Clinical Focus ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9): 773-777.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.09.001
Effect of levothyroxine for pregnancy outcomes due to subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy: A meta-analysis
Cai Kexin, Guo Hongju, Yu Shuxia, Chang Lirong( )
)
- Department of Pharmacy, Strategic Support Force Feature Medical Center of PLA, Beijing 100101, China
-
Received:2020-09-25Online:2021-09-20Published:2021-10-05 -
Contact:Chang Lirong E-mail:changlirong306@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cai Kexin, Guo Hongju, Yu Shuxia, Chang Lirong. Effect of levothyroxine for pregnancy outcomes due to subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy: A meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(9): 773-777.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.09.001
| 作者 | 国家 | 组别 | 受试者 (例) | 年龄 (岁) | 治疗方法 | 干预时间 | 入组时TSH (mU/L) | TPOAb 状态 | 结局指标 | 等级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 舒展[ | 中国 | T C | 67 67 | 29.7±2.5 29.1±2.0 | 饮食干预+LT4 50 μg/d 饮食干预 | 干预至分娩为止 | 5. 52±0. 58 5. 47±0. 64 | 阴性 | ①②⑧⑨⑩ | C |
| Nazarpour[ | 伊朗 | T C | 183 183 | - | LT4治疗 不进行药物干预 | 整个孕期 | >2.5 | 阴性 | ⑦ | B |
| 刘志明[ | 中国 | T C | 43 43 | 27.42±3.02 27.48±3.04 | 初始剂量12.5~25 μg/d LT4,每隔2~4 周增加12.5~25 μg 不接受任何药物治疗 | 产后 40 d 左右停止 用药 | >5.06 | - | ③④⑤⑧ | C |
| 刘亚琼[ | 中国 | T C | 65 70 | - - | LT4 25~50 μg/次 | - | T1期TSH>2.5;T2、T3期TSH>3.0 不进行药物干预 | 阳性或 阴性 | ①②④⑤⑦⑨⑩ | C |
| 苏颉[ | 中国 | T C | 63 63 | 28.5±1.8 28.1±1.6 | LT4 50~100 μg/d 六味地黄丸,30粒/次, 2次/d | 当TSH恢复正常时 停止用药 | T1期TSH>2.5; T2、T3期:TSH>3.0 | - | ①②④⑥⑨⑩ | C |
| 管小玲[ | 中国 | T C | 35 35 | 30.1±3.2 30.6±2.7 | LT4 50~150 μg/d 不采用药物治疗 | - | - | 阳性 | ①②④⑤⑦⑨⑩ | C |
| 顾成敏[ | 中国 | T V | 53 44 | 29.98±4.17 | LT4 50~200 μg/d 不给予任何治疗 | - | - | 阳性或 阴性 | ①②④⑤⑥⑦⑨ | C |
| Ju[ | 中国 | T C | 184 273 | 29.31±3.36 28.88±3.53 | LT4治疗 不给予任何治疗 | <4周,4~8周 且>8周 | 5.09±1.58 4.92±1.64 | 阴性 | ①②④⑤⑦⑨⑩ | C |
| Maraka[ | 美国 | T C | 82 284 | - - | LT4治疗 | - | T1期TSH>2.5 或T2、T3期TSH >3,但是<10 不给予任何治疗 | 阳性或 阴性 | ①②③⑤⑦⑩ | C |
| 徐冬岩[ | 中国 | T C | 30 30 | 28.12±4.58 | LT4 50~100 μg/d 不进行任何干预治疗 | - | TSH>4.94 | 阴性 | ①②⑦⑧ | C |
| 张洁芳[ | 中国 | T C | 570 570 | 24.6±3.8 | 给予LT4治疗 不给予治疗 | 至妊娠结束 | 5.17<TSH<10 | 阴性 | ①⑥⑦⑧ ⑩ | C |
| 成萍[ | 中国 | T C | 120 120 | 29.3±6.7 30.2±5.9 | LT4 50~100 μg/d 不给予药物治疗 | 直至TSH降到妊娠 特异参考值上限以下 | T1期TSH>2.5; T2、T3期:TSH>3.0 | - | ①②③④⑥⑦⑧ | C |
| 李春仙[ | 中国 | T C | 81 42 | 27.1±6.8 27.9±8.3 | LT4 50 μg/d 不给予药物治疗 | - | T1期TSH>2.57;T2期TSH>3.5;T3期TSH>4.9 | - | ①②⑦⑧⑩ | C |
| Wang[ | 中国 | T C | 28 168 | - | LT4治疗 不给予药物治疗 | 直至分娩 | TSH>2.5 | - | ①④⑥⑦⑧⑩ | C |
| 作者 | 国家 | 组别 | 受试者 (例) | 年龄 (岁) | 治疗方法 | 干预时间 | 入组时TSH (mU/L) | TPOAb 状态 | 结局指标 | 等级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 舒展[ | 中国 | T C | 67 67 | 29.7±2.5 29.1±2.0 | 饮食干预+LT4 50 μg/d 饮食干预 | 干预至分娩为止 | 5. 52±0. 58 5. 47±0. 64 | 阴性 | ①②⑧⑨⑩ | C |
| Nazarpour[ | 伊朗 | T C | 183 183 | - | LT4治疗 不进行药物干预 | 整个孕期 | >2.5 | 阴性 | ⑦ | B |
| 刘志明[ | 中国 | T C | 43 43 | 27.42±3.02 27.48±3.04 | 初始剂量12.5~25 μg/d LT4,每隔2~4 周增加12.5~25 μg 不接受任何药物治疗 | 产后 40 d 左右停止 用药 | >5.06 | - | ③④⑤⑧ | C |
| 刘亚琼[ | 中国 | T C | 65 70 | - - | LT4 25~50 μg/次 | - | T1期TSH>2.5;T2、T3期TSH>3.0 不进行药物干预 | 阳性或 阴性 | ①②④⑤⑦⑨⑩ | C |
| 苏颉[ | 中国 | T C | 63 63 | 28.5±1.8 28.1±1.6 | LT4 50~100 μg/d 六味地黄丸,30粒/次, 2次/d | 当TSH恢复正常时 停止用药 | T1期TSH>2.5; T2、T3期:TSH>3.0 | - | ①②④⑥⑨⑩ | C |
| 管小玲[ | 中国 | T C | 35 35 | 30.1±3.2 30.6±2.7 | LT4 50~150 μg/d 不采用药物治疗 | - | - | 阳性 | ①②④⑤⑦⑨⑩ | C |
| 顾成敏[ | 中国 | T V | 53 44 | 29.98±4.17 | LT4 50~200 μg/d 不给予任何治疗 | - | - | 阳性或 阴性 | ①②④⑤⑥⑦⑨ | C |
| Ju[ | 中国 | T C | 184 273 | 29.31±3.36 28.88±3.53 | LT4治疗 不给予任何治疗 | <4周,4~8周 且>8周 | 5.09±1.58 4.92±1.64 | 阴性 | ①②④⑤⑦⑨⑩ | C |
| Maraka[ | 美国 | T C | 82 284 | - - | LT4治疗 | - | T1期TSH>2.5 或T2、T3期TSH >3,但是<10 不给予任何治疗 | 阳性或 阴性 | ①②③⑤⑦⑩ | C |
| 徐冬岩[ | 中国 | T C | 30 30 | 28.12±4.58 | LT4 50~100 μg/d 不进行任何干预治疗 | - | TSH>4.94 | 阴性 | ①②⑦⑧ | C |
| 张洁芳[ | 中国 | T C | 570 570 | 24.6±3.8 | 给予LT4治疗 不给予治疗 | 至妊娠结束 | 5.17<TSH<10 | 阴性 | ①⑥⑦⑧ ⑩ | C |
| 成萍[ | 中国 | T C | 120 120 | 29.3±6.7 30.2±5.9 | LT4 50~100 μg/d 不给予药物治疗 | 直至TSH降到妊娠 特异参考值上限以下 | T1期TSH>2.5; T2、T3期:TSH>3.0 | - | ①②③④⑥⑦⑧ | C |
| 李春仙[ | 中国 | T C | 81 42 | 27.1±6.8 27.9±8.3 | LT4 50 μg/d 不给予药物治疗 | - | T1期TSH>2.57;T2期TSH>3.5;T3期TSH>4.9 | - | ①②⑦⑧⑩ | C |
| Wang[ | 中国 | T C | 28 168 | - | LT4治疗 不给予药物治疗 | 直至分娩 | TSH>2.5 | - | ①④⑥⑦⑧⑩ | C |
| 因素 | 纳入文献 | OR值 | 95%CI | I2(%) | Z值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
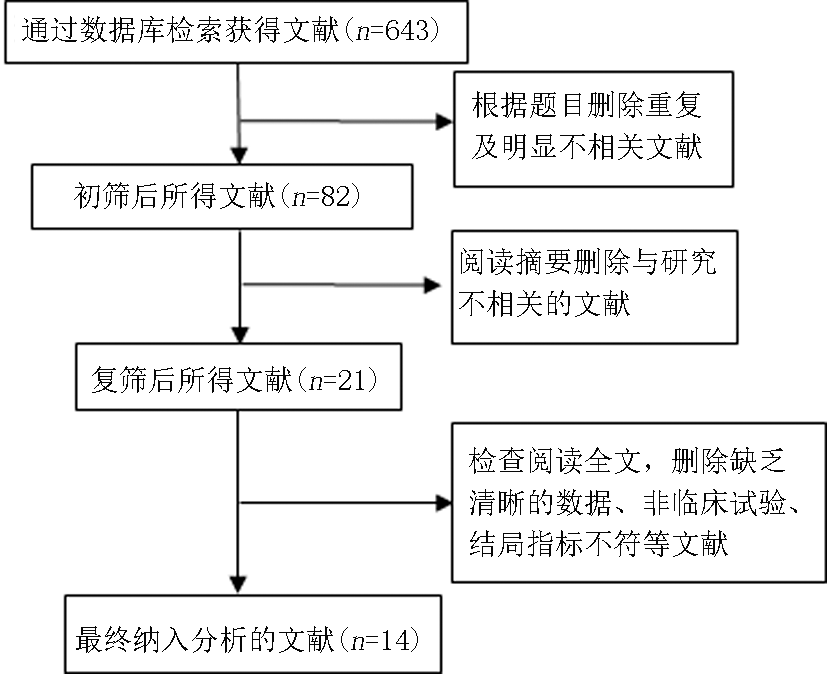
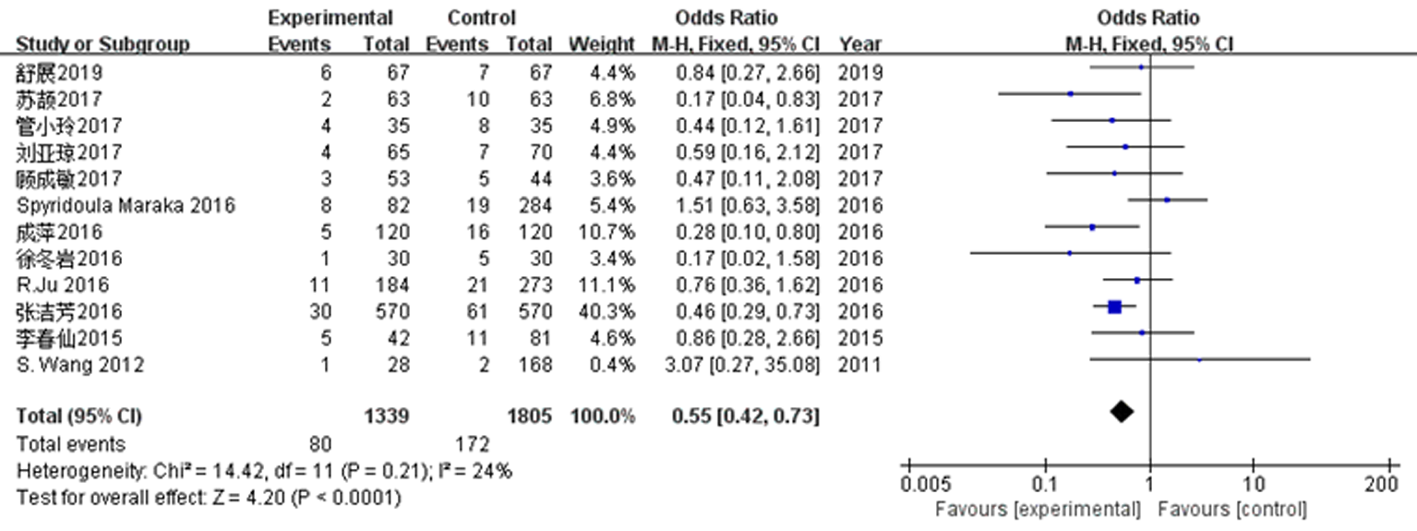
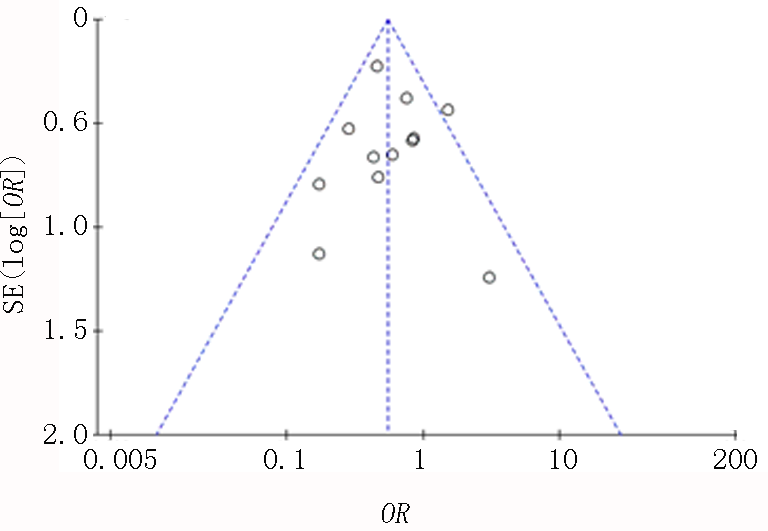
| 妊娠期高血压 | 8, 11~21 | 0.55 | 0.42 | 0.73 | 24 | 4.20 | P<0.01 |
| 妊娠期糖尿病 | 8, 11~17, 19, 20 | 0.63 | 0.46 | 0.87 | 71 | 2.81 | 0.005 |
| 先兆子痫 | 10, 16, 19 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.84 | 0 | 2.32 | 0.02 |
| 产后出血 | 10~15, 19, 21 | 0.52 | 0.29 | 0.92 | 0 | 2.24 | 0.03 |
| 胎膜早破 | 10, 11, 13~16 | 0.60 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 53 | 2.90 | 0.004 |
| 贫血 | 12, 14, 18, 19, 21 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.41 | 0 | 9.18 | P<0.01 |
| 早产 | 9, 11, 13~21 | 0.49 | 0.36 | 0.65 | 0 | 4.90 | P<0.01 |
| 流产 | 8, 10, 17~21 | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.50 | 0 | 6.17 | P<0.01 |
| 新生儿窘迫 | 8, 11~15 | 0.56 | 0.40 | 0.79 | 42 | 3.35 | 0.0008 |
| 低出生体重儿 | 8, 12~14, 16, 17, 19, 21~22 | 0.40 | 0.28 | 0.57 | 52 | 5.07 | P<0.01 |
| 因素 | 纳入文献 | OR值 | 95%CI | I2(%) | Z值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 妊娠期高血压 | 8, 11~21 | 0.55 | 0.42 | 0.73 | 24 | 4.20 | P<0.01 |
| 妊娠期糖尿病 | 8, 11~17, 19, 20 | 0.63 | 0.46 | 0.87 | 71 | 2.81 | 0.005 |
| 先兆子痫 | 10, 16, 19 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.84 | 0 | 2.32 | 0.02 |
| 产后出血 | 10~15, 19, 21 | 0.52 | 0.29 | 0.92 | 0 | 2.24 | 0.03 |
| 胎膜早破 | 10, 11, 13~16 | 0.60 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 53 | 2.90 | 0.004 |
| 贫血 | 12, 14, 18, 19, 21 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.41 | 0 | 9.18 | P<0.01 |
| 早产 | 9, 11, 13~21 | 0.49 | 0.36 | 0.65 | 0 | 4.90 | P<0.01 |
| 流产 | 8, 10, 17~21 | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.50 | 0 | 6.17 | P<0.01 |
| 新生儿窘迫 | 8, 11~15 | 0.56 | 0.40 | 0.79 | 42 | 3.35 | 0.0008 |
| 低出生体重儿 | 8, 12~14, 16, 17, 19, 21~22 | 0.40 | 0.28 | 0.57 | 52 | 5.07 | P<0.01 |
| [1] |
Dong AC, Stagnaro-Green A. Differences in diagnostic criteria mask the true prevalence of thyroid disease in pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Thyroid, 2019, 29(2):278-89.
doi: 10.1089/thy.2018.0475 URL |
| [2] | 妊娠和产后甲状腺疾病诊治指南》(第2版)编撰委员会, 中华医学会内分泌学分会, 中华医学会围产医学分会. 妊娠和产后甲状腺疾病诊治指南(第2版)[J]. 中华围产医学杂志, 2019, 22(8):505-539. |
| [3] |
Su PY, Huang K, Hao JH, et al. Maternal thyroid function in the first twenty weeks of pregnancy and subsequent fetal and infant development: A prospective population-based cohort study in China[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2011, 96(10):3234-3241.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-0274 URL |
| [4] |
Negro R, Stagnaro-Green A. Diagnosis and management of subclinical hypothyroidism in pregnancy[J]. BMJ, 2014, 349:g4929.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.g4929 URL |
| [5] |
Carney LA, Quinlan JD, West JM. Thyroid disease in pregnancy[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2014, 89(4):273-278.
pmid: 24695447 |
| [6] | 郭朋鸽. 妊娠合并亚临床甲状腺功能减退症相关因素分析及对妊娠结局的影响[D]. 山西医科大学, 2016. |
| [7] | 张晓璐. 妊娠期甲状腺疾病的临床流行病学调查[D]. 首都医科大学, 2013. |
| [8] | 舒展, 房秋霞, 马恩萍. 左旋甲状腺素对甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体阴性的妊娠合并亚临床甲状腺功能减退症患者妊娠激素水平、甲状腺功能及妊娠结局的影响[J]. 中国医院用药评价与分析, 2019, 19(17):815-817, 821. |
| [9] |
Nazarpour S, Ramezani Tehrani F, et al. Effects of levothyroxine on pregnant women with subclinical hypothyroidism, negative for thyroid peroxidase antibodies[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 103(3):926-935.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-01850 pmid: 29126290 |
| [10] | 刘志明, 白晓苏, 李木娇, 等. 早期治疗对妊娠合并亚临床甲状腺功能减退症患者妊娠结局的影响[J]. 临床医学工程, 2017, 24(2):205-206. |
| [11] | 刘亚琼, 王国华, 杨夫艳, 等. 左旋甲状腺素替代治疗对妊娠期亚临床甲减孕妇妊娠结局的影响[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2017, 17(69):5-6. |
| [12] | 苏颉. 左旋甲状腺素片对妊娠期亚临床甲状腺功能减退的疗效[J]. 北方药学, 2017, 14(12):70-71. |
| [13] | 管小玲. 左旋甲状腺素钠片治疗妊娠期亚临床甲状腺功能减退的效果[J]. 中国当代医药, 2017, 24(35):35-37. |
| [14] | 顾成敏, 陈妍华, 冯敏, 等. 妊娠期亚临床甲状腺功能减退症患者抗甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体水平与妊娠结局的相关性[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2017, 32(19):4631-4633. |
| [15] | Ju R, Lin L, Long Y, et al. Clinical efficacy of therapeutic intervention for subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy[J]. Genet Mol Res, 2016, 15(4). |
| [16] |
Maraka S, Singh Ospina NM, et al. Effects of levothyroxine therapy on pregnancy outcomes in women with subclinical hypothyroidism[J]. Thyroid, 2016, 26(7):980-986.
doi: 10.1089/thy.2016.0014 URL |
| [17] | 徐冬岩, 蒋鸿阳, 张宏宇, 等. 甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体阴性的妊娠期亚临床甲状腺功能减退症对妊娠结局及新生儿的影响[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2016, 31(24):5344-5347. |
| [18] | 张洁芳, 李远, 曹彦敏, 等. 左甲状腺素钠对妊娠早期甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体阴性的亚临床甲状腺功能减退患者围产结局的影响[J]. 临床荟萃, 2016, 31(3):293-295. |
| [19] | 成萍. 左旋甲状腺素片对妊娠期亚临床甲状腺功能减退患者妊娠结局的影响[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2016, 25(26):2944-2946. |
| [20] | 李春仙, 陈敏, 李美红, 等. 妊娠妇女亚临床甲状腺功能减退症对妊娠结局的影响[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2015, 31(11) :937-940. |
| [21] |
Wang S, Teng WP, Li JX, et al. Effects of maternal subclinical hypothyroidism on obstetrical outcomes during early pregnancy[J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2012, 35(3):322-325.
doi: 10.3275/7772 pmid: 21642766 |
| [22] |
Maraka S Ospina NM, O'Keeffe DT, et al. Subclinical hypothyroidism in pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Thyroid, 2016: 26(4):580-590.
doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0418 URL |
| [23] |
Stagnaro-Green A, Abalovich M, Alexander E, et al. Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and postpartum[J]. Thyroid, 2011, 21(10):1081-1125.
doi: 10.1089/thy.2011.0087 pmid: 21787128 |
| [24] | 单忠艳. 妊娠期甲状腺功能减退症的诊治进展[J]. 天津医药, 2016, 44(11):1297-1301. |
| [25] |
Li C, Shan Z, Mao J, et al. Assessment of thyroid function during first-trimester pregnancy: What is the rational upper limit of serum TSH during the first trimester in Chinese pregnant women?[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2014, 99(1):73-79.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-1674 URL |
| [26] |
Alexander EK, Pearce EN, Brent GA, et al. 2017 Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and the postpartum[J]. Thyroid, 2017, 27(3):315-389.
doi: 10.1089/thy.2016.0457 pmid: 28056690 |
| [27] |
Toloza FJK, Singh Ospina NM, Rodriguez-Gutierrez R, et al. Practice variation in the care of subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy: A national survey of physicians in the united states[J]. J Endocr Soc, 2019, 3(10):1892-1906.
doi: 10.1210/js.2019-00196 URL |
| [28] | Li J, Shen J, Qin L. Effects of levothyroxine on pregnancy outcomes in women with thyroid dysfunction: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Altern Ther Health Med, 2017, 23(2):49-58. |
| [29] | Maraka S, Mwangi R, McCoy RG, et al. Thyroid hormone treatment among pregnant women with subclinical hypothyroidism: US national assessment[J]. BMJ, 2017, 356:i6865. |
| [30] | Maraka S, Mwangi R, Yao X, et al. Variation in treatment practices for subclinical hypothyroidism in pregnancy: US national assessment[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2019, 104(9):3893-3901. |
| [31] |
Zhao L, Jiang G, Tian X, et al. Initiation timing effect of levothyroxine treatment on subclinical hypothyroidism in pregnancy[J]. Gynecol Endocrinol, 2018, 34(10):845-848.
doi: 10.1080/09513590.2018.1451836 URL |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 171
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 490
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||