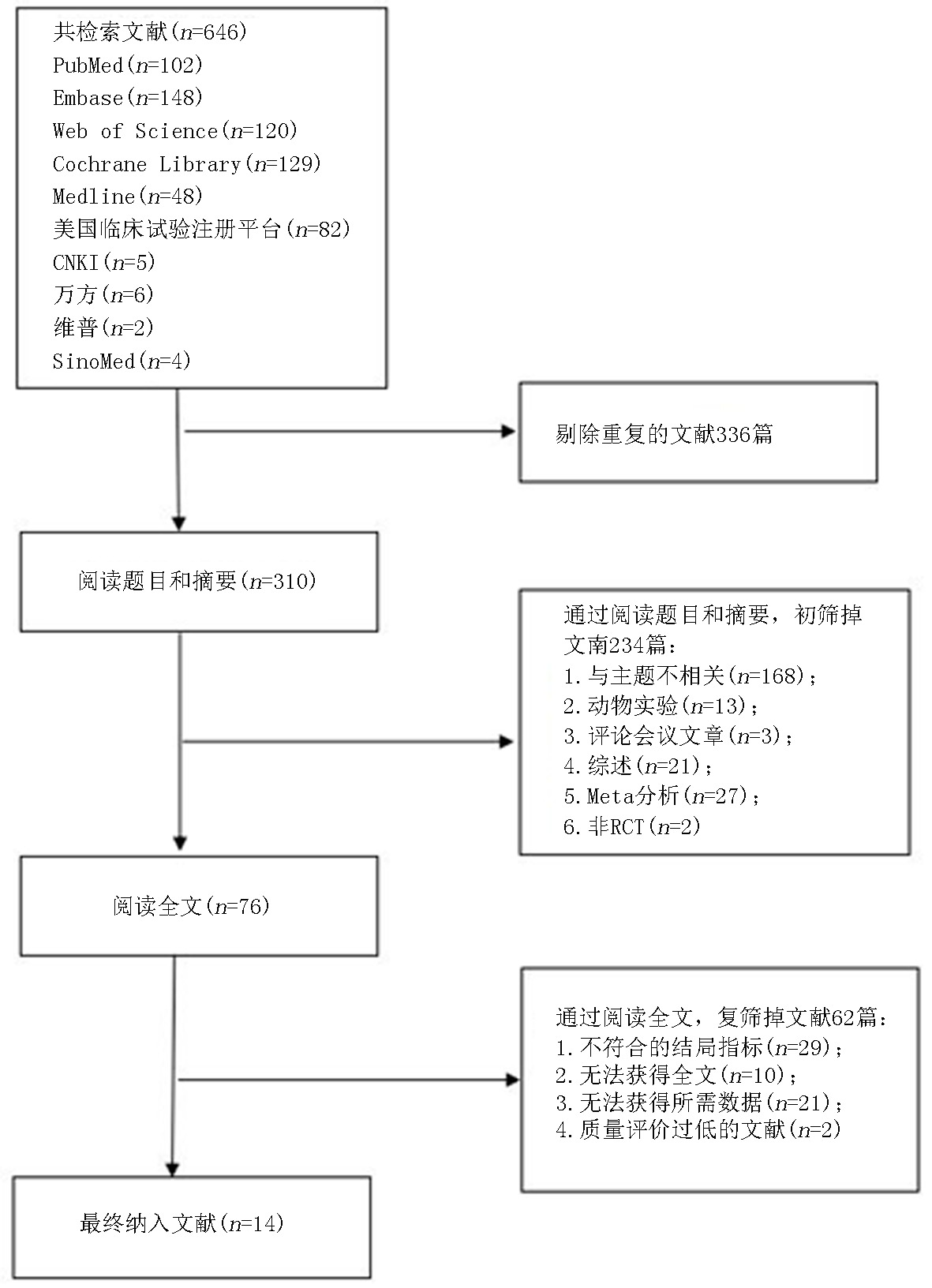
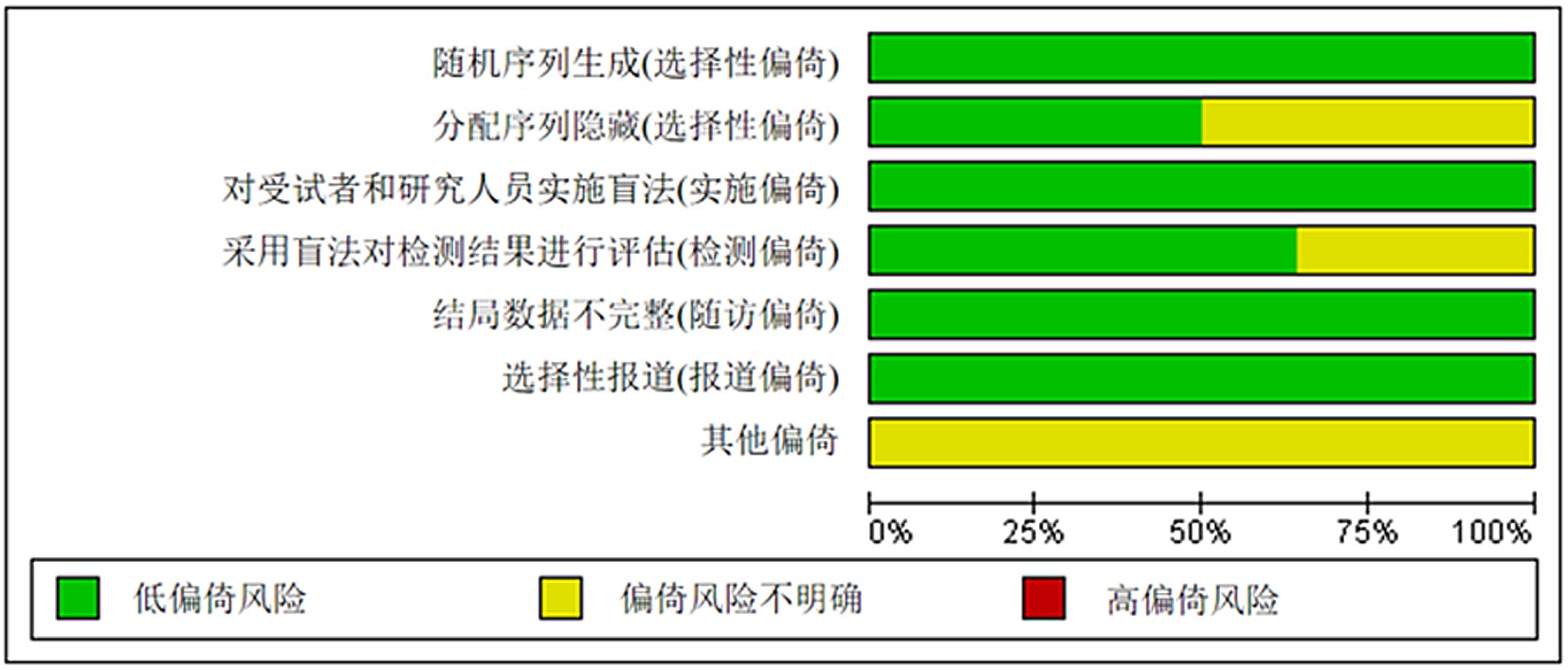
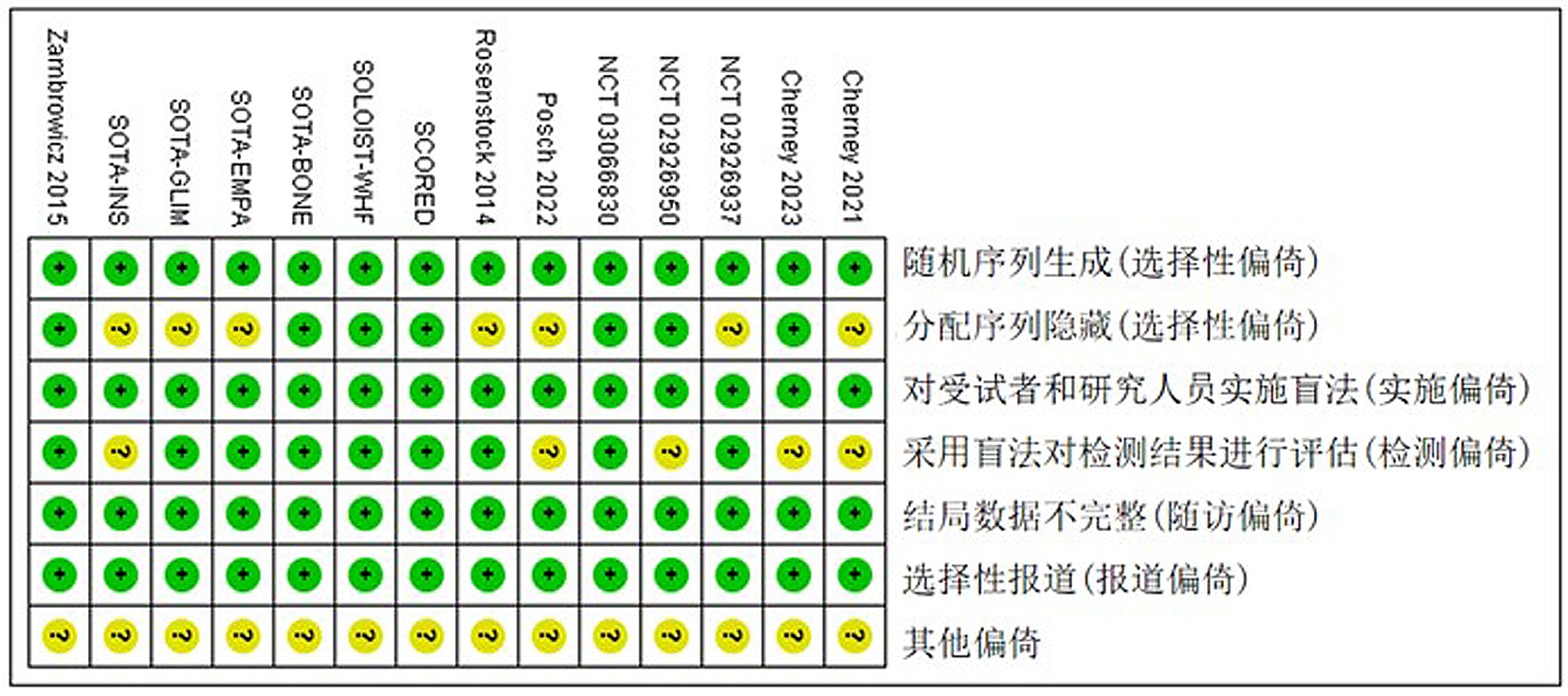
Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (7): 581-592.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.07.001
Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
Yue Jianghong1, Wang Heng2, Cai Gang3a, Zhang Xuanming3a, Peng Xi3b( )
)
- 1. Department of Pharmacy, the 7th Division Hospital of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, Kuitun 833200, China
2. College of Pharmacy, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832003, China
3a. Departmentof 'Traditional Chinese Medicine; b. Department of Pharmacy, the First A ffliated Hospital of Shihezi University, Xinjiang Shihezi 832008,China
-
Received:2024-01-08Online:2024-07-20Published:2024-08-02 -
Contact:Peng Xi E-mail:pxshz@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yue Jianghong, Wang Heng, Cai Gang, Zhang Xuanming, Peng Xi. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(7): 581-592.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.07.001
| 第一作者及 发表年限 | 组别 | 例数 | 年龄 (岁) | 女性比例 (%) | HbA1c(%) | 干预措施 | 研究 周期 | 结局指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
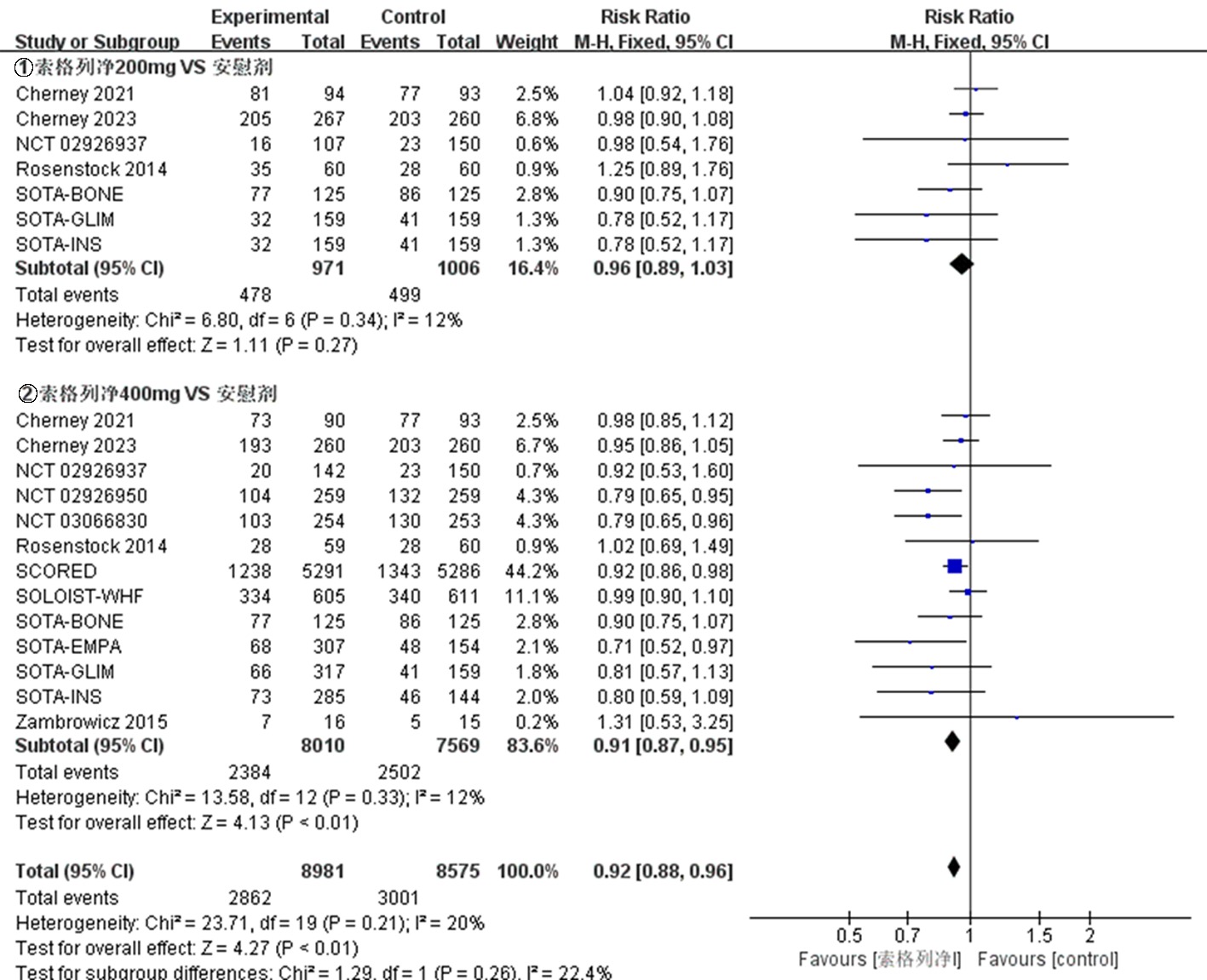
| NCT03315143 Bhatt 2021[ SCORED | 试验组 对照组 | 5292 5292 | 69(63~74) 69(63~74) | 44.3 45.5 | ≥7 | 索格列净400 mg qd 安慰剂 | 64 | ⑨ |
| NCT03521934 Bhatt 2021[ SOLOIST-WHF | 试验组 对照组 | 608 614 | 69(63~76) 70(64~76) | 32.6 34.9 | 7.1(6.4~8.3) 7.2(6.4~8.2) | 索格列净400 mg qd 安慰剂 | 36 | ⑨ |
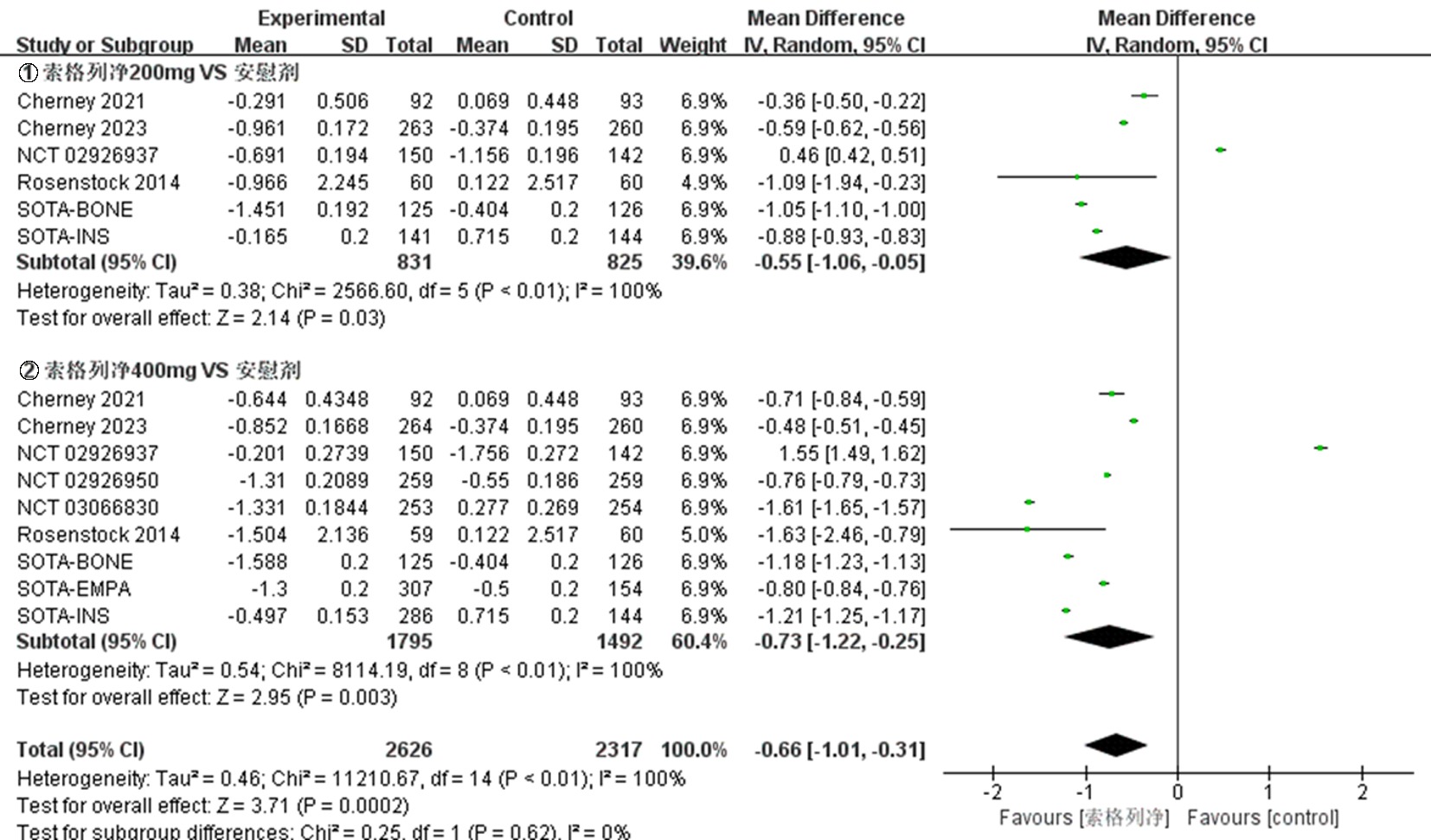
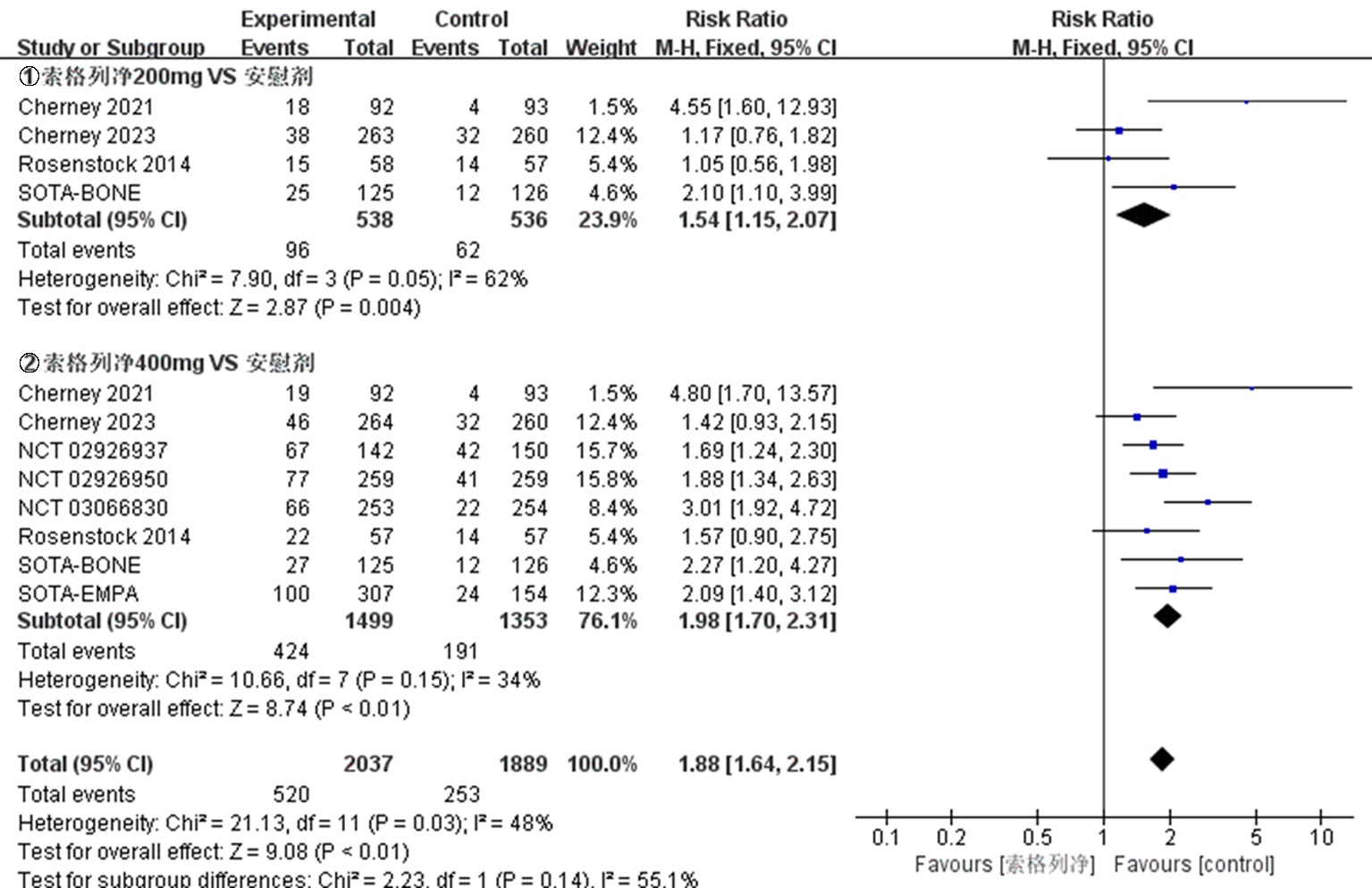
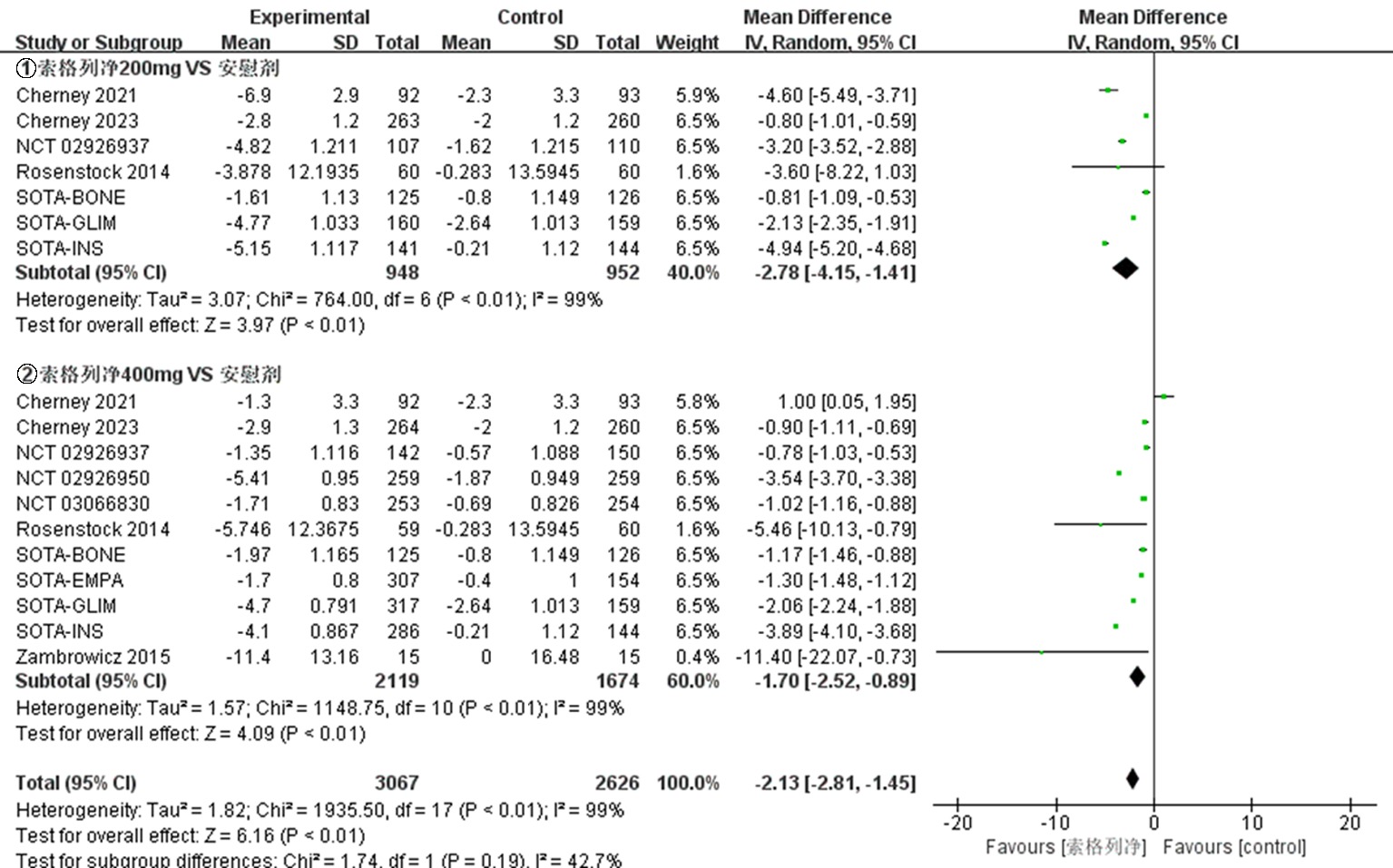
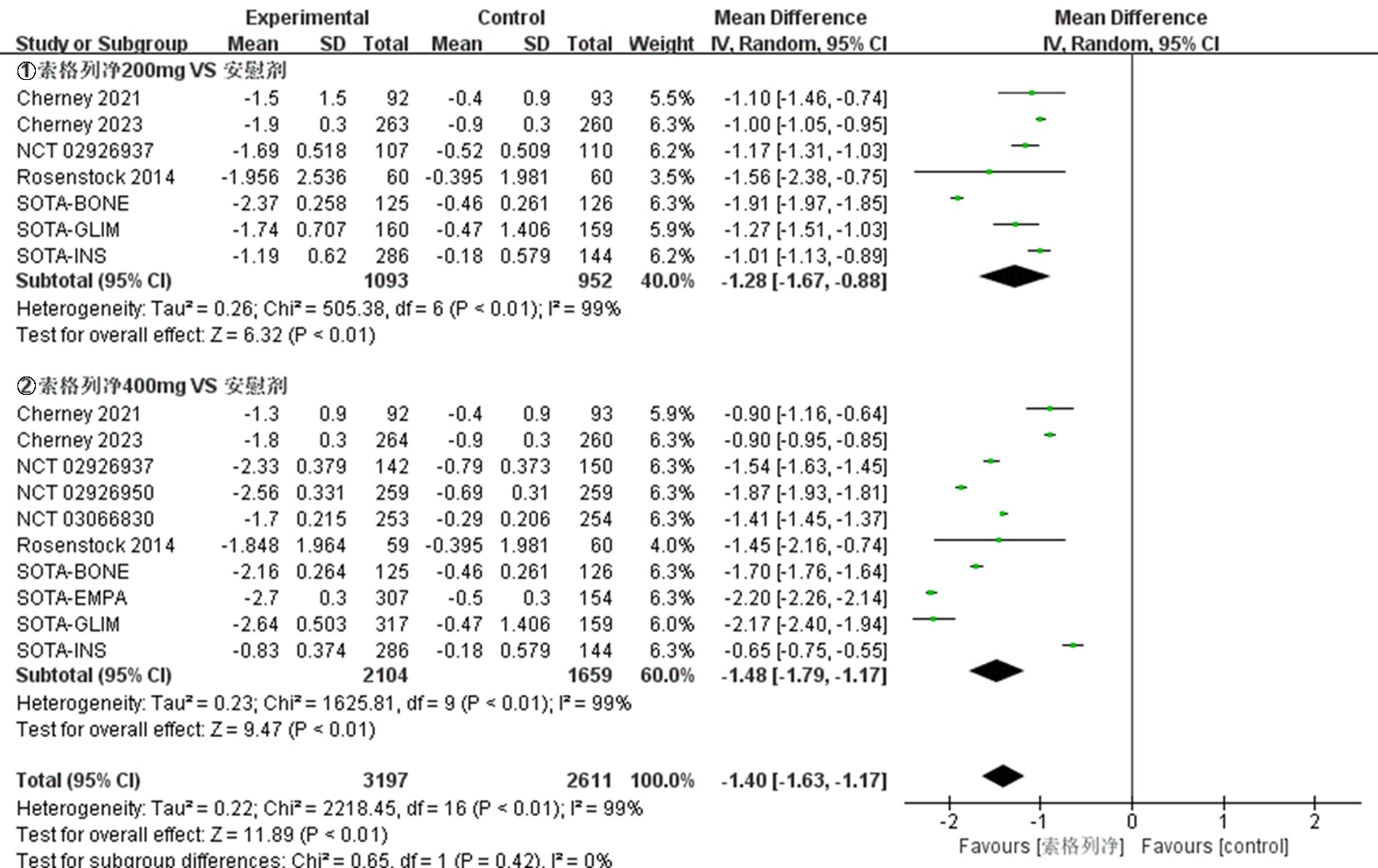
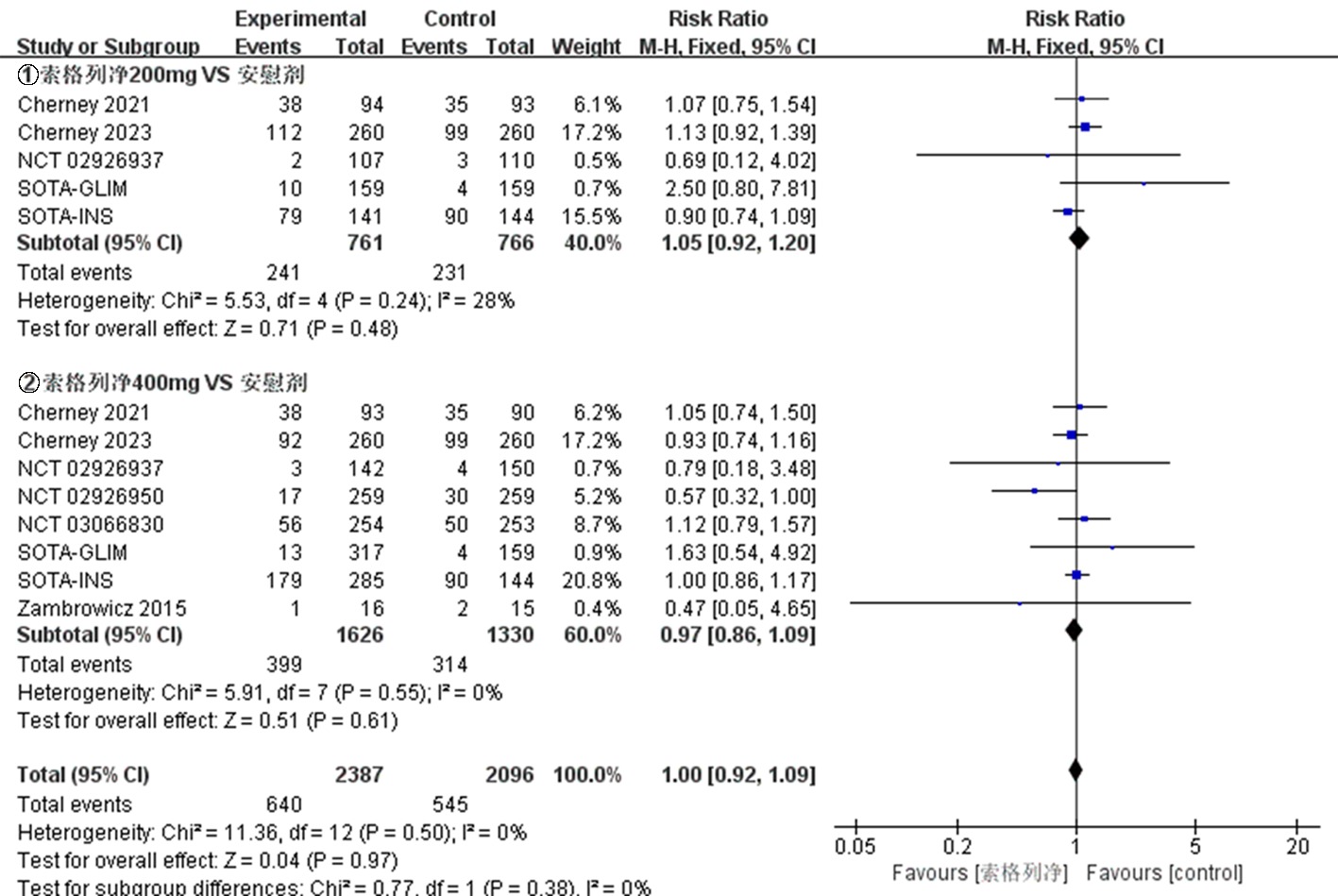
| NCT03242018 Cherney 2021[ | 试验组 | 92 | 66.8±10.0 | 52.2 | 8.3±1.0 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 92 | 67.3±9.6 | 46.7 | 8.3±0.9 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 52 | ①、②、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 93 | 68.0±8.3 | 54.8 | 8.4±1.1 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT03242252 Cherney 2023[ | 试验组 | 263 | 69.6±7.5 | 45.6 | 8.3±0.9 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 264 | 69.5±8.2 | 42.4 | 8.3±0.9 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 52 | ①、②、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 260 | 69.3±8.1 | 42.7 | 8.3±1.0 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT03462069 Posch 2022[ | 试验组 对照组 | 20 21 | 61.0±8.4 64.8±8.53 | 20.0 81.0 | 6.5-11 | 索格列净400 mg qd 恩格列净200 mg qd | 8 | ⑧、⑨ |
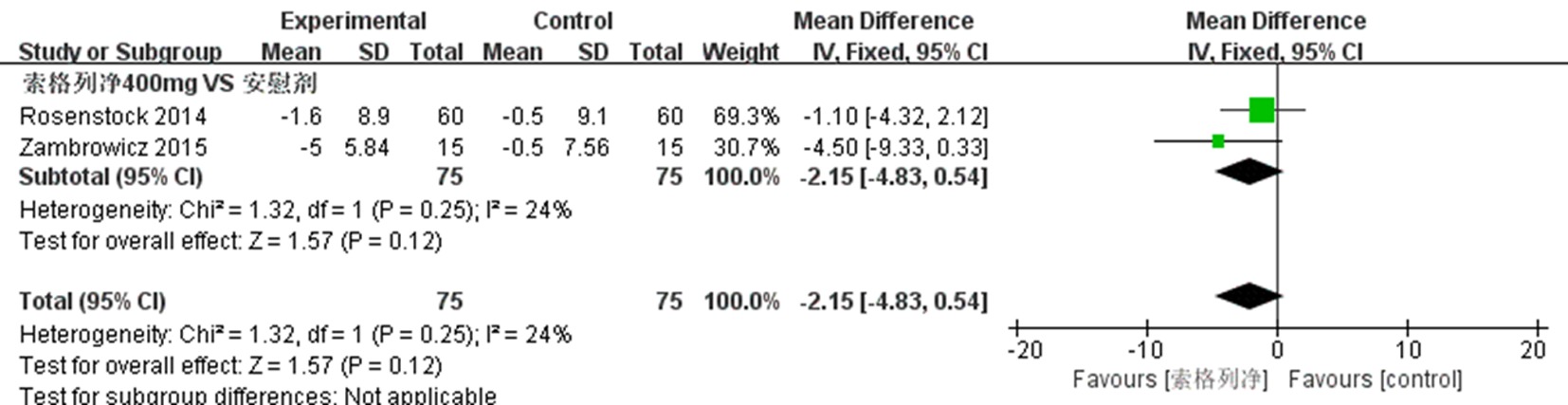
| NCT01555008 Zambrowicz 2015[ | 试验组 对照组 | 16 15 | 64.8±8.53 68.1±7.33 | 50.0 40.0 | 不清楚 不清楚 | 索格列净400 mg qd 安慰剂 | 1 | ⑤、⑥、⑧、⑨ |
| NCT01376557 Rosenstock 2014[ | 试验组 | 59 | 56± 9.61 | 42.4 | 8.0±0.9 | 索格列净75 mg qd | ||
| 60 | 55.6±9.25 | 71.7 | 8.3±1.0 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||||
| 60 | 56.1±9.51 | 51.7 | 8.1±1.0 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 12 | ①、②、④、⑤、⑥、⑦、⑨ | ||
| 60 | 56.4±8.76 | 51.7 | 8.4±0.9 | 索格列净200 mg bid | ||||
| 对照组 | 60 | 55.1±9.79 | 56.7 | 7.9±0.9 | 安慰剂 | |||
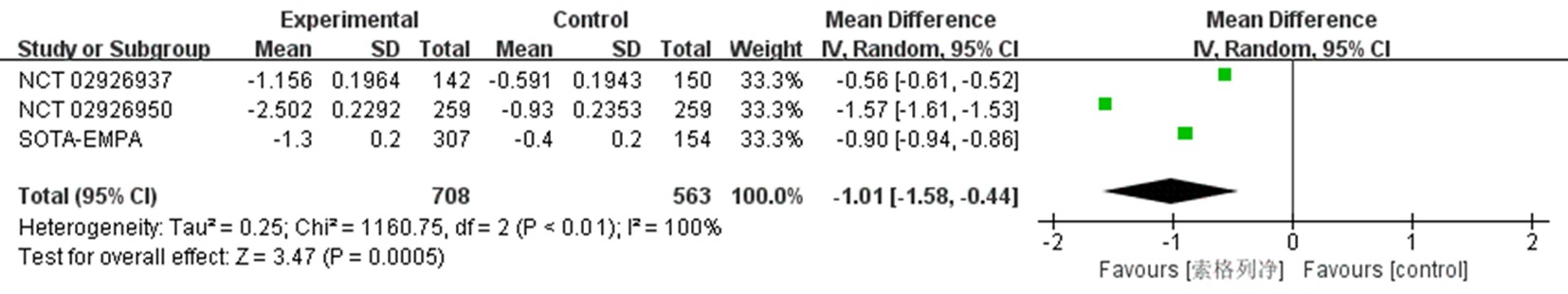
| NCT02926937[ | 试验组 | 107 | 52.3±11.4 | 49.5 | 8.00±0.81 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 142 | 54.7±11.2 | 47.9 | 8.14±0.92 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 26 | ①、②、③、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 150 | 55.3±11.2 | 48.0 | 8.11±0.88 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT02926950[ | 试验组 对照组 | 259 259 | 60.0±10.1 59.9±9.4 | 45.2 43.6 | 8.20±0.78 8.20±0.78 | 索格列净400 mg qd 安慰剂 | 26 | ①、②、③、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ |
| NCT03351478 SOTA-EMPA[ | 试验组 | 307 | 58.9±9.7 | 45.9 | 8.23±0.84 | 索格列净400 mg qd | ||
| 309 | 59.7±9.6 | 51.1 | 8.21±0.93 | 恩格列净25 mg qd | 26 | ①、②、③、④、⑤、⑦、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 154 | 59.8±9.6 | 48.7 | 8.21±0.93 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT03285594 SOTA-INS[ | 试验组 | 141 | 62.1±10.2 | 46.1 | 8.76±0.83 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 286 | 62.7±9.1 | 46.2 | 8.69±0.80 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 52 | ①、②、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 144 | 62.2±8.9 | 40.3 | 8.76±0.79 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT03066830[ | 试验组 对照组 | 253 254 | 63.3±8.8 63.0±9.9 | 41.1 48.8 | 8.20±0.83 8.18±0.83 | 索格列净400 mg qd 安慰剂 | 26 | ①、②、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ |
| NCT03332771 SOTA-GLIM[ | 试验组 | 160 | 58.6±9.9 | 46.9 | 8.11±0.86 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 317 | 59.7±10.4 | 49.5 | 8.09±0.78 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 52 | ①、④、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 159 | 58.8±11.2 | 48.4 | 8.12±0.73 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT03386344 SOTA-BONE[ | 试验组 | 125 | 66.1±6.7 | 44.8 | 8.32±0.96 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 125 | 66.5±6.9 | 44.0 | 8.32±0.95 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 26 | ①、②、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 126 | 66.3±5.7 | 44.4 | 8.38±0.91 | 安慰剂 |
Tab.1 Baseline characteristics of the included studies
| 第一作者及 发表年限 | 组别 | 例数 | 年龄 (岁) | 女性比例 (%) | HbA1c(%) | 干预措施 | 研究 周期 | 结局指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03315143 Bhatt 2021[ SCORED | 试验组 对照组 | 5292 5292 | 69(63~74) 69(63~74) | 44.3 45.5 | ≥7 | 索格列净400 mg qd 安慰剂 | 64 | ⑨ |
| NCT03521934 Bhatt 2021[ SOLOIST-WHF | 试验组 对照组 | 608 614 | 69(63~76) 70(64~76) | 32.6 34.9 | 7.1(6.4~8.3) 7.2(6.4~8.2) | 索格列净400 mg qd 安慰剂 | 36 | ⑨ |
| NCT03242018 Cherney 2021[ | 试验组 | 92 | 66.8±10.0 | 52.2 | 8.3±1.0 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 92 | 67.3±9.6 | 46.7 | 8.3±0.9 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 52 | ①、②、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 93 | 68.0±8.3 | 54.8 | 8.4±1.1 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT03242252 Cherney 2023[ | 试验组 | 263 | 69.6±7.5 | 45.6 | 8.3±0.9 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 264 | 69.5±8.2 | 42.4 | 8.3±0.9 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 52 | ①、②、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 260 | 69.3±8.1 | 42.7 | 8.3±1.0 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT03462069 Posch 2022[ | 试验组 对照组 | 20 21 | 61.0±8.4 64.8±8.53 | 20.0 81.0 | 6.5-11 | 索格列净400 mg qd 恩格列净200 mg qd | 8 | ⑧、⑨ |
| NCT01555008 Zambrowicz 2015[ | 试验组 对照组 | 16 15 | 64.8±8.53 68.1±7.33 | 50.0 40.0 | 不清楚 不清楚 | 索格列净400 mg qd 安慰剂 | 1 | ⑤、⑥、⑧、⑨ |
| NCT01376557 Rosenstock 2014[ | 试验组 | 59 | 56± 9.61 | 42.4 | 8.0±0.9 | 索格列净75 mg qd | ||
| 60 | 55.6±9.25 | 71.7 | 8.3±1.0 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||||
| 60 | 56.1±9.51 | 51.7 | 8.1±1.0 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 12 | ①、②、④、⑤、⑥、⑦、⑨ | ||
| 60 | 56.4±8.76 | 51.7 | 8.4±0.9 | 索格列净200 mg bid | ||||
| 对照组 | 60 | 55.1±9.79 | 56.7 | 7.9±0.9 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT02926937[ | 试验组 | 107 | 52.3±11.4 | 49.5 | 8.00±0.81 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 142 | 54.7±11.2 | 47.9 | 8.14±0.92 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 26 | ①、②、③、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 150 | 55.3±11.2 | 48.0 | 8.11±0.88 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT02926950[ | 试验组 对照组 | 259 259 | 60.0±10.1 59.9±9.4 | 45.2 43.6 | 8.20±0.78 8.20±0.78 | 索格列净400 mg qd 安慰剂 | 26 | ①、②、③、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ |
| NCT03351478 SOTA-EMPA[ | 试验组 | 307 | 58.9±9.7 | 45.9 | 8.23±0.84 | 索格列净400 mg qd | ||
| 309 | 59.7±9.6 | 51.1 | 8.21±0.93 | 恩格列净25 mg qd | 26 | ①、②、③、④、⑤、⑦、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 154 | 59.8±9.6 | 48.7 | 8.21±0.93 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT03285594 SOTA-INS[ | 试验组 | 141 | 62.1±10.2 | 46.1 | 8.76±0.83 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 286 | 62.7±9.1 | 46.2 | 8.69±0.80 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 52 | ①、②、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 144 | 62.2±8.9 | 40.3 | 8.76±0.79 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT03066830[ | 试验组 对照组 | 253 254 | 63.3±8.8 63.0±9.9 | 41.1 48.8 | 8.20±0.83 8.18±0.83 | 索格列净400 mg qd 安慰剂 | 26 | ①、②、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ |
| NCT03332771 SOTA-GLIM[ | 试验组 | 160 | 58.6±9.9 | 46.9 | 8.11±0.86 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 317 | 59.7±10.4 | 49.5 | 8.09±0.78 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 52 | ①、④、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 159 | 58.8±11.2 | 48.4 | 8.12±0.73 | 安慰剂 | |||
| NCT03386344 SOTA-BONE[ | 试验组 | 125 | 66.1±6.7 | 44.8 | 8.32±0.96 | 索格列净200 mg qd | ||
| 125 | 66.5±6.9 | 44.0 | 8.32±0.95 | 索格列净400 mg qd | 26 | ①、②、④、⑤、⑦、⑧、⑨ | ||
| 对照组 | 126 | 66.3±5.7 | 44.4 | 8.38±0.91 | 安慰剂 |
| 结局指标 | 随机效应模型 | 固定效应模型 | 去除权重大的研究 | 去除权重小的研究 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD/RR(95%CI) | P值 | MD/RR(95%CI) | P值 | MD/RR(95%CI) | P值 | MD/RR(95%CI) | P值 | |||||||||
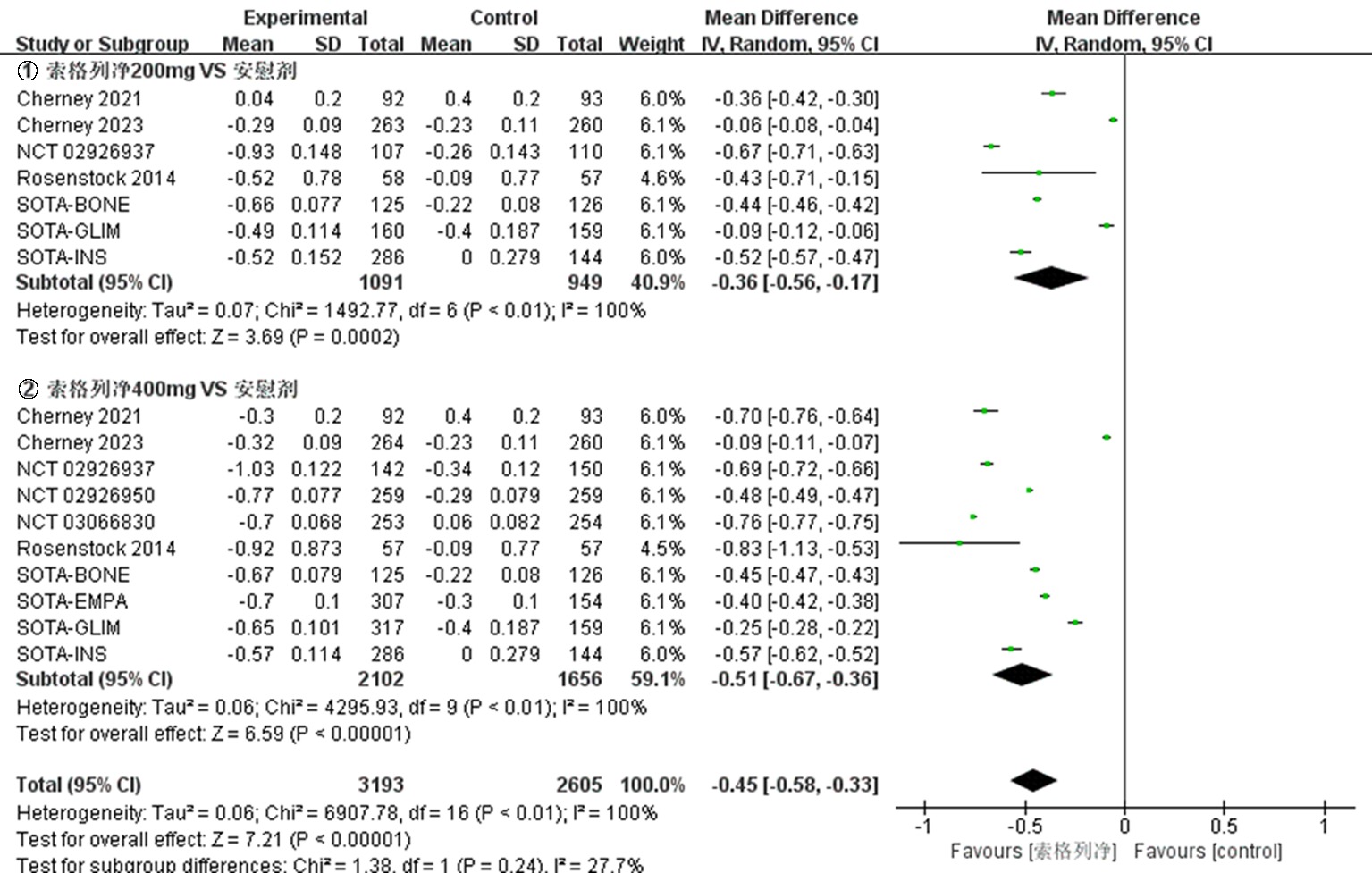
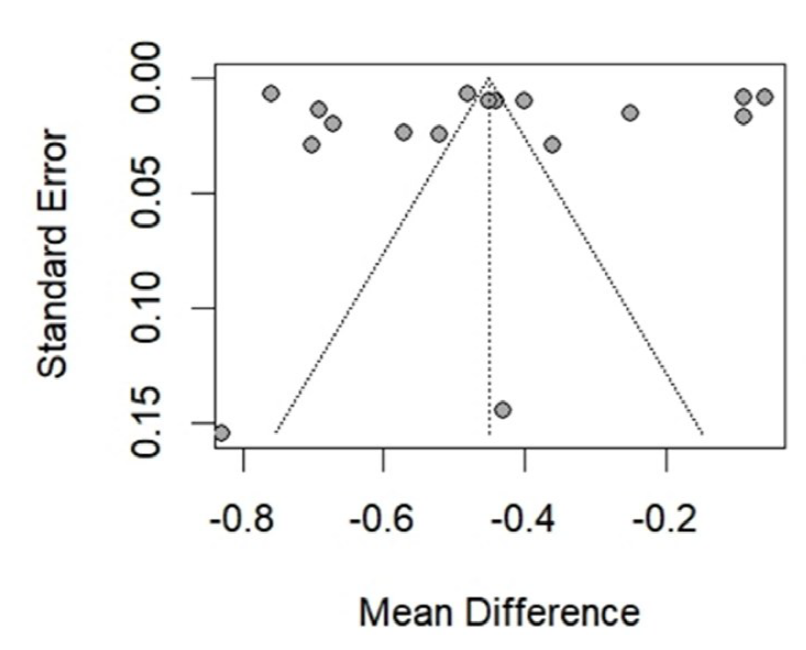
| HbA1c水平 | -0.45[-0.58,-0.33] | <0.01 | -0.43[-0.44,-0.42] | <0.01 | -0.50[-0.60,-0.41] | <0.01 | -0.44[-0.56,-0.31] | <0.01 | ||||||||
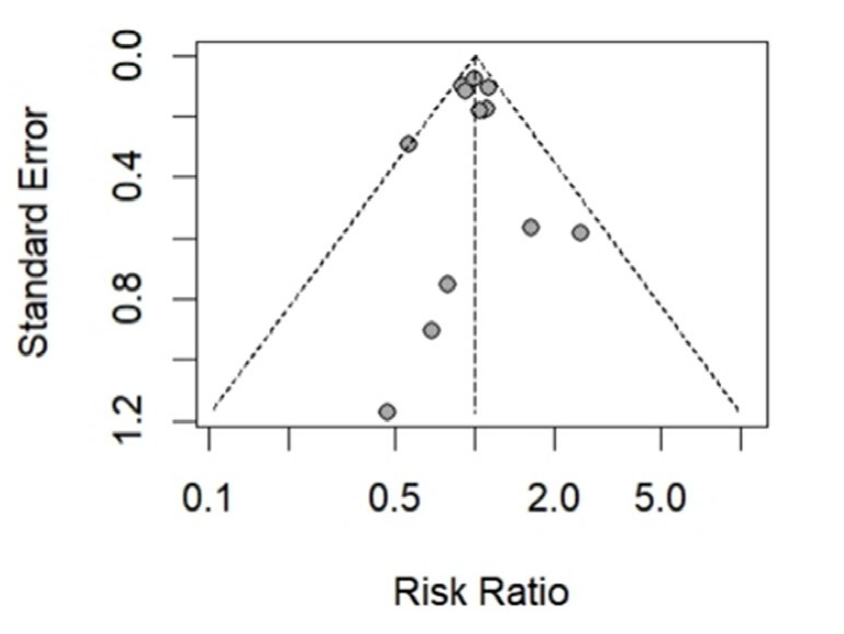
| 低血糖事件发生率 | 1.00[0.92,1.08] | 0.94 | 1.00[0.92,1.09] | 0.97 | 1.00[0.90,1.11] | 0.98 | 1.00[0.92,1.10] | 0.93 | ||||||||
Tab.2 Sensitivity analysis
| 结局指标 | 随机效应模型 | 固定效应模型 | 去除权重大的研究 | 去除权重小的研究 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD/RR(95%CI) | P值 | MD/RR(95%CI) | P值 | MD/RR(95%CI) | P值 | MD/RR(95%CI) | P值 | |||||||||
| HbA1c水平 | -0.45[-0.58,-0.33] | <0.01 | -0.43[-0.44,-0.42] | <0.01 | -0.50[-0.60,-0.41] | <0.01 | -0.44[-0.56,-0.31] | <0.01 | ||||||||
| 低血糖事件发生率 | 1.00[0.92,1.08] | 0.94 | 1.00[0.92,1.09] | 0.97 | 1.00[0.90,1.11] | 0.98 | 1.00[0.92,1.10] | 0.93 | ||||||||
| [1] | Petersmann A, Müller-Wieland D, Müller UA, et al. Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus[J]. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes, 2019, 127(S01): S1-S7. |
| [2] | Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045[J]. Diabetes Care, 2022, 183: 109119. |
| [3] | Ali MK, Pearson-Stuttard J, Selvin E, et al. Interpreting global trends in type 2 diabetes complications and mortality[J]. Diabetologia, 2022, 65(1): 3-13. |
| [4] | American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2018 abridged for primary care providers[J]. Clin Diabetes, 2018, 36(1):14-37. |
| [5] | Min T, Bain SC. The role of tirzepatide, dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in the management of type 2 diabetes: The SURPASS clinical trials[J]. Diabetes Ther, 2021, 12(5): 143-157. |
| [6] |
Mannucci E, Candido R, Monache LD, et al. Italian guidelines for the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J]. Acta Diabetologica, 2022, 59(5): 579-622.
doi: 10.1007/s00592-022-01857-4 pmid: 35288805 |
| [7] | 陆菊明. 《中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)》读后感[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2021, 13(4): 301-304. |
| [8] | Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD[J]. Eur Heart J, 2019, 41(2): 255-323. |
| [9] |
Pandey J, Patents AK. SGLT2 inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes: A patent review (2013-2018)[J]. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents, 2019, 29(5): 369-384.
doi: 10.1080/13543776.2019.1612879 pmid: 31026402 |
| [10] | Young CF, Farnoudi N, Chen J, et al. SGLT-2 Inhibitors: Benefits beyond the glucose-lowering effect-what is new in 2023?[J]. Endocrines, 2023, 4(3): 630-655. |
| [11] | Cefalo CMA, Cinti F, Moffa S, et al. Sotagliflozin, the first dual SGLT inhibitor: Current outlook and perspectives[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2019, 18(1): 1-14. |
| [12] | Avgerinos I, Karagiannis T, Kakotrichi P, et al. Sotagliflozin for patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2022, 24(1): 106-114. |
| [13] | Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Pitt B, et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(2): 129-139. |
| [14] | Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Steg PG, et al. Sotagliflozin in Patients with Diabetes and Recent Worsening Heart Failure[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(2): 117-128. |
| [15] |
Cherney DZI, Ferrannini E, Umpierrez GE, et al. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and severe renal impairment[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2021, 23(12): 2632-2642.
doi: 10.1111/dom.14513 pmid: 34338408 |
| [16] | Cherney DZI, Ferrannini E, Umpierrez GE, et al. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and stage 3 chronic kidney disease[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2023, 25(6): 1646-1657. |
| [17] |
Posch M, Walther N, Ferrannini E, et al. Metabolic, intestinal, and cardiovascular effects of sotagliflozin compared with empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2022, 45(9): 2118-2126.
doi: 10.2337/dc21-2166 pmid: 35817022 |
| [18] |
Zambrowicz B, Lapuerta P, Strumph P, et al. LX4211 Therapy reduces postprandial glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment despite low urinary glucose excretion[J]. Clin Ther, 2015, 37(1): 71-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.10.026 pmid: 25529979 |
| [19] | Rosenstock J, Cefalu WT, Lapuerta P, et al. Greater dose-ranging effects on A1C levels than on glucosuria with LX4211, a dual inhibitor of SGLT1 and SGLT2, in patients with type 2 diabetes on metformin monotherapy[J]. Diabetes Care, 2014, 38(3): 431-438. |
| [20] | Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus not currently treated with antidiabetic therapy[EB/OL].https://clinicaltrialsgov/show/NCT02926937, 2016-10-06/2021-07-21. |
| [21] | Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on background of metformin[EB/OL].https://clinicaltrialsgov/show/NCT02926950, 2016-10-06/2021-05-11. |
| [22] | Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin versus placebo and empagliflozin in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus who have inadequate glycemic control while taking a DPP4 inhibitor alone or with metformin[EB/OL].https://clinicaltrialsgov/show/NCT03351478, 2017-11-22/2021-05-11. |
| [23] | Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin versus placebo in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus who have inadequate glycemic control while taking insulin alone or with other oral antidiabetic agents[EB/OL].https://clinicaltrialsgov/show/NCT03285594, 2017-09-18/2021-05-11. |
| [24] | Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on background of sulfonylurea alone or with metformin[EB/OL].https://clinicaltrialsgov/show/NCT03066830, 2017-02-28/2021-05-11. |
| [25] | Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin versus glimepiride and placebo in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus that are taking metformin monotherapy[EB/OL].https://clinicaltrialsgov/show/NCT03332771, 2017-11-06/2021-05-11. |
| [26] | Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. Efficacy and bone safety of sotagliflozin dose 1 and dose 2 versus placebo in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus who have inadequate glycemic control[EB/OL].https://clinicaltrialsgov/show/NCT03386344, 2017-12-29/2021-06-25. |
| [27] | Talha M, Ali MHJCPiC. Latest FDA approved drug sotagliflozin (Inpefa): A glance at its prospectives for heart failure[J]. Curr Probl Cardiol, 2023: 101897. |
| [28] | Baker C, Wason S, Banks P, et al. Dose-dependent glycometabolic effects of sotagliflozin on type 1 diabetes over 12 weeks: The inTandem4 trial[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2019, 21(11): 2440-2449. |
| [29] | 徐建华, 王世亚. 索格列净在心血管疾病中的研究进展[J]. 世界临床药物, 2023, 44(11): 1215-1218. |
| [30] | 朱思梅, 杨汉跃, 王建涛. SGLT1/SGLT2双重抑制剂索格列净用于1型糖尿病的研究进展[J]. 中国新药与临床杂志, 2018, 37(10): 537-540. |
| [31] | Powell DR, Zambrowicz B, Morrow L, et al. Sotagliflozin decreases postprandial glucose and insulin concentrations by delaying intestinal glucose absorption[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2020, 105(4): e1235-e1249. |
| [32] | Liu L, Shi FH, Xu H, et al. Efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 12:752440. |
| [33] | Mazidi M, Rezaie P, Gao HK, et al. Effect of sodium-glucose cotransport-2 inhibitors on blood pressure in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 randomized control trials with 22 528 patients[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2017, 6(6): e004007. |
| [34] | Wu J, Zhao X, Chen H, et al. Metabolic effects of the dual SGLT 1/2 inhibitor sotagliflozin on blood pressure and body weight reduction in people with diabetes: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. J Diabetes Complications, 2022, 36(12): 108352. |
| [35] |
Danne T, Cariou B, Buse JB, et al. Improved time in range and glycemic variability with sotagliflozin in combination with insulin in adults with type 1 diabetes: A pooled analysis of 24-week continuous glucose monitoring data from the inTandem program[J]. Diabetes Care, 2019, 42(5): 919-930.
doi: 10.2337/dc18-2149 pmid: 30833371 |
| [36] |
Buse JB, Garg SK, Rosenstock J, et al. Sotagliflozin in combination with optimized insulin therapy in adults with type 1 diabetes: The North American inTandem1 study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2018, 41(9): 1970-1980.
doi: 10.2337/dc18-0343 pmid: 29937430 |
| [37] | Development MRJDD, Therapy. The journey from gene knockout to clinical medicine: Telotristat and sotagliflozin[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2019, 13: 817-824. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||