Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 1061-1066.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.12.001
Risk assessment of pancreatic cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with sitagliptin: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Zhu Chenglou1, Wu Qiong1, Da Mingxu1,2( )
)
- 1. The Frist School of Clinical Medicine,Lanzhou University,Lanzhou 730000,China
2. Department of Surgical Oncology,Gansu Provincial Hospital,Lanzhou 730000,China
-
Received:2023-03-29Online:2023-12-20Published:2024-01-30 -
Contact:Da Mingxu E-mail:hxdamingxu@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Chenglou, Wu Qiong, Da Mingxu. Risk assessment of pancreatic cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with sitagliptin: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(12): 1061-1066.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.12.001
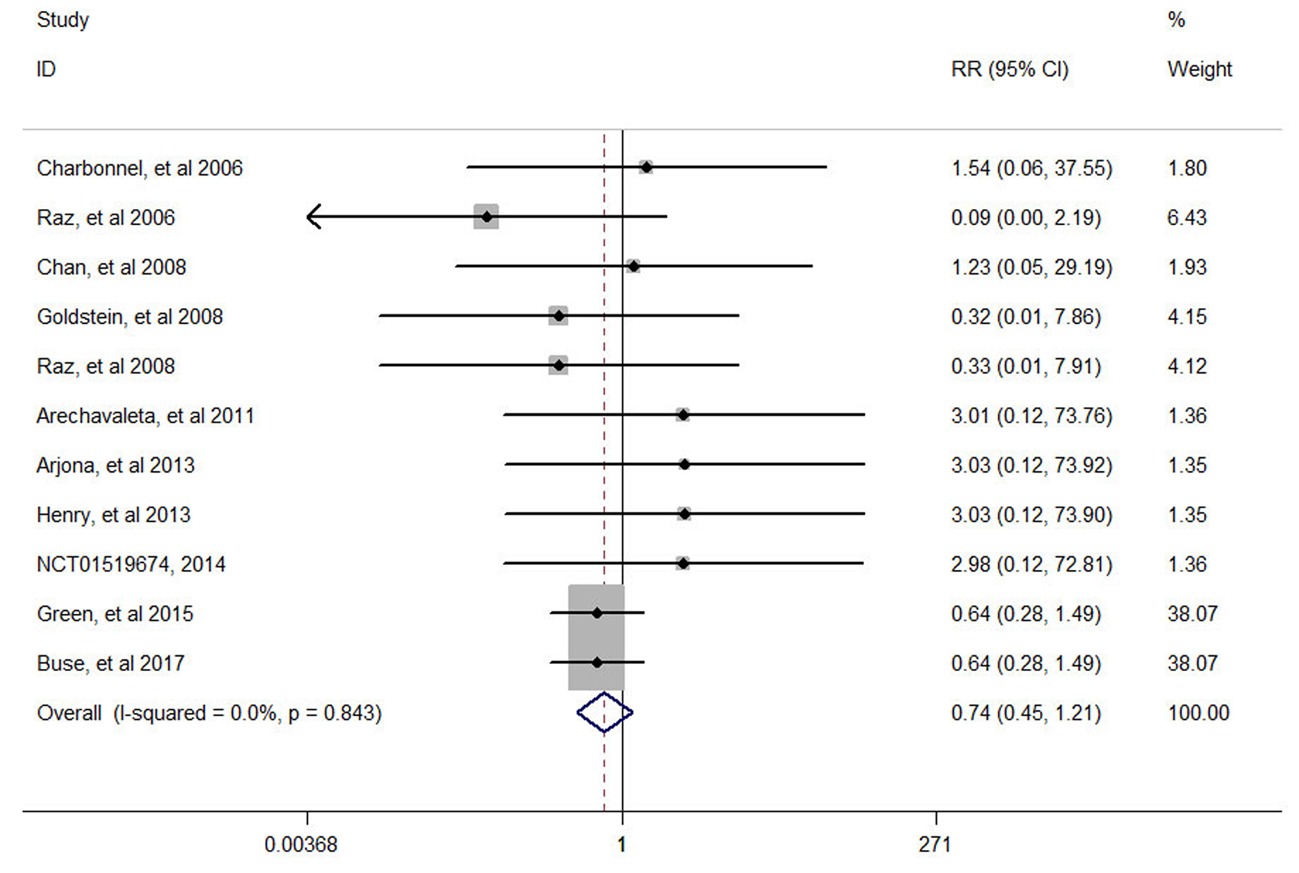
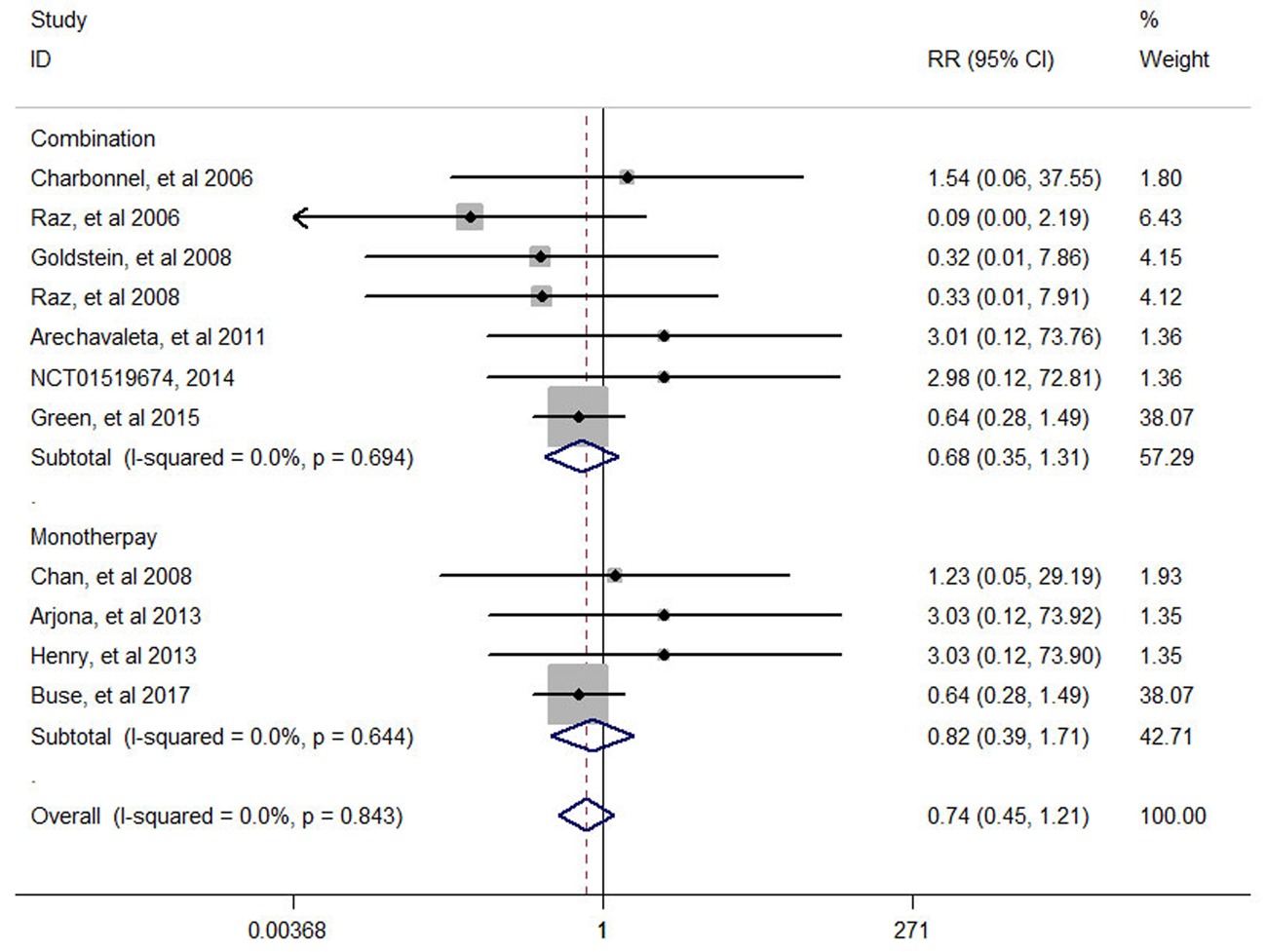
| 第一作者 | 国家 | 类型 | 治疗方案 | 样本量(PCevents) | 疗程(周) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干预组 | 对照组 | |||||
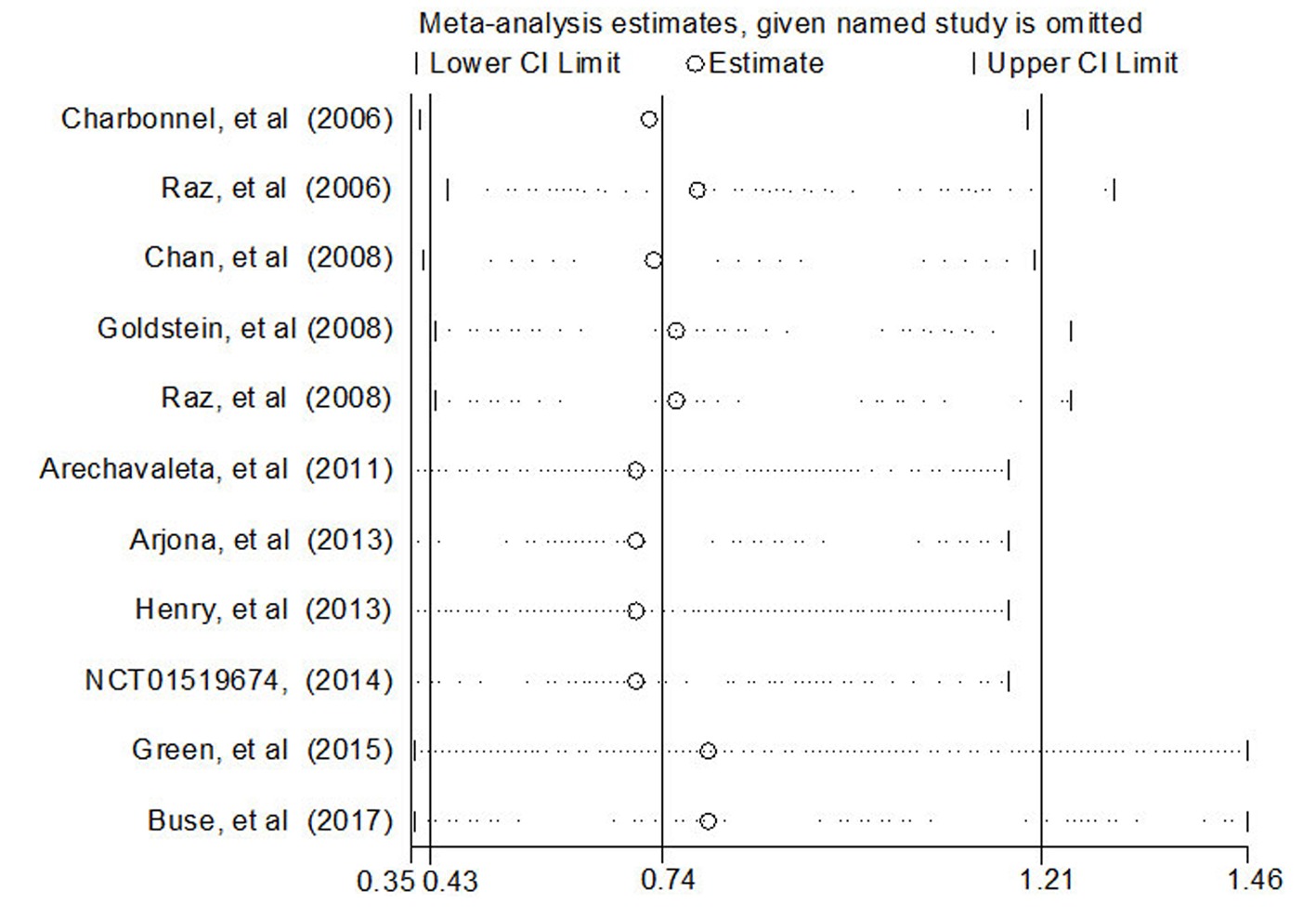
| Charbonnel[ | 法国 | RCT | 西格列汀+安慰剂 | 格列吡嗪+安慰剂 | 464(1) vs 237(0) | 104 |
| Raz[ | 以色列 | RCT | 西格列汀+安慰剂 | 吡格列酮+安慰剂 | 411(0) vs 110(1) | 54 |
| Chan[ | 中国 | RCT | 西格列汀 | 安慰剂 | 65 (1) vs 26 (0) | 54 |
| Goldstein[ | 美国 | RCT | 西格列汀+二甲双胍 | 二甲双胍 | 182(0) vs 176(1) | 24 |
| Raz[ | 以色列 | RCT | 西格列汀+二甲双胍 | 安慰剂+二甲双胍 | 96 (0) vs 94 (1) | 30 |
| Arechavaleta[ | 墨西哥 | RCT | 西格列汀+二甲双胍 | 格列美脲+二甲双胍 | 516(1) vs 518(0) | 30 |
| Arjona[ | 美国 | RCT | 西格列汀 | 格列美脲 | 210(1) vs 212(0) | 54 |
| Henry[ | 美国 | RCT | 西格列汀+吡格列酮 | 吡格列酮 | 231(1) vs 233(0) | 54 |
| Linjawi[ | 阿根廷 | RCT | 胰岛素+西格列汀+二甲双胍 | 胰岛素+二甲双胍 | 193(1) vs 192(0) | 24 |
| Green[ | 美国 | RCT | 西格列汀 | 安慰剂 | 7257(9) vs 7266(14) | 260 |
| Buse[ | 美国 | RCT | 西格列汀 | 安慰剂 | 7332(9) vs 7339(14) | 144 |
Tab.1 Basic characteristics of included literatures
| 第一作者 | 国家 | 类型 | 治疗方案 | 样本量(PCevents) | 疗程(周) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干预组 | 对照组 | |||||
| Charbonnel[ | 法国 | RCT | 西格列汀+安慰剂 | 格列吡嗪+安慰剂 | 464(1) vs 237(0) | 104 |
| Raz[ | 以色列 | RCT | 西格列汀+安慰剂 | 吡格列酮+安慰剂 | 411(0) vs 110(1) | 54 |
| Chan[ | 中国 | RCT | 西格列汀 | 安慰剂 | 65 (1) vs 26 (0) | 54 |
| Goldstein[ | 美国 | RCT | 西格列汀+二甲双胍 | 二甲双胍 | 182(0) vs 176(1) | 24 |
| Raz[ | 以色列 | RCT | 西格列汀+二甲双胍 | 安慰剂+二甲双胍 | 96 (0) vs 94 (1) | 30 |
| Arechavaleta[ | 墨西哥 | RCT | 西格列汀+二甲双胍 | 格列美脲+二甲双胍 | 516(1) vs 518(0) | 30 |
| Arjona[ | 美国 | RCT | 西格列汀 | 格列美脲 | 210(1) vs 212(0) | 54 |
| Henry[ | 美国 | RCT | 西格列汀+吡格列酮 | 吡格列酮 | 231(1) vs 233(0) | 54 |
| Linjawi[ | 阿根廷 | RCT | 胰岛素+西格列汀+二甲双胍 | 胰岛素+二甲双胍 | 193(1) vs 192(0) | 24 |
| Green[ | 美国 | RCT | 西格列汀 | 安慰剂 | 7257(9) vs 7266(14) | 260 |
| Buse[ | 美国 | RCT | 西格列汀 | 安慰剂 | 7332(9) vs 7339(14) | 144 |
| [1] |
Scott LJ. Sitagliptin: A review in type 2 diabetes[J]. Drugs, 2017, 77(2):209-224.
doi: 10.1007/s40265-016-0686-9 pmid: 28078647 |
| [2] |
Qaseem A, Barry MJ, Humphrey LL, et al. Oral pharmacologic treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A clinical practice guideline update from the American college of physicians[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2017, 166(4): 279-290.
doi: 10.7326/M16-1860 pmid: 28055075 |
| [3] |
Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, et al. Consensus statement by the American association of clinical endocrinologists and american college of endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm-2017 executive summary[J]. Endocr Pract, 2017, 23(2): 207-238.
doi: 10.4158/EP161682.CS pmid: 28095040 |
| [4] |
Mulvihill EE, Drucker DJ. Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of action of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors[J]. Endocr Rev, 2014, 35(6): 992-1019.
doi: 10.1210/er.2014-1035 pmid: 25216328 |
| [5] |
Stoian AP, Sachinidis A, Stoica RA, et al. The efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors compared to other oral glucose-lowering medications in the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J]. Metabolism, 2020, 109: 154295.
doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154295 URL |
| [6] |
Scheen AJ. The safety of gliptins: Updated data in 2018[J]. Expert Opin Drug Saf, 2018, 17(4): 387-405.
doi: 10.1080/14740338.2018.1444027 URL |
| [7] |
Egan AG, Blind E, Dunder K, et al. Pancreatic safety of incretin-based drugs-FDA and EMA assessment[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 370(9): 794-797.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1314078 URL |
| [8] |
Drucker DJ, Yusta B. Physiology and pharmacology of the enteroendocrine hormone glucagon-like peptide-2[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2014, 76:561-583.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021113-170317 pmid: 24161075 |
| [9] |
Fujiwara K, Inoue T, Henmi Y, et al. Sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, suppresses CXCL5 and SDF-1 and does not accelerate intestinal neoplasia formation in ApcMin/+ mice fed a high-fat diet[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14(4): 4355-4360.
doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6698 pmid: 28943949 |
| [10] |
Charbonnel B, Karasik A, Liu J, et al. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin alone[J]. Diabetes Care, 2006, 29(12): 2638-2643.
doi: 10.2337/dc06-0706 pmid: 17130197 |
| [11] |
Raz I, Hanefeld M, Xu L, et al. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin as monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetologia, 2006, 49(11): 2564-2571.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0416-z pmid: 17001471 |
| [12] |
Chan JC, Scott R, Arjona Ferreira JC, et al. Safety and efficacy of sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic renal insufficiency[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2008, 10(7): 545-555.
doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.00914.x pmid: 18518892 |
| [13] |
Goldstein BJ, Feinglos MN, Lunceford JK, et al. Effect of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and metformin on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Care, 2007, 30(8): 1979-1987.
doi: 10.2337/dc07-0627 pmid: 17485570 |
| [14] |
Raz I, Chen Y, Wu M, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Curr Med Res Opin, 2008, 24(2): 537-550.
doi: 10.1185/030079908X260925 pmid: 18194595 |
| [15] |
Arechavaleta R, Seck T, Chen Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of treatment with sitagliptin or glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy: A randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2011, 13(2): 160-168.
doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01334.x pmid: 21199268 |
| [16] |
Arjona Ferreira JC, Marre M, Barzilai N, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin versus glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate-to-severe chronic renal insufficiency[J]. Diabetes Care, 2013, 36(5): 1067-1073.
doi: 10.2337/dc12-1365 pmid: 23248197 |
| [17] |
Henry RR, Staels B, Fonseca VA, et al. Efficacy and safety of initial combination treatment with sitagliptin and pioglitazone-a factorial study[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2014, 16(3): 223-230.
doi: 10.1111/dom.12194 pmid: 23909985 |
| [18] |
Linjawi S, Sothiratnam R, Sari R, et al. The study of once- and twice-daily biphasic insulin aspart 30 (BIAsp 30) with sitagliptin, and twice-daily BIAsp 30 without sitagliptin, in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on sitagliptin and metformin-The Sit2Mix trial[J]. Prim Care Diabetes, 2015, 9(5):370-376.
doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2014.11.001 pmid: 25488587 |
| [19] |
Green JB, Bethel MA, Armstrong PW, et al. Effect of sitagliptin on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 373(3): 232-242.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1501352 URL |
| [20] |
Buse JB, Bethel MA, Green JB, et al. Pancreatic safety of sitagliptin in the TECOS study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2017, 40(2): 164-170.
doi: 10.2337/dc15-2780 pmid: 27630212 |
| [21] |
Elashoff M, Matveyenko AV, Gier B, et al. Pancreatitis, pancreatic, and thyroid cancer with glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies[J]. Gastroenterology, 2011, 141(1): 150-156.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.018 pmid: 21334333 |
| [22] |
Vlavcheski F, O'Neill EJ, Gagacev F, et al. Effects of berberine against pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(23):8630.
doi: 10.3390/molecules27238630 URL |
| [23] |
Tseng CH. Sitagliptin and pancreatic cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Eur J Clin Invest, 2016, 46(1): 70-79.
doi: 10.1111/eci.2016.46.issue-1 URL |
| [24] |
Ohnuma K, Hatano R, Komiya E, et al. A novel role for CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV as a therapeutic target[J]. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2018, 23(9):1754-1779.
doi: 10.2741/4671 pmid: 29772527 |
| [25] |
Mega C, Vala H, Rodrigues-Santos P, et al. Sitagliptin prevents aggravationof endocrine and exocrine pancreatic damage in the zucker diabetic Fatty rat-focus on amelioration of metabolic profile and tissue cytoprotective properties[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2014, 6:42.
doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-6-42 |
| [26] |
Gokhale M, Buse JB, Gray CL, et al. Dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitors and pancreatic cancer: A cohort study[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2014, 16(12):1247-1256.
doi: 10.1111/dom.12379 pmid: 25109825 |
| [27] |
Tseng CH. New-onset diabetes with a history of dyslipidemia predicts pancreatic cancer[J]. Pancreas, 2013, 42(1):42-48.
doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182571ba9 URL |
| [28] |
Currie CJ, Poole CD, Gale EA. The influence of glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetologia, 2009, 52(9):1766-1777.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1440-6 pmid: 19572116 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||