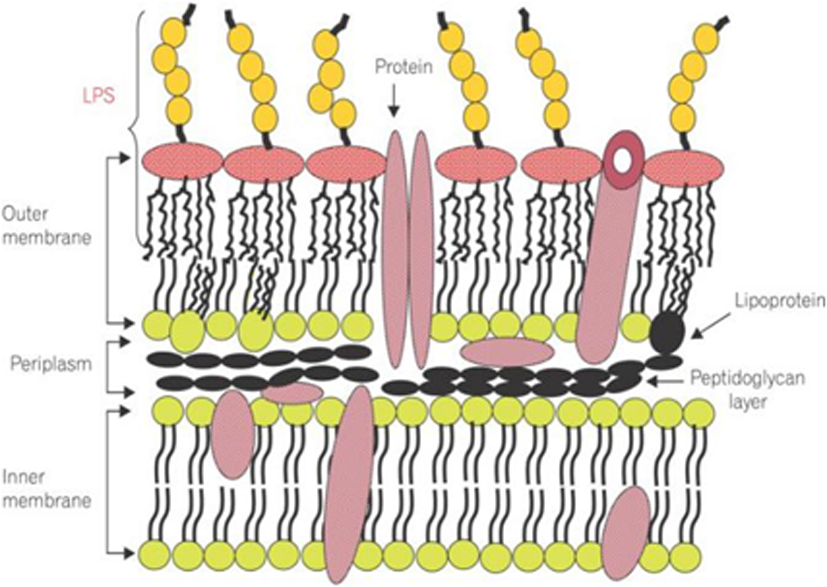
图1 革兰阴性菌包膜组成中的LPS (摘自于Rhee SH. Lipopolysaccharide: basic biochemistry, intracellular signaling, and physiological impacts in the gut[J]. Intest Res, 2014, 12(2):90-95)
| [1] | Bhattacharjee S, Lukiw WJ . Alzheimer's disease and the microbiome[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2013,7(153):153. |
| [2] |
Galland L. The gut microbiome and the brain[J]. J Med Food, 2014,17(12):1261-1272.
doi: 10.1089/jmf.2014.7000 pmid: 25402818 |
| [3] |
Liu Y, Du Y, Liu W, et al. Lack of association between NLGN3, NLGN4, SHANK2 and SHANK3 gene variants and autism spectrum disorder in a Chinese population[J]. PLoS One, 2013;, 8(2):e56639.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056639 URL |
| [4] |
Tükel C, Wilson RP, Nishimori JH, et al. Responses to amyloids of microbial and host origin are mediated through toll-like receptor 2[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2009,6(1):45-53.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2009.05.020 URL |
| [5] |
Youssef NH, Couger MB, McCully AL, et al. Assessing the global phylum level diversity within the bacterial domain: A review[J]. J Adv Res, 2015,6(3):269-282.
doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2014.10.005 pmid: 26257925 |
| [6] |
Lukiw WJ. The microbiome, microbial-generated proinflammatory neurotoxins, and Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Sport Health Sci, 2016,5(4):393-396.
doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2016.08.008 URL |
| [7] |
Sassá MF, Saturi AE, Souza LF, et al. Response of macrophage Toll-like receptor 4 to a Sporothrix schenckii lipid extract during experimental sporotrichosis[J]. Immunology, 2009,128(2):301-309.
doi: 10.1111/imm.2009.128.issue-2 URL |
| [8] |
Kram V, Kilts TM, Bhattacharyya N, et al. Small leucine rich proteoglycans, a novel link to osteoclastogenesis[J]. Sci Rep, 2017,7(1):12627.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12651-6 URL |
| [9] |
Blanco LP, Evans ML, Smith DR, et al. Diversity, biogenesis and function of microbial amyloids[J]. Trends Microbiol, 2012,20:66-73.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2011.11.005 URL |
| [10] |
Zhao Y, Dua P, Lukiw WJ. Microbial Sources of Amyloid and Relevance to Amyloidogenesis and Alzheimer's Disease (AD)[J]. J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism, 2015,5(1):177.
pmid: 25977840 |
| [11] | Hill JM, Lukiw WJ. Microbial-generated amyloids and Alzheimer's disease (AD)[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2015,7:9. |
| [12] |
Sampson TR, Mazmanian SK. Control of brain development, function, and behavior by the microbiome cell host microbe[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2015,17:565-576.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.04.011 URL |
| [13] |
von Mikecz A. Pathology and function of nuclear amyloid. Protein homeostasis matters[J]. Nucleus, 2014,5(4):311-317.
doi: 10.4161/nucl.29404 pmid: 25482120 |
| [14] |
Maldonado RF, Sá-Correia I, Valvano MA. Lipopolysaccharide modification in Gram-negative bacteria during chronic infection[J]. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 2016,40(4):480-493.
doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuw007 URL |
| [15] | Barczynska R, Slizewska K, Litwin M, et al. Effects of dietary fiber preparations made from maize starch on the growth and activity of selected bacteria from the Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria phyla in fecal samples from obese children[J]. Acta Biochim Pol, 2016,63(2):261-266. |
| [16] |
Rhee SH. Lipopolysaccharide: basic biochemistry, intracellular signaling, and physiological impacts in the gut[J]. Intest Res, 2014,12(2):90-95.
doi: 10.5217/ir.2014.12.2.90 URL |
| [17] |
Xiao X, Sankaranarayanan K, Khosla C. Biosynjournal and structure-activity relationships of the lipid a family of glycolipids[J]. Curr Opin Chem Biol, 2017,40:127-137.
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.07.008 URL |
| [18] |
Choi VM, Herrou J, Hecht AL, et al. Activation of Bacteroides fragilis toxin by a novel bacterial protease contributes to anaerobic sepsis in mice[J]. Nat Med, 2016,22(5):563-567.
doi: 10.1038/nm.4077 URL |
| [19] |
Sonnenburg ED, Smits SA, Tikhonov M, et al. Diet-induced extinctions in the gut microbiota compound over generations[J]. Nature, 2016,529(7585):212-215.
doi: 10.1038/nature16504 pmid: 26762459 |
| [20] |
Sears CL, Geis AL, Housseau F. Bacteroides fragilis subverts mucosal biology: from symbiont to colon carcinogenesis[J]. J Clin Invest, 2014,124(10):4166-4172.
doi: 10.1172/JCI72334 URL |
| [21] |
Lukiw WJ. Gastrointestinal (GI) tract microbiome-derived neurotoxins-potent neuro-inflammatory signals from the GI tract via the systemic circulation into the brain[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2020,10:22.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00022 URL |
| [22] |
Varatharaj A, Galea I. The blood-brain barrier in systemic inflammation[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2017,60:1-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.03.010 URL |
| [23] |
Rivest S. Regulation of innate immune responses in the brain[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2009,9(6):429-439.
doi: 10.1038/nri2565 URL |
| [24] |
Sasaki H, White SH. Aggregation behavior of an ultra-pure lipopolysaccharide that stimulates TLR-4 receptors[J]. Biophys J, 2008,95(2):986-993.
doi: 10.1529/biophysj.108.129197 URL |
| [25] |
Dowhan W. Lipids and extracellular materials[J]. Annu Rev Biochem, 2014,83:45-49.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-010314-112017 URL |
| [26] | Lukiw WJ. Bacteroides fragilis Lipopolysaccharide and Inflammatory Signaling in Alzheimer's Disease[J]. Front Microbiol, 2016,7:1544. |
| [27] |
Chen SG, Stribinskis V, Rane MJ, et al. Exposure to the functional bacterial amyloid protein curli enhances alpha-synuclein aggregation in aged fischer 344 rats and caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Sci Rep, 2016,6:34477.
doi: 10.1038/srep34477 URL |
| [28] | Javan GT, Finley SJ, Abidin Z, et al. The thanatomicrobiome: A missing piece of the microbial puzzle of death[J]. Front Microbiol, 2016,7:225. |
| [29] |
Liu YJ, Chen J, Li X, et al. Research progress on adenosine in central nervous system diseases[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2019,25(9):899-910.
doi: 10.1111/cns.v25.9 URL |
| [30] |
Tap J, Mondot S, Levenez F, et al. Towards the human intestinal microbiota phylogenetic core[J]. Environ Microbiol, 2009,11(10):2574-2584.
doi: 10.1111/emi.2009.11.issue-10 URL |
| [31] |
Walker WA. Initial intestinal colonization in the human infant and immune homeostasis[J]. Ann Nutr Metab, 2013,63(Suppl 2):8-15.
doi: 10.1159/000354907 URL |
| [32] |
Laparra JM, Sanz Y. Interactions of gut microbiota with functional food components and nutraceuticals[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2010,61(3):219-225.
doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2009.11.001 URL |
| [33] | Wang N, Huo G, Li C, et al. Recent progress in research on probiotics effect on nervous system diseases[J]. Food Sci, 2019,40(11):338-342. |
| [34] |
Anand S, Mande SS. Diet, microbiota and gut-lung connection[J]. Front Microbiol, 2018,9:2147.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02147 URL |
| [35] |
Leclercq S, Matamoros S, Cani PD, et al. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014,111(42):E4485-E4493.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415174111 URL |
| [36] |
Takashima A. Mechanism of neurodegeneration through tau and therapy for Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Sport Health Sci, 2016,5(4):391-392.
doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2016.08.009 pmid: 30356578 |
| [37] |
Grigoleit JS, Kullmann JS, Wolf OT, et al. Dose-dependent effects of endotoxin on neurobehavioral functions in humans[J]. PLoS One, 2011,6:e28330.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028330 URL |
| [38] | Chen D. Neuroprotective effect of amorphophallus canpanulatus in STZ induced Alzheimer rat model[J]. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med, 2016,13(4):47-54. |
| [39] |
Yuyama K, Takahashi K, Usuki S, et al. Plant sphingolipids promote extracellular vesicle release and alleviate amyloid-β pathologies in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2019,9(1):16827.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53394-w URL |
| [1] | 肖煌怡, 袁建坤, 严梓予, 曾雯姝, 鲁兰莫, 王峻. 认知干预对遗忘型轻度认知障碍老年患者干预效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 12-19. |
| [2] | 谢少为, 吕小涵, 董艳红, 吕佩源. 抗炎细胞因子在阿尔茨海默病中的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(2): 185-188. |
| [3] | 李瑞珍, 李星辉, 曾璟, 姚晓涛, 杨珂欣, 张展. 高血压认知功能障碍机制的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(1): 88-92. |
| [4] | 赵小玲, 郑吉敏, 杜季康. 肠道菌群与自身免疫性肝病的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(6): 574-576. |
| [5] | 马光宇, 宋崇东, 韩语纯, 张荣福, 张哲, 程爽, 苏亚楠. 肠道菌群与阿尔茨海默病的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(2): 174-178. |
| [6] | 任玲, 江珊. 血清淀粉样蛋白A、高敏C反应蛋白、一氧化氮与稳定型冠心病不良心血管事件的关系[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(1): 16-20. |
| [7] | 陈梅1,付丛会1,沈志强1,徐英1,贾杰2,吴毅2. 互动式歌唱表演对轻中度阿尔茨海默病患者抑郁、精神行为和运动训练参与率的影响[J]. 临床荟萃, 2020, 35(4): 357-361. |
| [8] | 詹雅萍, 李娴, 朱香顺, 王国芬, 童筱君. 双歧杆菌四联活菌辅助治疗对高尿酸血症的临床分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2020, 35(4): 344-347. |
| [9] | 尹海庆1a,姚宝国2a,陈万贞1b,苏莉2b. 恶性肿瘤患者耐碳青霉烯肠杆菌感染危险因素及耐药性分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2020, 35(2): 166-169. |
| [10] | 吝娜1,曹磊2. 水通道蛋白4在中枢神经系统疾病中的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2019, 34(6): 567-571. |
| [11] | 游超,尹恝. 缺血性卒中与肠道菌群研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(3): 194-198. |
| [12] | 张曦濛1,蔡晓莹2,方燕南2. 认知障碍患者血浆集落刺激因子、炎性因子分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2017, 32(9): 774-777. |
| [13] | 梁庆华a,何本进a,韦勇a,利荣乔a,秦娇琴b,周琴b. 血液同型半胱氨酸及超氧化物歧化酶水平与阿尔茨海默病相关性研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2017, 32(11): 1000-1003. |
| [14] | 吴敬芝,李芳君,陈波,刘爱霞. 血清淀粉样蛋白A、白细胞介素6在新生儿危重症中的变化及意义[J]. 临床荟萃, 2016, 31(8): 889-892. |
| [15] | 孙橙橙,江学良. 粪菌移植在溃疡性结肠炎治疗中的临床应用[J]. 临床荟萃, 2016, 31(8): 838-842. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||