Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 965-971.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.11.001
Meta-analysis of the antihypertensive effects of rosuvastatin
- 1. Basic Medicine College of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, China
2. Department of Emergen Medicine,Wuhan First Hospital,Wuhan 430022,China
-
Received:2023-04-12Online:2023-11-20Published:2024-01-17 -
Contact:Ke Mengting E-mail:348358046@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ke Mengting, Chen Wei. Meta-analysis of the antihypertensive effects of rosuvastatin[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(11): 965-971.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.11.001
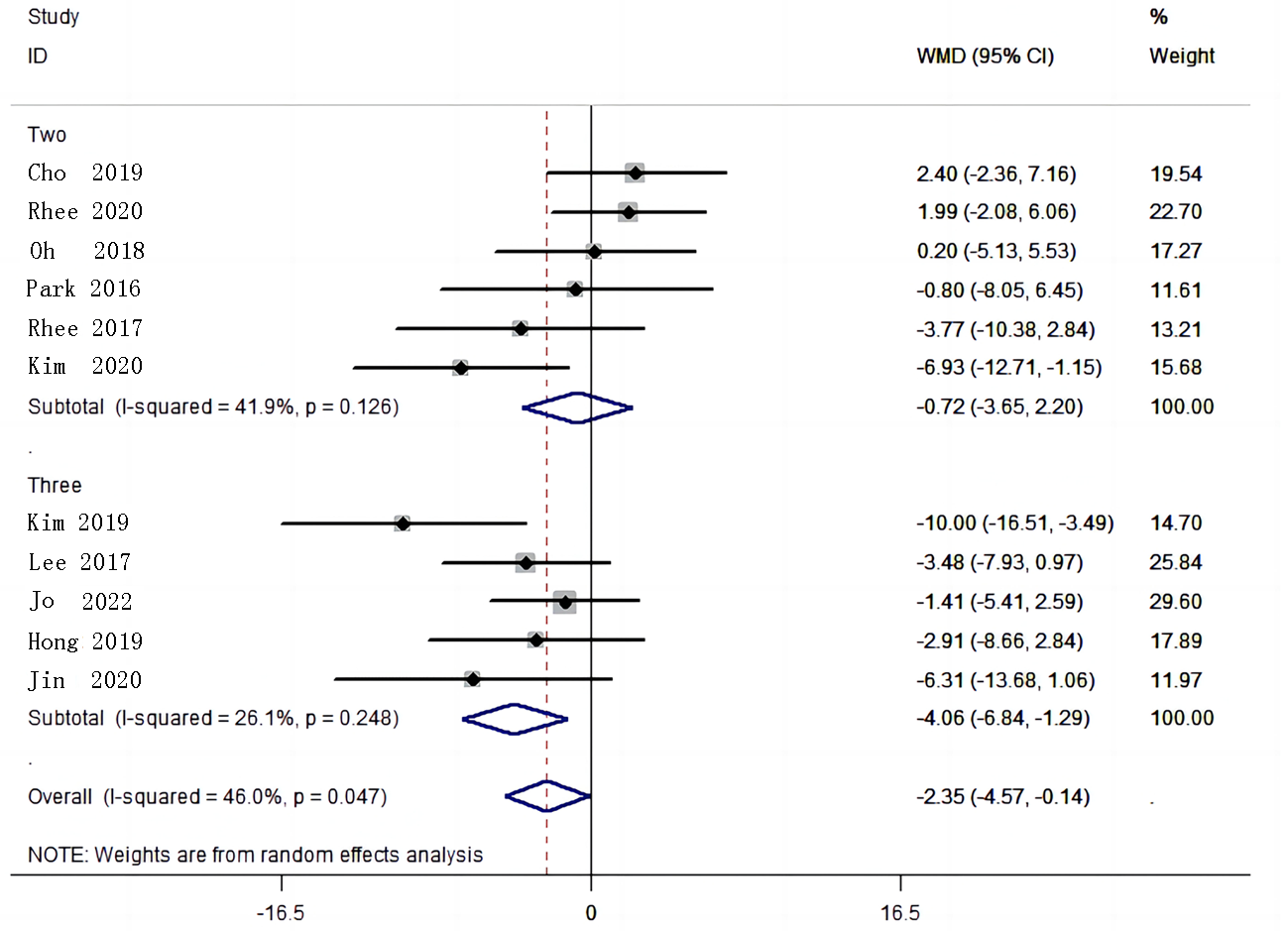
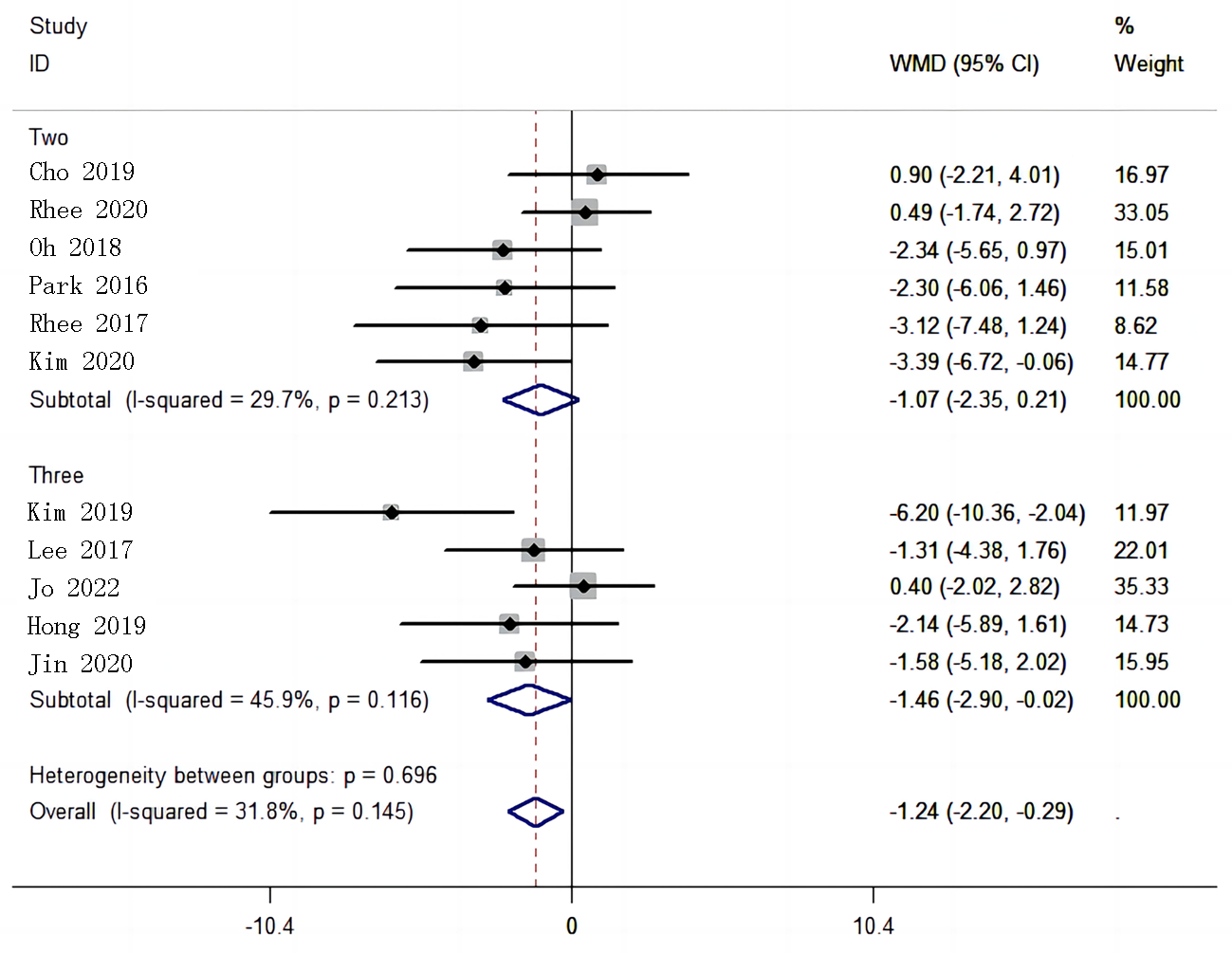
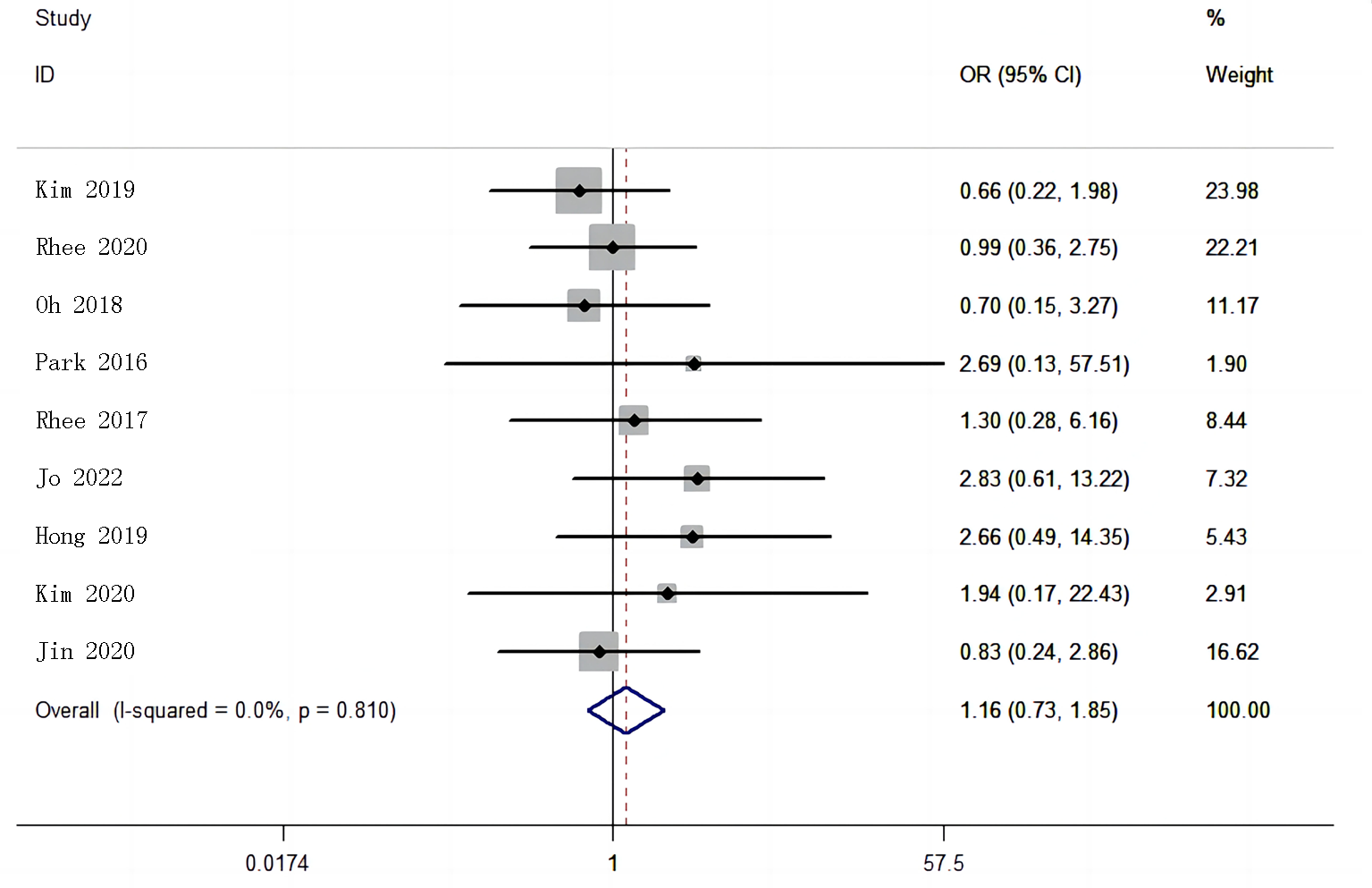
| 纳入研究 | 年份 | 例数 | 干预措施 | 疗程 (周) | 基线 比较 | 结局指标 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||||
| Jo[ | 2022 | 105 | 52 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平+奥美沙坦 | 氨氯地平+奥美沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Kim[ | 2020 | 35 | 34 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平 | 氨氯地平 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Lee[ | 2017 | 54 | 46 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平+氯沙坦 | 氨氯地平+氯沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Cho[ | 2019 | 70 | 72 | 瑞舒伐他汀+坎地沙坦 | 坎地沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Jin[ | 2020 | 66 | 66 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Park[ | 2016 | 61 | 36 | 瑞舒伐他汀+奥美沙坦 | 奥美沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Oh[ | 2018 | 80 | 43 | 瑞舒伐他汀+替米沙坦 | 替米沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Rhee[ | 2020 | 92 | 93 | 瑞舒伐他汀+奈必洛尔 | 奈必洛尔 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Hong[ | 2019 | 47 | 49 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Kim[ | 2019 | 40 | 43 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Rhee[ | 2017 | 46 | 45 | 瑞舒伐他汀+非马沙坦 | 非马沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
Tab.1 Characteristic of included studies of the meta-analysis
| 纳入研究 | 年份 | 例数 | 干预措施 | 疗程 (周) | 基线 比较 | 结局指标 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||||
| Jo[ | 2022 | 105 | 52 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平+奥美沙坦 | 氨氯地平+奥美沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Kim[ | 2020 | 35 | 34 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平 | 氨氯地平 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Lee[ | 2017 | 54 | 46 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平+氯沙坦 | 氨氯地平+氯沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Cho[ | 2019 | 70 | 72 | 瑞舒伐他汀+坎地沙坦 | 坎地沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Jin[ | 2020 | 66 | 66 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Park[ | 2016 | 61 | 36 | 瑞舒伐他汀+奥美沙坦 | 奥美沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Oh[ | 2018 | 80 | 43 | 瑞舒伐他汀+替米沙坦 | 替米沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Rhee[ | 2020 | 92 | 93 | 瑞舒伐他汀+奈必洛尔 | 奈必洛尔 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Hong[ | 2019 | 47 | 49 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Kim[ | 2019 | 40 | 43 | 瑞舒伐他汀+氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 氨氯地平+替米沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
| Rhee[ | 2017 | 46 | 45 | 瑞舒伐他汀+非马沙坦 | 非马沙坦 | 8 | 是 | SBP、DBP | |
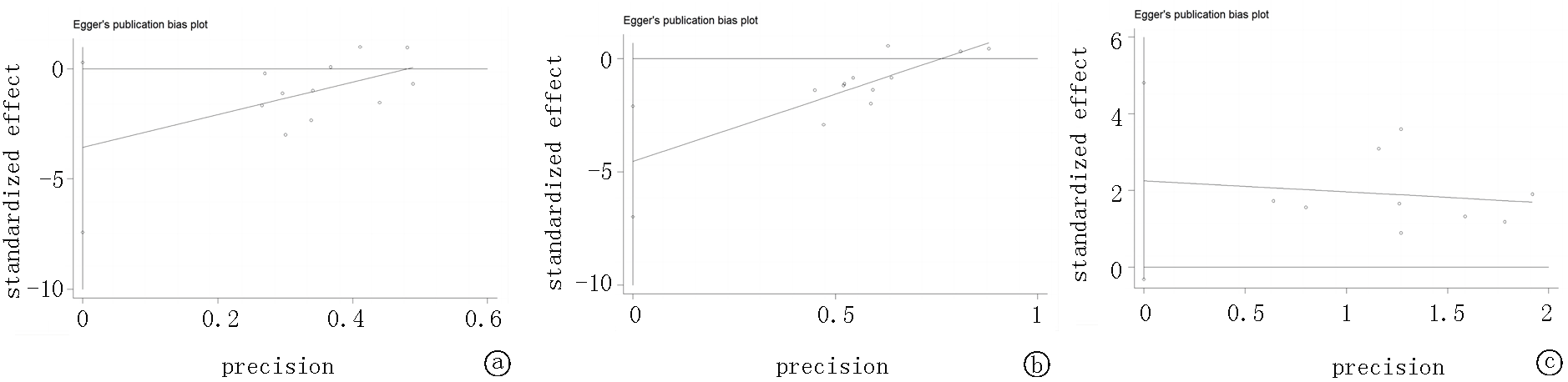
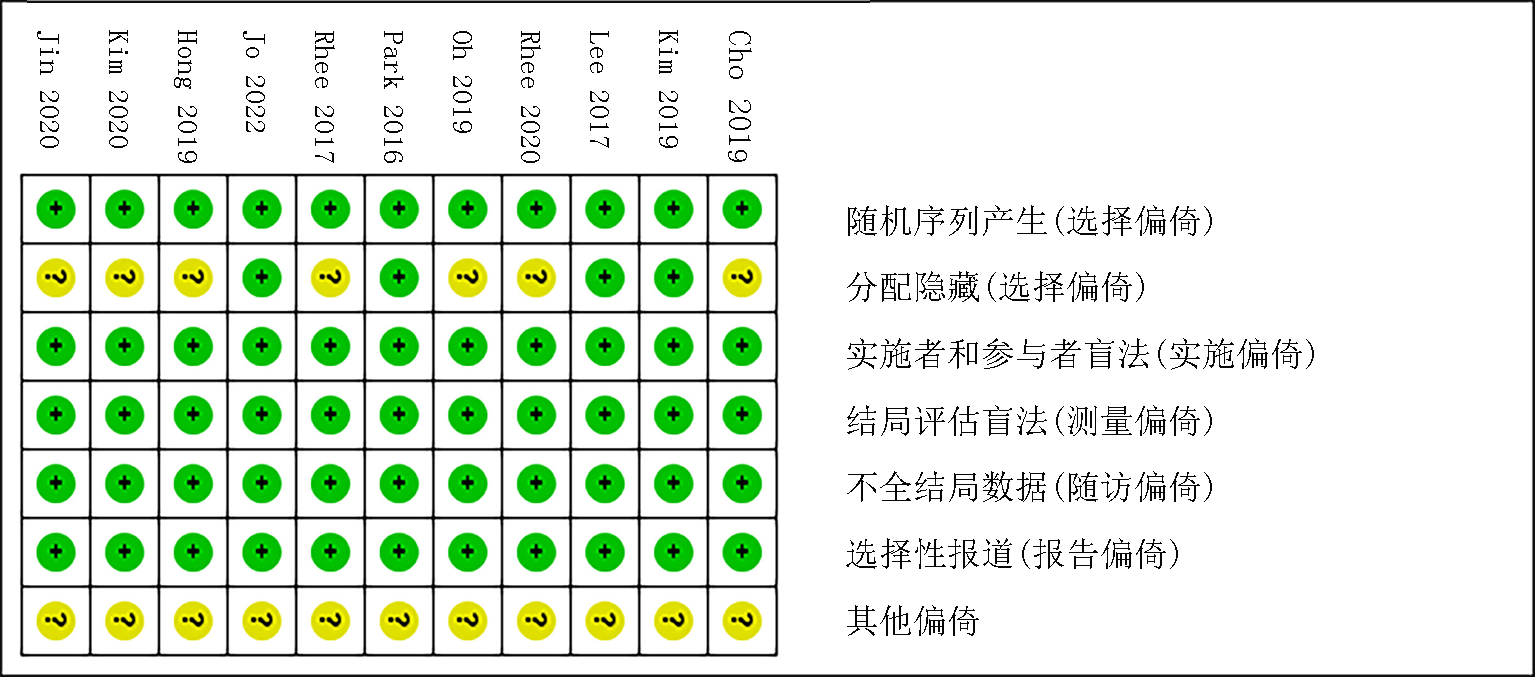
Fig. 6 Bias risk diagram a. the diagram for comparing the systolic pressure difference; b. the diagram for comparing the diastolic pressure difference; c. the diagram for comparing the adverse drug reactions
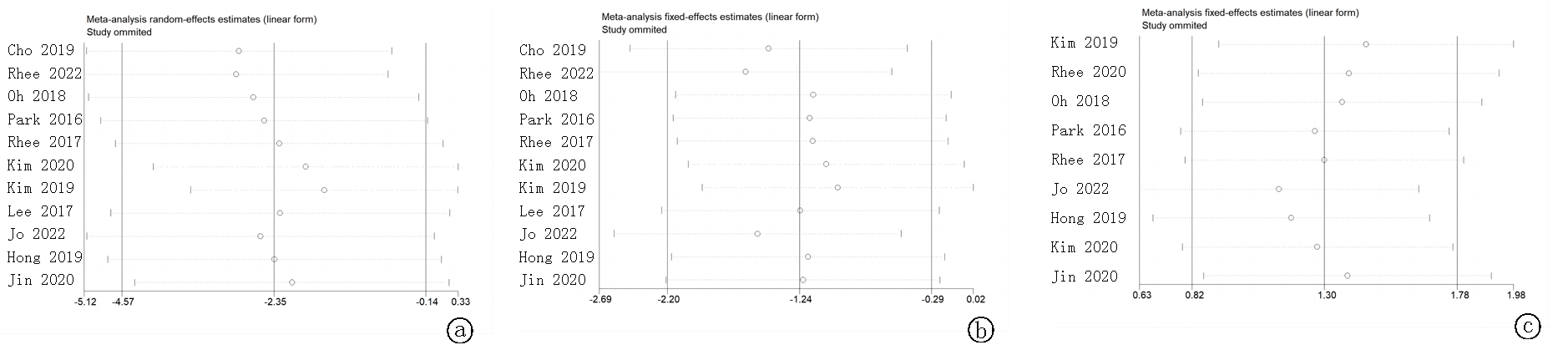
Fig. 7 Sensitivity analysis diagram a. the diagram for comparing the systolic pressure difference; b. the diagram for comparing the diastolic pressure difference; c. the diagram for comparing the adverse drug reactions
| [1] |
Parati G, Kjeldsen S, Coca A, et al. Adherence to single-pill versus free-equivalent combination therapy in hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hypertension, 2021, 77(2):692-705.
doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15781 pmid: 33390044 |
| [2] |
Weisser B, Predel HG, Gillessen A, et al. Single pill regimen leads to better adherence and clinical outcome in daily practice in patients suffering from hypertension and/or dyslipidemia: Results of a meta-analysis[J]. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev, 2020, 27(2):157-164.
doi: 10.1007/s40292-020-00370-5 pmid: 32219670 |
| [3] |
Jo SH, Kang SM, Yoo BS, et al. A Prospective randomized, double-blind, multi-center, phase iii clinical trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of olmesartan/amlodipine plus rosuvastatin combination treatment in patients with concomitant hypertension and dyslipidemia: A LEISURE Study[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(2):350.
doi: 10.3390/jcm11020350 URL |
| [4] |
Kim W, Chang K, Cho EJ, et al. A randomized, double-blind clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination of amlodipine/rosuvastatin in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension[J]. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich), 2020, 22(2):261-269.
doi: 10.1111/jch.13774 pmid: 32003938 |
| [5] |
Lee HY, Kim SY, Choi KJ, et al. A Randomized, Multicenter, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and the tolerability of a triple combination of amlodipine/losartan/rosuvastatin in patients with comorbid essential hypertension and hyperlipidemia[J]. Clin Ther, 2017, 39(12):2366-2379.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.10.013 URL |
| [6] |
Cho KI, Kim BH, Park YH, et al. Efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination of candesartan and rosuvastatin on blood pressure and cholesterol in patients with hypertension and hypercholesterolemia: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel phase iii clinical study[J]. Clin Ther, 2019, 41(8):1508-1521.
doi: S0149-2918(19)30252-8 pmid: 31307833 |
| [7] |
Jin X, Kim MH, Han KH, et al. Efficacy and safety of co-administered telmisartan/amlodipine and rosuvastatin in subjects with hypertension and dyslipidemia[J]. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich), 2020, 22(10):1835-1845.
doi: 10.1111/jch.v22.10 URL |
| [8] |
Park JS, Shin JH, Hong TJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of fixed-dose combination therapy with olmesartan medoxomil and rosuvastatin in Korean patients with mild to moderate hypertension and dyslipidemia: an 8-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, factorial-design study (OLSTA-D RCT: OLmesartan rosuvaSTAtin from Daewoong)[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2016, 10:2599-2609.
doi: 10.2147/DDDT URL |
| [9] |
Oh GC, Han JK, Han KH, et al. Efficacy and safety of fixed-dose combination therapy with telmisartan and rosuvastatin in Korean patients with hypertension and dyslipidemia: TELSTA-YU (TELmisartan-rosuvaSTAtin from YUhan), a multicenter, randomized, 4-arm, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase III study[J]. Clin Ther, 2018, 40(5):676-691.
doi: S0149-2918(18)30103-6 pmid: 29673890 |
| [10] |
Rhee MY, Kim CH, Ahn Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of nebivolol and rosuvastatin combination treatment in patients with concomitant hypertension and hyperlipidemia[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2020, 14:5005-5017.
doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S280055 URL |
| [11] |
Hong SJ, Jeong HS, Cho JM, et al. Efficacy and safety of triple therapy with telmisartan, amlodipine, and rosuvastatin in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension: The jeil telmisartan, amlodipine, and rosuvastatin randomized clinical trial[J]. Clin Ther, 2019, 41(2):233-248.
doi: S0149-2918(18)30607-6 pmid: 30665829 |
| [12] |
Kim TS, Rha SW, Kim SY, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of telmisartan/amlodipine and rosuvastatin coadministration in hypertensive patients with hyperlipidemia: A phase iii, multicenter, randomized, double-blind study[J]. Clin Ther, 2019, 41(4):728-741.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.02.013 URL |
| [13] |
Rhee MY, Ahn T, Chang K, et al. The efficacy and safety of co-administration of fimasartan and rosuvastatin to patients with hypertension and dyslipidemia[J]. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol, 2017, 18(1):2.
doi: 10.1186/s40360-016-0112-7 URL |
| [14] |
You T, Liu XG, Hou XD, et al. Effect of statins on blood pressure: Analysis on adverse events released by FDA[J]. Clin Exp Hypertens, 2017, 39(4):325-329.
doi: 10.1080/10641963.2016.1254224 URL |
| [15] |
Briasoulis A, Agarwal V, Valachis A, et al. Antihypertensive effects of statins: a meta analysis of prospective controlled studies[J]. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2013, 15(5):310-320.
doi: 10.1111/jch.2013.15.issue-5 URL |
| [16] |
Sundstrom J, Gulliksson G, Wiren M. Synergistic effects of blood pressure-lowering drugs and statins: Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMJ Evid Based Med, 2018, 23(2):64-69.
doi: 10.1136/bmjebm-2017-110888 pmid: 29595132 |
| [17] | Lee S, Yang S, Chang M J. Antihypertensive effects of rosuvastatin in patients with hypertension and dyslipidemia: A systemic review and meta-analysis of randomized studies[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(11):e260391. |
| [18] |
Lee SG, Lee SJ, Thuy NVP, et al. Synergistic protective effects of a statin and an angiotensin receptor blocker for initiation and progression of atherosclerosis[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(5):e0215604.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215604 URL |
| [19] |
Oh M, Ghim JL, Park SE, et al. Pharmacokinetic comparison of a fixed-dose combination versus concomitant administration of fimasartan, amlodipine, and rosuvastatin using partial replicated design in healthy adult subjects[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2018, 12:1157-1164.
doi: 10.2147/DDDT URL |
| [20] |
Yoon DY, Park SI, Jung JA, et al. Comparison of pharmacokinetics of a fixed-dose combination of amlodipine/losartan/rosuvastatin with concomitant administration of amlodipine/losartan and rosuvastatin in healthy volunteers[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2020, 14:661-668.
doi: 10.2147/DDDT URL |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 28
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 107
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||